Comprehensive Guide to the Connection Between Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure
Explore the detailed relationship between blood sugar and blood pressure, understanding how they influence each other and discover effective strategies for managing both. Learn about physiological mechanisms and the importance of integrated health management to prevent serious complications like heart disease, stroke, and kidney issues.
The Relationship Between Blood Sugar Levels and Blood Pressure: An In-Depth Analysis
Understanding the complex relationship between blood sugar and blood pressure is crucial for maintaining optimal health, especially for individuals diagnosed with diabetes or hypertension. This comprehensive guide explores how these two vital health metrics influence each other, the underlying physiological mechanisms, and effective strategies to manage both conditions effectively.
What Is Blood Sugar?
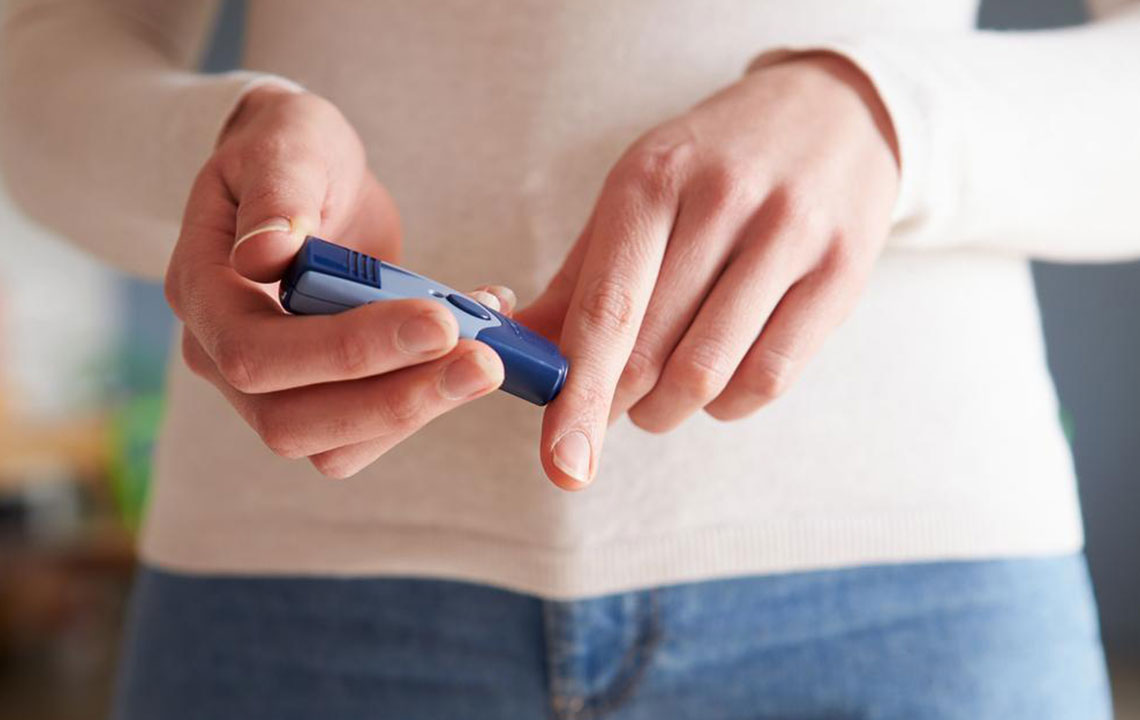
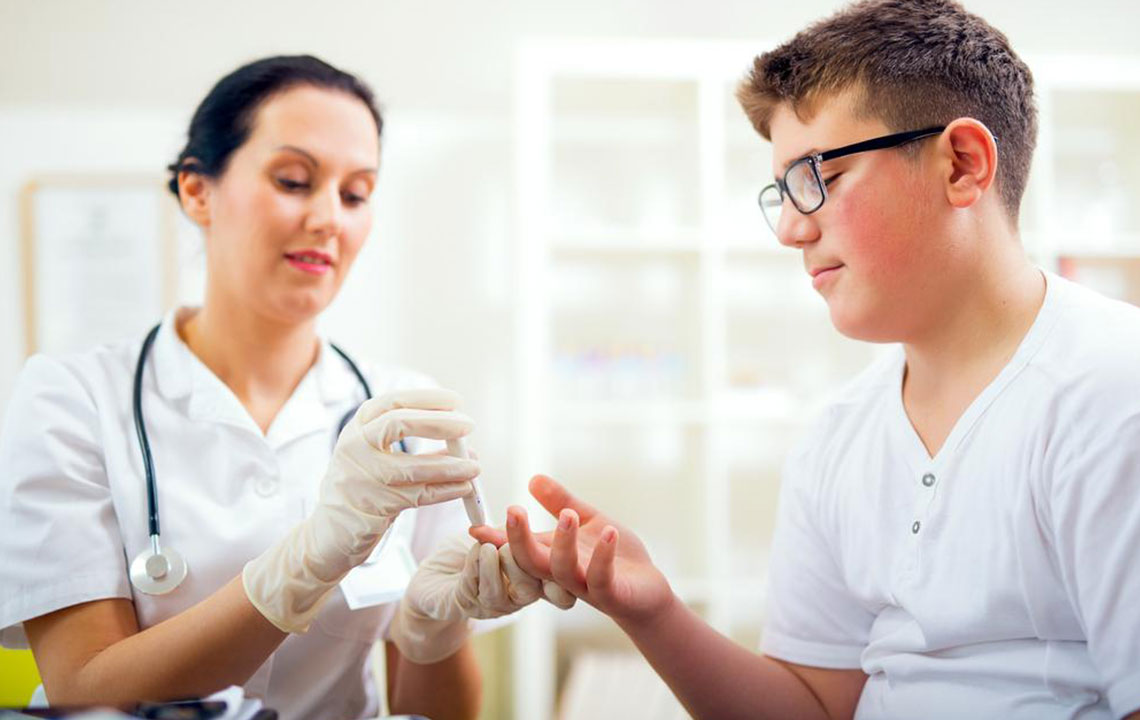
Blood sugar, also known as blood glucose, represents the concentration of glucose present in your bloodstream. Glucose is a primary energy source for your body’s cells and is derived from the food you consume. During routine health assessments, blood tests measure these glucose levels against standard reference ranges to assess whether they are within healthy limits or if they indicate a potential health concern such as diabetes.
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a central role in regulating blood sugar levels. It facilitates the conversion of glucose into energy that your cells can utilize. When functioning properly, insulin helps maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. However, in conditions like diabetes mellitus, either the body does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes), or the cells become resistant to insulin's effects (Type 2 diabetes), resulting in consistently elevated blood sugar levels—a condition known as hyperglycemia.
What Is Blood Pressure?
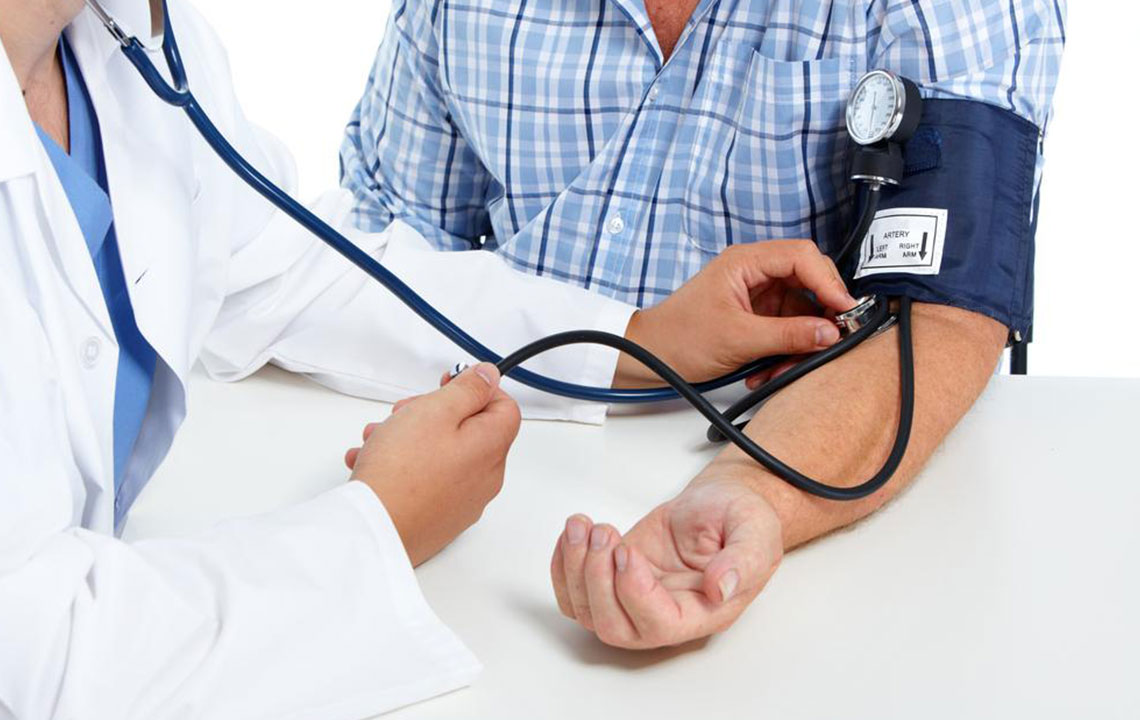
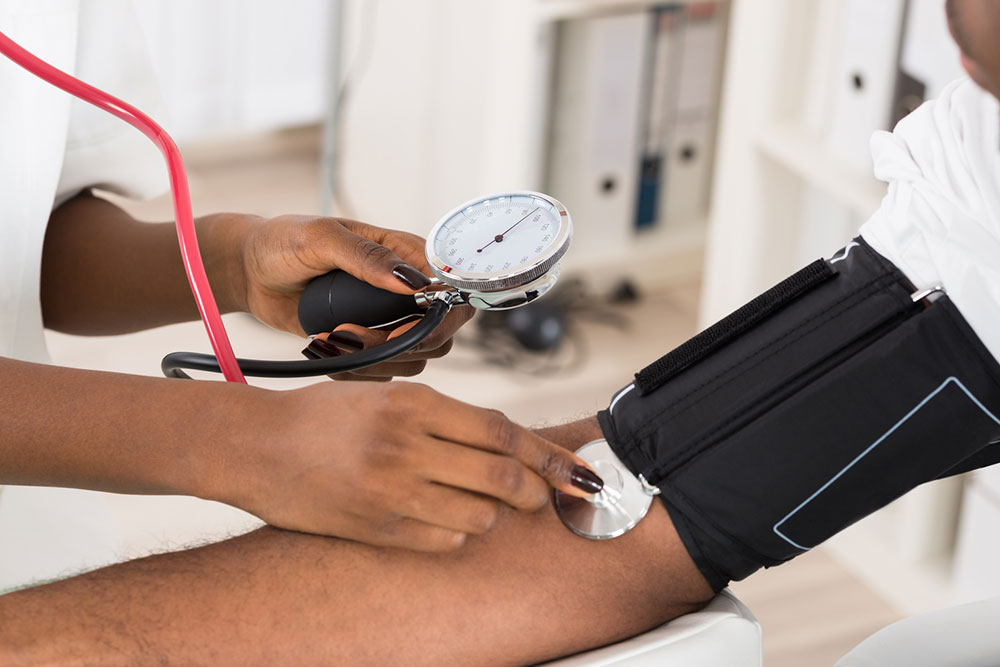
Blood pressure measures the force that circulating blood exerts against the walls of your arteries. It is determined by the strength and rate of your heartbeat along with the degree of vessel constriction or relaxation. High blood pressure, medically known as hypertension, occurs when this force becomes consistently elevated, putting extra strain on your cardiovascular system.
Understanding the Interconnection Between Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure
Research indicates that elevated blood sugar levels can contribute to the development of arterial changes such as narrowing (atherosclerosis) and increased stiffness. These arterial alterations can, in turn, raise blood pressure levels. Individuals diagnosed with diabetes tend to have a higher prevalence of hypertension, owing partly to these vascular modifications.
Moreover, high blood sugar levels can promote inflammation and damage to blood vessel linings, further exacerbating hypertension risks. Conversely, high blood pressure can impair the proper regulation of blood flow and glucose delivery, illustrating the bidirectional relationship between these two health issues.
Effective management of either condition often necessitates a focus on the other. Controlling blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, medication, and lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the risk of developing hypertension. Conversely, managing blood pressure effectively can help prevent diabetes-related complications and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Individuals with both high blood sugar and high blood pressure face increased risks of severe health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and nerve damage. Therefore, an integrated approach to managing these conditions is essential for long-term health and well-being.
Strategies for optimal management include regular monitoring, adopting a balanced diet low in processed sugars and salt, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding tobacco use, and adhering to prescribed medications. Healthcare professionals often recommend lifestyle adjustments alongside pharmacological treatments to achieve comprehensive control over both blood sugar and blood pressure.
Understanding the connection between these two health parameters empowers patients to take proactive steps in preventing complications and improving their quality of life. Staying informed, making healthy lifestyle choices, and working closely with healthcare providers are vital components of effective management strategies for individuals impacted by these conditions.