Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Recognizing Symptoms and Understanding Causes
This comprehensive guide explores psoriasis symptoms, risk factors, and management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of lifestyle changes and medical treatments in controlling this chronic skin disorder. Learn how genetics, immune health, stress, and lifestyle contribute to psoriasis development and flare-ups, and discover practical tips to improve skin health and reduce symptoms for a better quality of life.
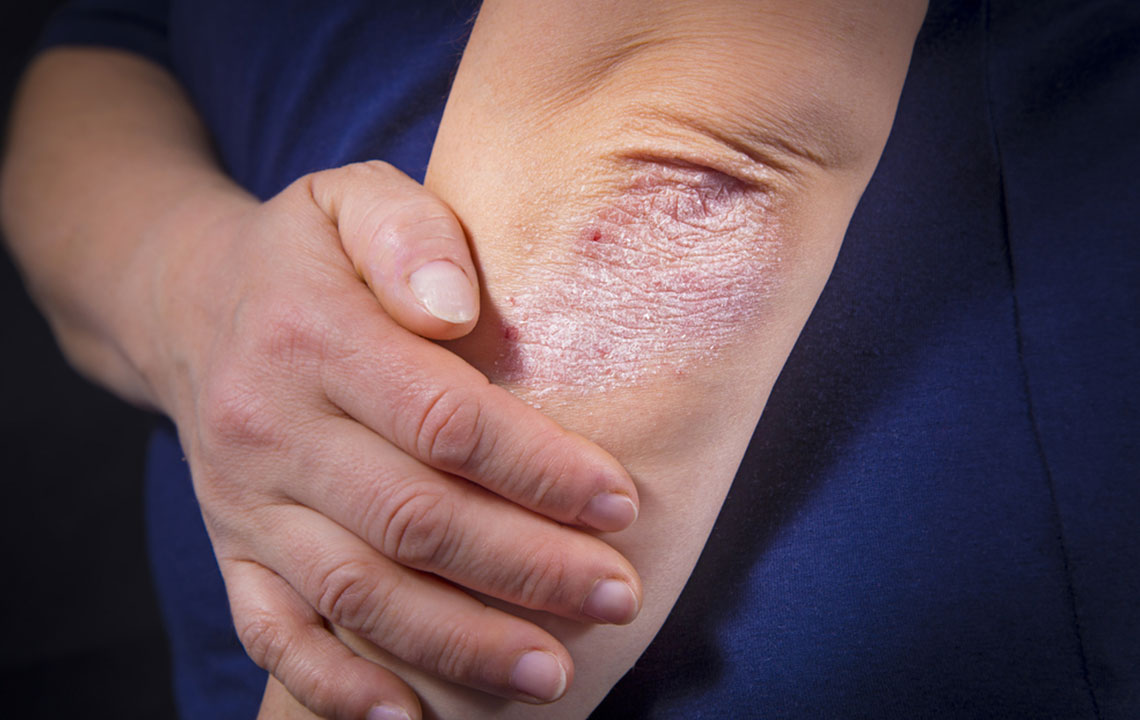
Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis: Recognizing Symptoms and Understanding Causes
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by an accelerated rate of skin cell growth, leading to the development of distinctive skin lesions. These lesions typically appear as red patches covered with silvery, flaky scales, often accompanied by discomfort such as itching, burning, or soreness. While psoriasis is a lifelong condition, its severity and symptoms can vary greatly from person to person, with periods of flare-ups and remission.
Understanding psoriasis is essential for effective management and improving quality of life. Though there is no complete cure for this condition, a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent complications. Lifestyle factors such as quitting smoking, managing stress, maintaining optimal skin hydration, and adopting a healthy diet can play vital roles in controlling the disease's progression and minimizing flare-ups.
Explore detailed information regarding the symptoms and risk factors associated with psoriasis.
Key Symptoms of Psoriasis
Symptoms can differ among individuals, but there are common signs to watch for, including:
Red, inflamed patches of skin covered with silvery or white scales
Scaly lesions that often peel or flake, especially in children
Dry, cracked skin that might bleed if scratched
Persistent itching, burning sensations, or soreness in affected areas
Nail changes such as ridges, thickening, or pitting of nails
Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, indicative of psoriatic arthritis in some cases
Psoriasis lesions may present as small dandruff-like flakes or large inflamed areas. The condition tends to follow a pattern of periodic flare-ups and periods of remission, which can last weeks or even months.
Understanding the Risk Factors for Psoriasis
While anyone can develop psoriasis, certain factors significantly increase susceptibility:
Genetics
A family history of psoriasis greatly raises the chances of developing the condition, especially if multiple close relatives are affected. Specific genes are linked to the immune system's response, contributing to disease development.
Infections and Immune System Issues
Individuals with compromised immune responses, such as those living with HIV/AIDS, or children with recurrent infections, are at higher risk. Certain bacterial or viral infections can trigger or worsen psoriasis outbreaks.
Psychological Stress
Elevated stress levels can impair immune regulation and exacerbate psoriasis symptoms. Both emotional stress and physical stressors like trauma or injury to the skin can trigger flare-ups.
Obesity and Lifestyle Factors
Excess body weight is linked to increased skin inflammation and can worsen existing psoriasis, especially in skin folds or areas where skin contacts skin.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking not only heightens the risk of developing psoriasis but can also intensify the severity of the disease. The chemicals in cigarettes can impair immune function and skin health, making management more challenging.
Recognizing these factors can help in early diagnosis and targeted management to reduce the disease's impact.
In summary, psoriasis is a complex skin condition influenced by genetic, immune, and environmental factors. While understanding and managing these contributing factors can help control symptoms, ongoing medical treatment and lifestyle strategies are crucial in maintaining a better quality of life for those affected.