Comprehensive Guide to the Health Risks Associated with Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a prevalent sleep disorder with serious health risks including hypertension, heart disease, and diabetes. Early diagnosis and effective treatments like CPAP therapy can greatly reduce these dangers. This comprehensive guide highlights the importance of recognizing symptoms, understanding associated health risks, and exploring available management options to ensure better health and improved quality of life.

Understanding the Health Risks Associated with Sleep Apnea
Getting quality sleep is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. When sleep patterns are disrupted, it can lead to a multitude of health problems that may affect various body systems. One of the most common sleep disorders impacting millions worldwide is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This condition is characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, often signaled by loud snoring and frequent awakenings. If left untreated, sleep apnea can significantly increase the risk of developing serious health complications, making early diagnosis and proper management crucial.
Obstructive sleep apnea has seen a rise in prevalence over recent years, partly due to lifestyle factors such as obesity, sedentary behavior, and aging populations. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the potential health dangers are fundamental steps toward effective treatment and prevention. This comprehensive guide delves into the various health risks associated with sleep apnea, emphasizing the importance of prompt intervention and effective management strategies.
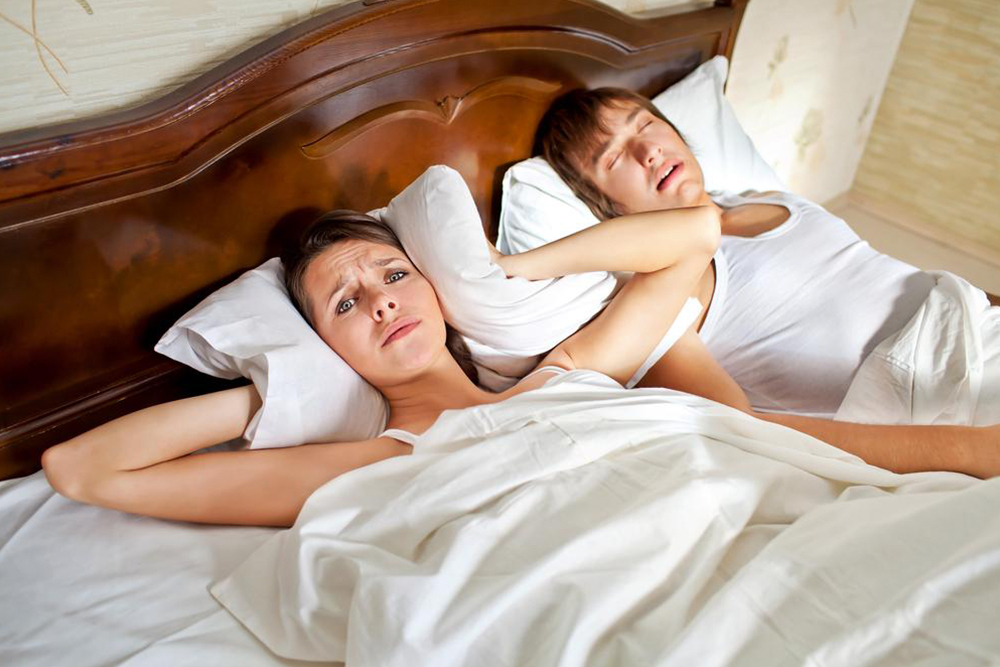
The hallmark symptom of sleep apnea is often loud snoring, which occurs due to the vibration of throat tissues as airflow is obstructed. However, many individuals with sleep apnea are unaware of their condition, and it is often only diagnosed after a bed partner notices the symptoms. Sleep apnea is not just a matter of disruptive sleep; it can have far-reaching consequences for cardiovascular health, metabolic regulation, mental health, and overall quality of life.
Let’s explore the primary health risks linked to sleep apnea in detail:
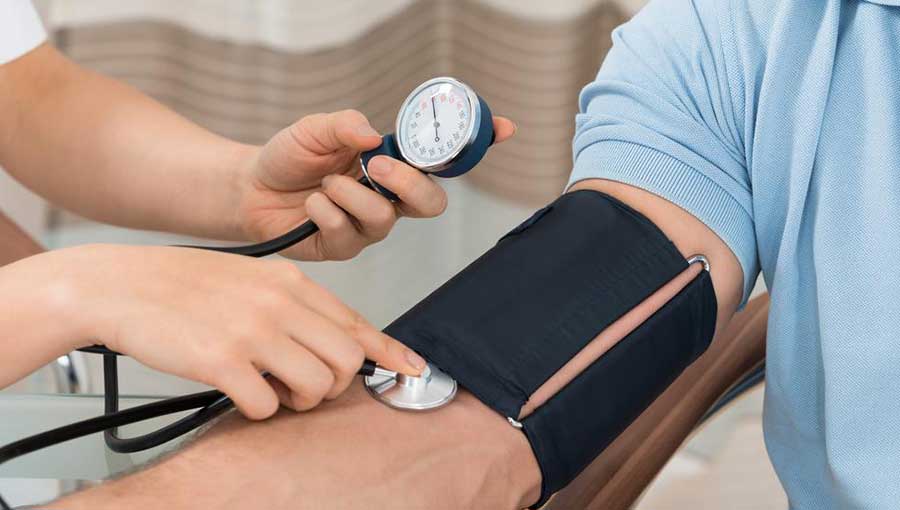
1. Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease: Chronic sleep apnea significantly elevates the risk of high blood pressure. The recurrent pauses in breathing cause sudden drops in blood oxygen levels, which in turn activate stress responses that constrict blood vessels and raise blood pressure. Over time, this can lead to sustained hypertension, increasing the likelihood of stroke, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular issues. Individuals with pre-existing hypertension are especially vulnerable, as sleep apnea can exacerbate their condition. Effectively treating sleep apnea often leads to better blood pressure regulation.
2. Heart Health Concerns: The irregular oxygen supply during sleep causes strain on the heart, increasing the risk of arrhythmias, heart failure, and coronary artery disease. Night-time stress responses, such as surges in adrenaline, further compromise heart health. The fatigue and sleep deprivation linked with sleep apnea can also impair overall cardiac function, emphasizing the importance of diagnosis and management.
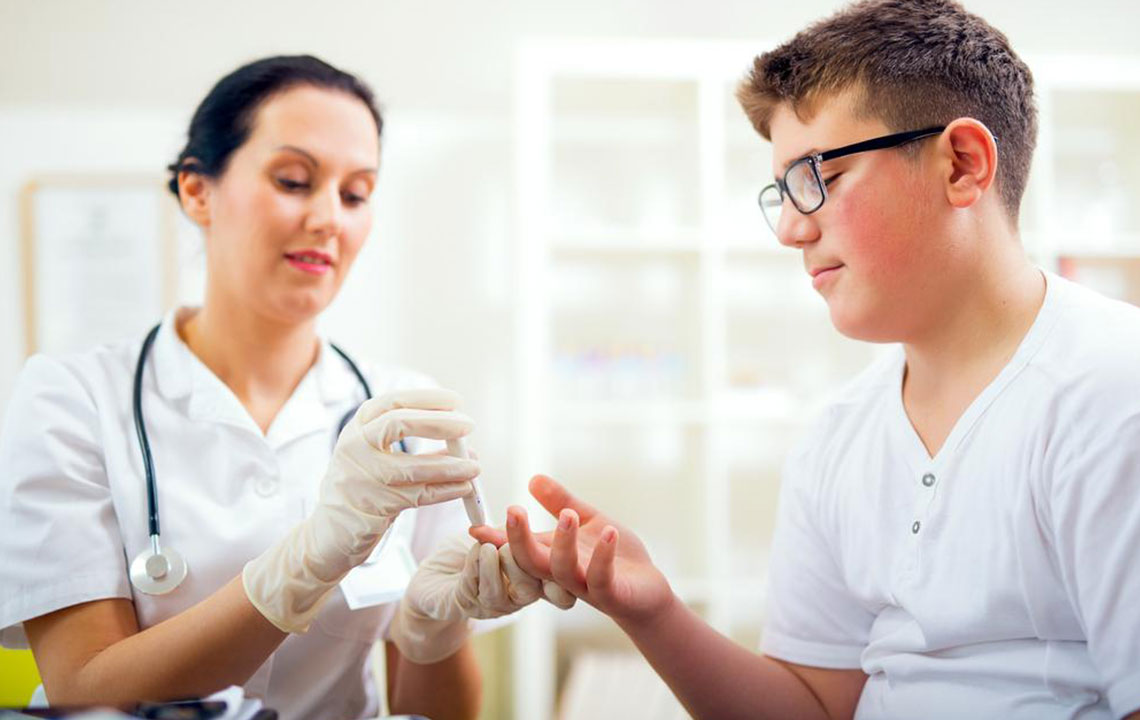
3. Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Research indicates that individuals with untreated sleep apnea are at an approximately 80% higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The disrupted sleep and intermittent hypoxia impair insulin sensitivity, leading to insulin resistance—a precursor to diabetes. Additionally, sleep deprivation influences hormonal regulation, increasing levels of ghrelin, a hormone responsible for stimulating appetite, particularly sugar cravings. This hormonal imbalance often results in weight gain, which worsens sleep apnea, creating a cyclical pattern of health deterioration.
4. Obesity and Weight Management Challenges: Obesity is both a cause and consequence of sleep apnea. Excess weight, particularly around the neck and throat, narrows the airway and makes obstruction more likely. Conversely, sleep apnea-induced fatigue can reduce physical activity levels, contributing to further weight gain. The cycle of poor sleep, hormonal disruption, and weight gain complicates management and heightens health risks.
5. Mental and Cognitive Health: Sleep apnea often leads to daytime fatigue, cognitive impairment, and mood disturbances. Sleep fragmentation prevents restorative sleep stages, impairing memory, concentration, and decision-making abilities. Over time, untreated sleep apnea is linked to increased risks of depression, anxiety, and reduced overall mental health.
Beyond these primary concerns, sleep apnea has been associated with an increased likelihood of developing other health issues, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), stroke, and metabolic syndrome. Addressing sleep apnea through timely diagnosis and effective treatment can significantly reduce these risks and improve quality of life.
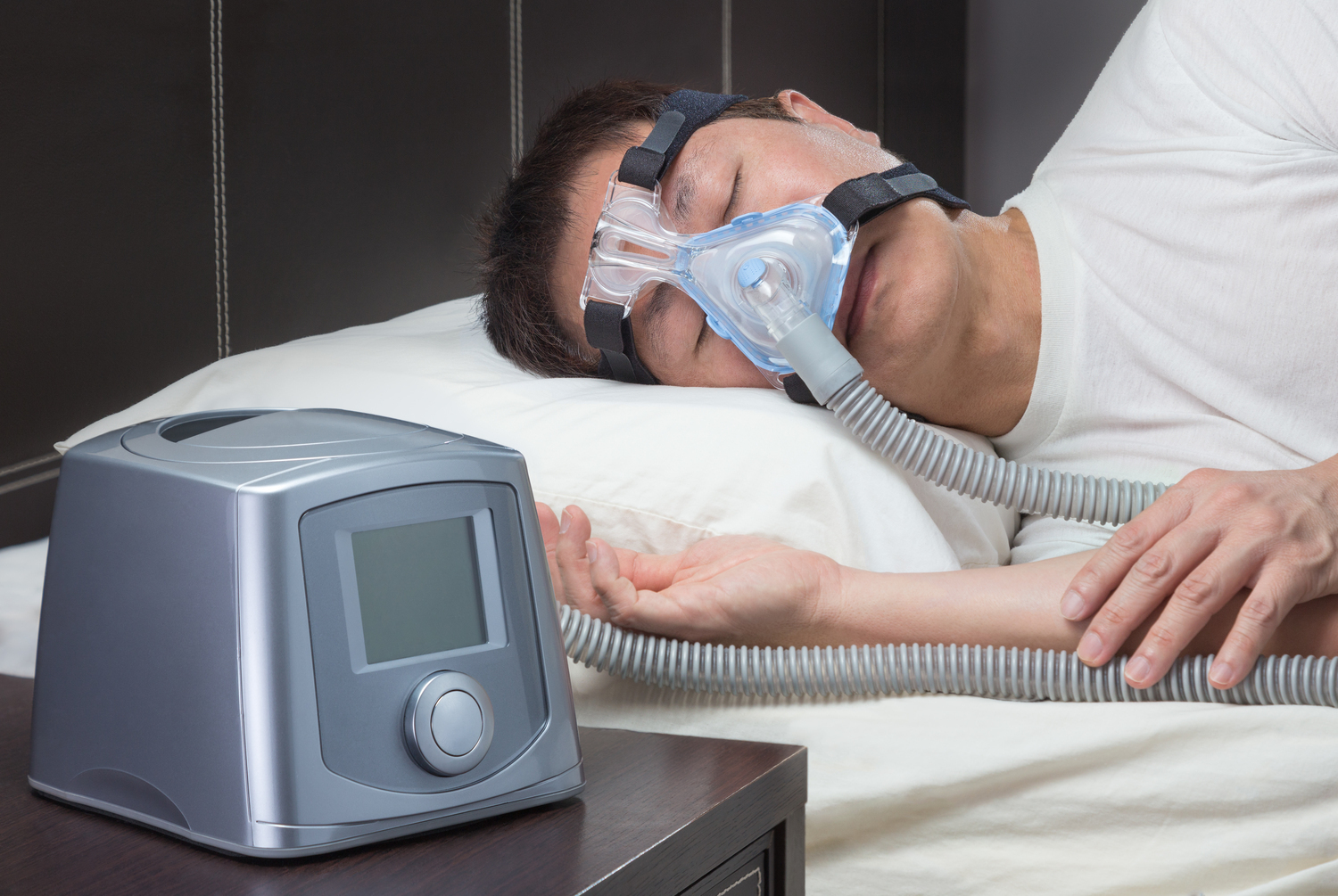
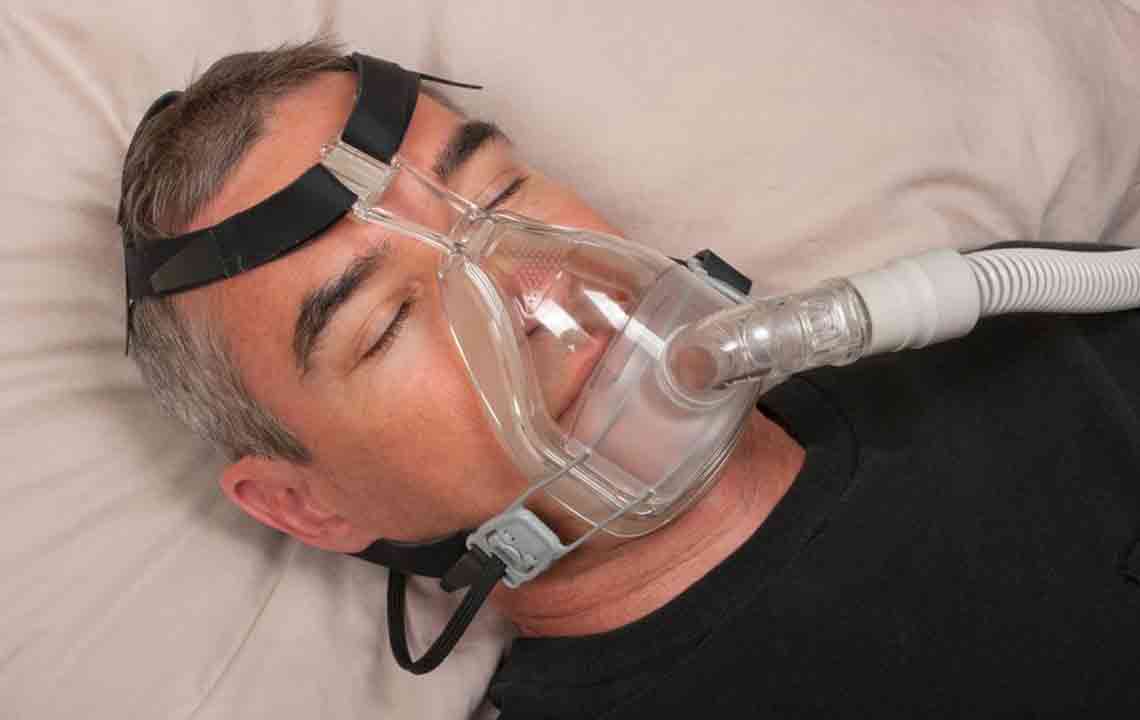
Effective management strategies play a vital role in mitigating health risks. Among the most widely employed therapies is Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP), which involves wearing a mask connected to a machine that delivers a constant stream of pressurized air to keep the airways open during sleep. Other options include dental appliances, lifestyle modifications—such as weight loss, quitting smoking, and sleep position adjustments—and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
Early recognition and treatment of sleep apnea can drastically improve health outcomes, prevent serious complications, and restore restful sleep. If you suspect you might suffer from sleep apnea, consulting a healthcare professional for comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment options is strongly recommended. With proper care, the adverse health effects of sleep apnea can be minimized, enhancing overall well-being and longevity.