Comprehensive Guide to Blood Pressure Levels and Their Critical Role in Heart Health
This comprehensive guide explains the importance of understanding blood pressure levels, what constitutes healthy ranges, and how different stages of hypertension impact your heart health. Learn practical tips for maintaining optimal blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medical interventions to prevent serious health complications.
A Complete Overview of Blood Pressure Levels and Their Significance for Your Well-being
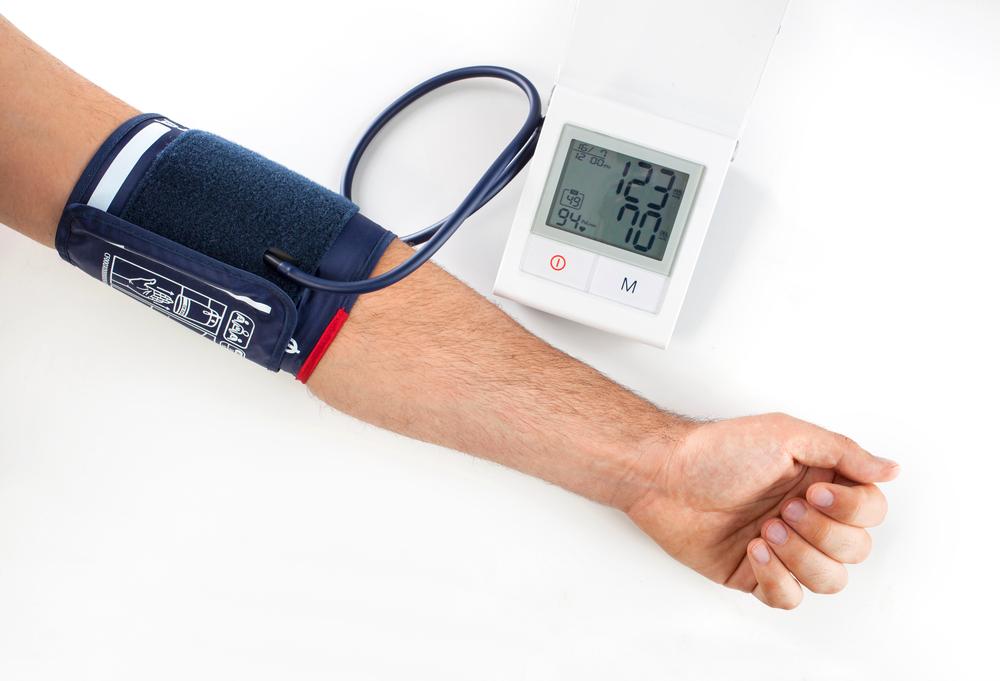
Monitoring your blood pressure is a vital aspect of maintaining overall health. When your healthcare provider takes your blood pressure, they usually record it as a fraction, such as 120/80 mmHg. Understanding what these numbers mean, how they fluctuate, and their implications can empower you to make informed lifestyle choices to protect your heart and prevent potential health issues.
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings
Blood pressure readings consist of two values: systolic and diastolic. The systolic pressure, the higher number, measures the force of blood against artery walls when your heart contracts. The diastolic pressure, the lower number, measures the pressure when your heart relaxes between beats. Both figures are critical indicators of cardiovascular health.
What Constitutes a Healthy Blood Pressure Range?
Typically, a normal blood pressure reading is around 120/80 mmHg. For optimal health, systolic should ideally be maintained between 90 and 120 mmHg, while diastolic should be between 60 and 80 mmHg. Consistently staying within this range significantly reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke.
The American Heart Association (AHA) defines normal blood pressure within these parameters. Readings are measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Maintaining blood pressure within this healthy window minimizes the necessity for medical intervention and encourages a lifestyle focused on balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, weight management, and stress control.
Recognizing Elevated and Prehypertensive Levels
If your blood pressure exceeds 120/80 mmHg, it's important to pay attention and adopt healthier habits immediately. Elevated blood pressure is categorized when systolic pressure falls between 120-129 mmHg, and diastolic remains below 80 mmHg. While not officially classified as hypertension, these thresholds indicate an increased risk for future cardiovascular problems.
Prehypertension occurs when systolic ranges from 120 to 139 mmHg, and diastolic ranges from 80 to 89 mmHg. Although these readings do not constitute high blood pressure diagnosis, they serve as warning signs that lifestyle modifications are necessary to prevent progression to hypertension.
Hypertension Stage 1: The Beginning of High Blood Pressure
Stage 1 hypertension is diagnosed when systolic pressure is between 140-159 mmHg or diastolic between 90-99 mmHg. Persistent elevation in blood pressure during this stage requires medical attention. Doctors often recommend integrating medication with lifestyle changes such as diet adjustments, physical activity, weight loss, and stress reduction to effectively control blood pressure and prevent complications.
Hypertension Stage 2: Advanced High Blood Pressure
When blood pressure readings reach 160 mmHg or higher systolic, or 100 mmHg and above diastolic, it is classified as Stage 2 hypertension. This level necessitates careful management, often involving antihypertensive medications prescribed by a healthcare provider. Lifestyle modifications remain essential, including a heart-healthy diet, increased physical activity, and weight management to help lower and stabilize blood pressure levels.
Hypertensive Crisis: A Medical Emergency
A blood pressure reading exceeding 180/110 mmHg indicates a hypertensive crisis, calling for immediate medical attention. Such extreme levels can lead to severe complications such as stroke, heart attack, kidney damage, or aneurysm. Symptoms accompanying a hypertensive crisis include severe headache, chest pain, dizziness, visual disturbances, or blood in urine. Quick medical intervention is crucial to prevent catastrophic outcomes.
Understanding your blood pressure readings and their significance is vital in preventing cardiovascular diseases. Regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and timely medical intervention can significantly improve your heart health and overall well-being. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific health condition.