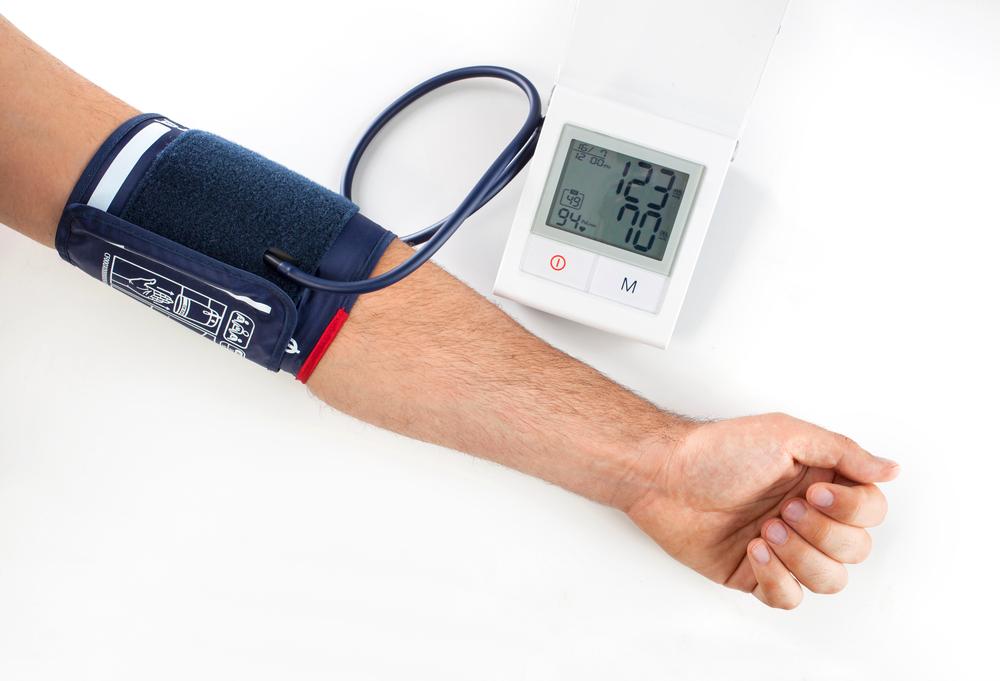
Comprehensive Guide to Blood Pressure Measurements and Classification Charts
This detailed guide provides an in-depth look at blood pressure readings, their classifications, and the significance of monitoring your cardiovascular health. Understanding these metrics helps in early detection and management of hypertension, reducing the risk of severe health complications. Learn about normal, elevated, hypertensive, and hypertensive crisis levels, along with lifestyle tips for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Regular check-ups and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in preventing hypertension and safeguarding your overall health. Stay informed and proactive to protect your heart health effectively.
Comprehensive Guide to Blood Pressure Measurements and Classification Charts
High blood pressure, medically known as hypertension, is a prevalent health condition that affects millions worldwide. It occurs when there is consistent exertion of excessive force by blood against arterial walls, which can lead to serious health complications if left unmanaged. While factors such as genetics and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in its development, underlying conditions like kidney disease or hormonal imbalances can also contribute. Understanding blood pressure readings and their classifications is essential for early detection, effective management, and prevention of associated health risks.
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings: The Basics
Blood pressure is a vital indicator of cardiovascular health, measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). It is expressed as two numbers — systolic over diastolic — for example, 120/80 mm Hg. The systolic value reflects the pressure in your arteries during each heartbeat when the ventricles of your heart contract. Conversely, the diastolic value indicates the pressure in your arteries when the heart is at rest between beats. Both readings provide critical information about your heart health and vascular condition.
To interpret your blood pressure readings accurately, it's vital to understand what these numbers mean within the context of standard health guidelines. Here is an overview of blood pressure classifications based on the latest recommendations from authoritative health organizations like the American Heart Association.
Blood Pressure Classifications: What Do The Numbers Say?
Normal Blood Pressure: Readings below 120/80 mm Hg are considered healthy. Maintaining such levels typically requires a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Elevated Blood Pressure: When systolic readings are consistently between 120-129 mm Hg, and diastolic remains below 80 mm Hg, this indicates elevated blood pressure. While not yet classified as hypertension, elevated levels serve as a warning sign and should prompt lifestyle changes to prevent progression.
Without intervention, elevated blood pressure can develop into hypertension. Therefore, routine monitoring and lifestyle adjustments are essential at this stage.
Stage 1 Hypertension: This stage is characterized by systolic readings ranging from 130-139 mm Hg or diastolic levels between 80-89 mm Hg. At this level, healthcare providers might recommend dietary modifications, physical activity, weight management, and possibly medication, especially if there are additional risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Stage 2 Hypertension: Persistent readings at or above 140 mm Hg systolic or 90 mm Hg diastolic data indicate Stage 2 hypertension. Management at this stage often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and antihypertensive medications to effectively control blood pressure and reduce health risks.
Hypertensive Crisis (Emergency): When blood pressure spikes to 180/110 mm Hg or higher, it constitutes a hypertensive crisis requiring immediate medical attention. This critical condition increases the risk of life-threatening events such as strokes, heart attacks, or organ damage. Emergency treatment aims to reduce blood pressure gradually to prevent further complications, often initiated with hospital interventions and medications.
Statistics reveal that nearly 50% of adults over 20 in many countries suffer from high blood pressure, often without noticeable symptoms. This silent condition can lead to serious consequences like cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes, if left untreated. Regular screening, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and adhering to medical advice are fundamental steps toward preventing hypertension-related health issues.