Comprehensive Guide to Low Blood Sugar: Recognizing Symptoms and Effective Management Techniques
This comprehensive guide offers valuable insights into hypoglycemia, highlighting its symptoms, causes, and effective management strategies. Learn how to recognize early warning signs, undertake immediate remedies, and adopt preventive measures to maintain stable blood glucose levels. Proper understanding and prompt action can prevent severe complications like unconsciousness and ensure you stay healthy and active. Whether you have diabetes or are concerned about blood sugar fluctuations, this article provides essential information for maintaining optimal glucose balance and overall well-being.

Comprehensive Guide to Low Blood Sugar: Recognizing Symptoms and Effective Management Techniques
Blood sugar regulation is a crucial aspect of maintaining overall health, especially for individuals living with diabetes. However, anyone can experience episodes of low blood sugar, medically known as hypoglycemia. This condition manifests when blood glucose levels fall below 70 mg/dL, posing immediate health risks if not promptly addressed. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies of hypoglycemia is vital for preventing serious complications and maintaining optimal energy levels.
Hypoglycemia is most commonly associated with diabetes management, particularly those on insulin or other glucose-lowering medications. Nonetheless, it can also occur due to various other factors such as dietary irregularities, excessive physical activity, certain medications, or underlying health conditions that affect glucose metabolism. The importance of maintaining stable blood glucose levels cannot be overstated, as glucose serves as the brain's primary energy source, influencing cognitive functions, mood, and motor coordination.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia can develop suddenly and often include a diverse range of physiological and neurological signs. Typical warning signs encompass feelings of intense hunger, anxiety, irritability, mood swings, and weakness. Physical manifestations may include muscle twitching, rapid heart rate, sweating, headaches, blurred or double vision, confusion, and unsteadiness. In severe cases, individuals may experience unconsciousness or seizures if the hypoglycemia is not promptly treated.
Recognizing these symptoms early enables individuals to take immediate corrective actions to restore blood glucose levels. Common interventions include consuming quick-absorbing carbohydrates such as glucose tablets, fruit juices, or candies, which can rapidly elevate blood sugar. In cases where the person cannot swallow or loses consciousness, emergency interventions like glucagon injections administered by healthcare professionals or trained caregivers are essential. These treatments can quickly reverse hypoglycemia, preventing potential complications like seizures or coma.
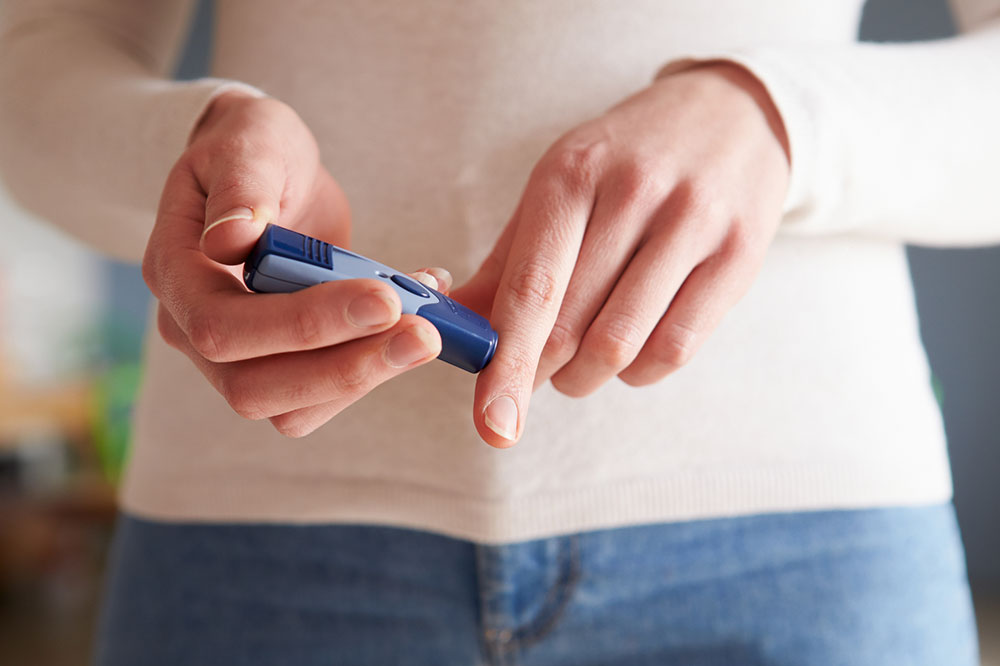
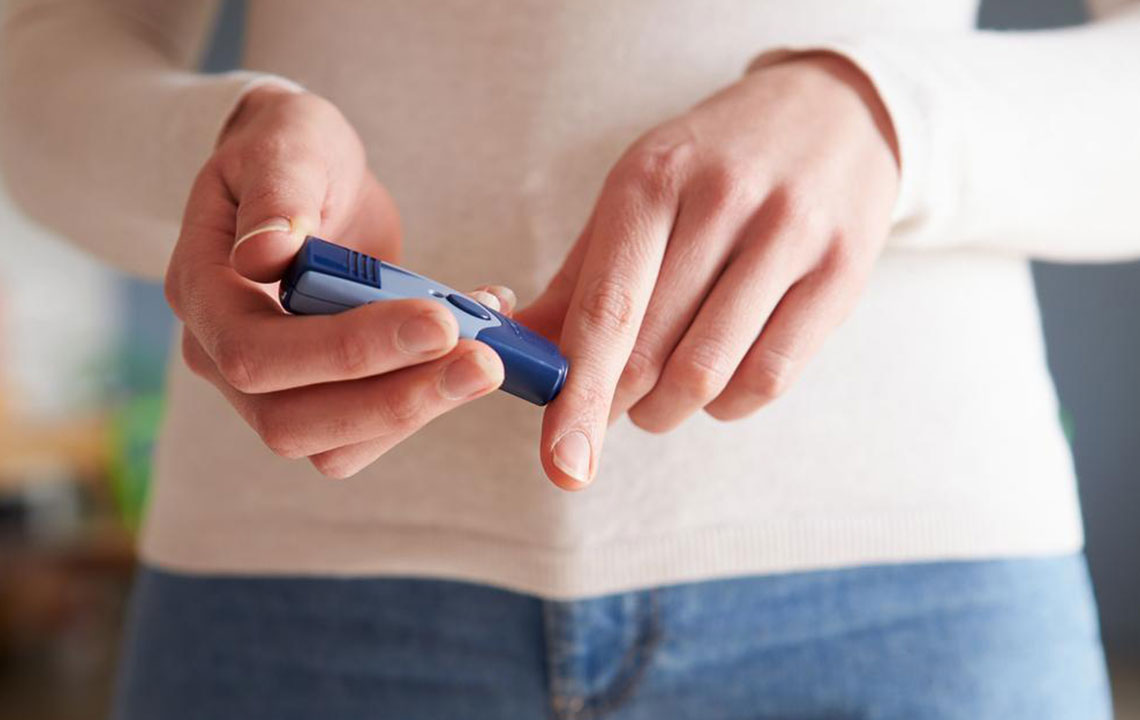
Prevention plays a significant role in managing hypoglycemia effectively. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels using glucose meters allows individuals to detect lows before symptoms escalate. Establishing a consistent eating schedule, balanced diet rich in fiber, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates, and ensuring adequate sleep are crucial preventive measures. Adjusting medication doses, especially for diabetic patients, under medical supervision also helps mitigate the risk of hypoglycemia. Maintaining physical activity levels within safe limits and understanding personal triggers contribute significantly to prevention strategies.
In addition to individual efforts, routine consultations with healthcare providers are vital for personalized management plans. Educating oneself about hypoglycemia, its symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals to act swiftly in emergencies. Keeping emergency supplies such as glucose tablets, sugary drinks, and glucagon kits accessible can make a difference during sudden episodes.
Ultimately, vigilant blood sugar management combined with lifestyle modifications and medical guidance can greatly reduce the risks associated with hypoglycemia. Staying informed, proactive, and prepared ensures that individuals can maintain their health, avoid emergencies, and lead active, balanced lives. Managing blood sugar levels is not just about preventing illness — it’s a fundamental aspect of overall wellness and quality of life.