Comprehensive Guide to Managing Psoriasis: Causes, Treatments, and Lifestyle Tips
This comprehensive guide explores psoriasis, its causes, triggers, and cutting-edge treatments. Learn about effective management strategies, from topical applications and phototherapy to systemic medications and natural remedies. By understanding immune system dynamics and lifestyle tips, individuals can better control flare-ups and improve skin health. Whether you are newly diagnosed or looking for advanced options, this article provides valuable insights into managing psoriasis effectively to enhance quality of life.
Understanding Psoriasis: Essential Facts and Insights
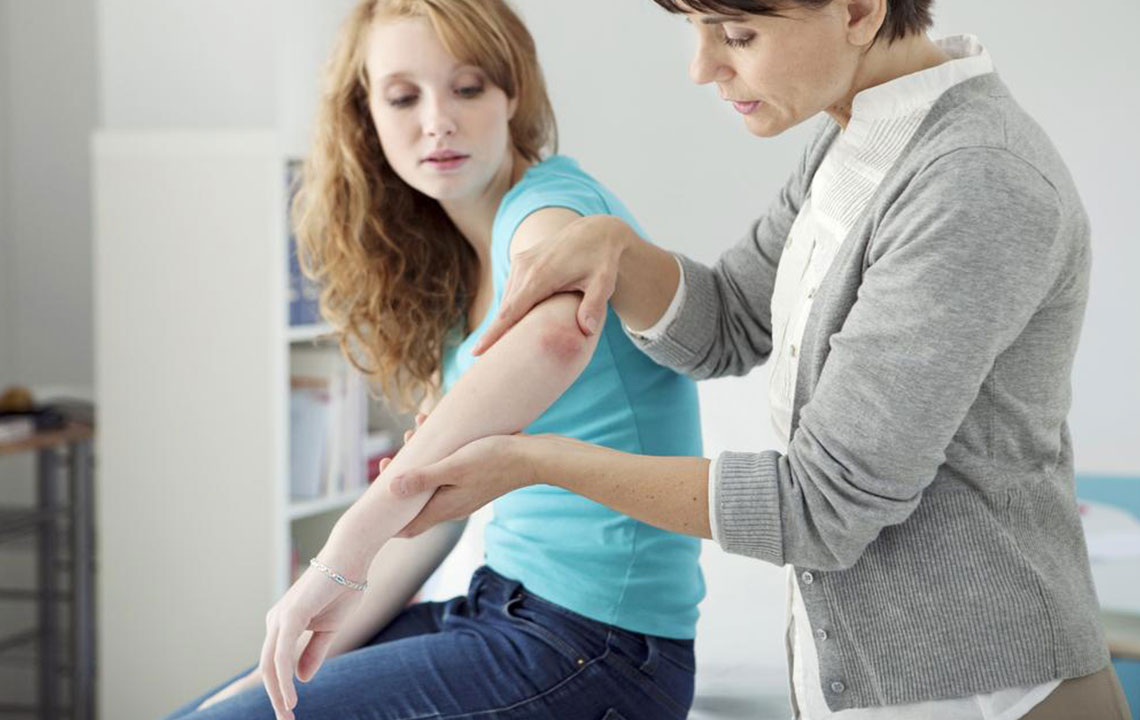
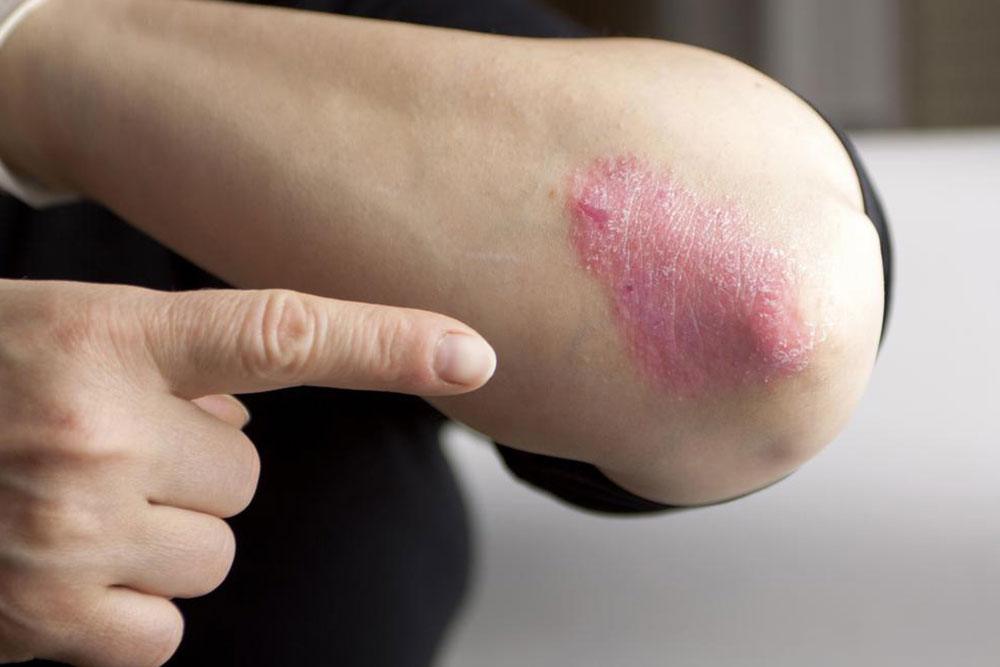
Psoriasis is a long-term chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, it results in thick, scaly, and often itchy patches that can appear on various parts of the body. Although it is primarily a skin disorder, psoriasis is actually an autoimmune condition involving immune system dysregulation. While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, a variety of treatment options are available to control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve quality of life.
This condition most commonly manifests in adulthood, although it can occur at any age, including childhood. The most frequently affected areas include regions like elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, and palms, though other parts may also be involved. The severity of psoriasis varies significantly, from small, localized patches to extensive, widespread skin involvement that can impair daily activities.
Understanding the Causes and Triggers of Psoriasis
The precise cause of psoriasis remains elusive, making it a complex disease influenced by multiple factors. It is considered an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin tissues, leading to inflammation and rapid skin cell growth. Genetics play a notable role, with research indicating that about one-third of psoriasis cases have a hereditary component. Over 10% of the American population carries genes associated with the condition, although not everyone with genetic predisposition develops psoriasis.
Environmental factors serve as catalysts, activating the disease in genetically susceptible individuals. Common triggers include exposure to cold weather, significant emotional or physical stress, infections (such as strep throat), certain medications like beta-blockers or lithium, skin injuries, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Recognizing these triggers can help manage and possibly prevent flare-ups.
The Role of the Immune System in Psoriasis
At the core of psoriasis lies immune system dysfunction. Normally, the immune system protects the body from harmful pathogens by activating immune cells to fight infections. However, in psoriasis, immune cells such as T-cells become overactive and mistakenly target healthy skin cells. This abnormal immune response causes the skin to produce new cells at an accelerated rate, often within days, rather than the usual weeks. The excess skin cells pile up, forming thick, scaly patches that are characteristic of psoriasis.
In addition to excess cell production, inflammation is a key feature, leading to redness, swelling, and discomfort. cytokines—protein messengers used by the immune system—are involved in promoting inflammation and skin cell growth, making them targets for various psoriasis treatments.
Effective Management and Treatment Strategies for Psoriasis
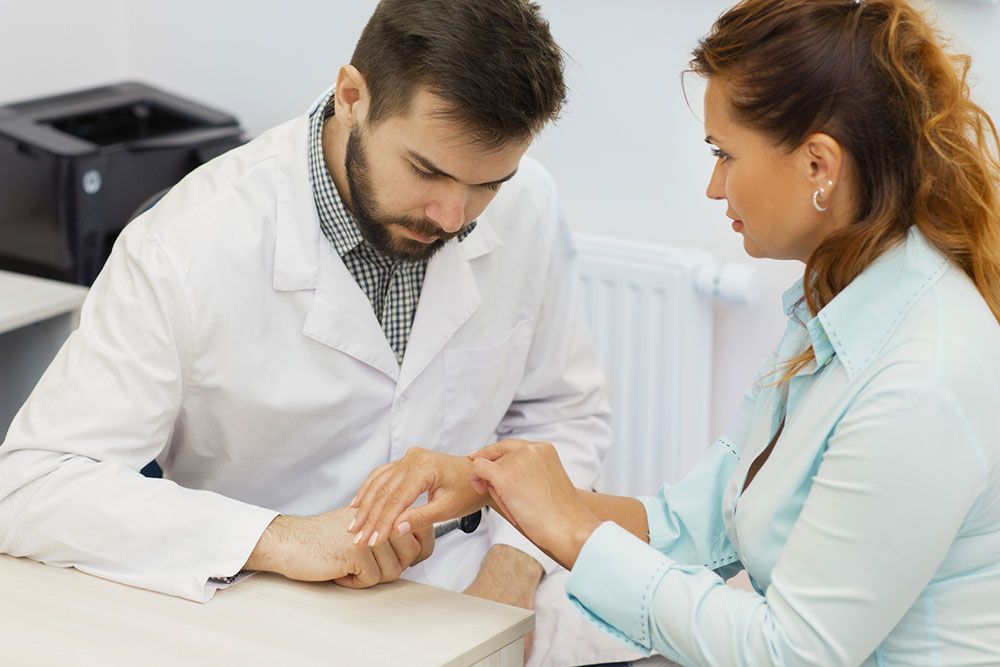
Current management of psoriasis focuses on controlling symptoms, minimizing flare-ups, and improving the patient's overall well-being. Although no cure exists, advances in medical treatments have provided patients with effective options tailored to the severity and location of their psoriasis. Treatment plans are usually customized by dermatologists to suit individual needs, incorporating topical therapies, phototherapy, systemic medications, and lifestyle modifications.
Topical treatments are the first line of defense and include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, vitamin D analogs like calcipotriol to regulate skin cell growth, retinoids derived from vitamin A to normalize skin cell production, and keratolytic agents such as salicylic acid to remove scales and relieve itching. Proper application and dosing are crucial to maximize benefits and minimize side effects.
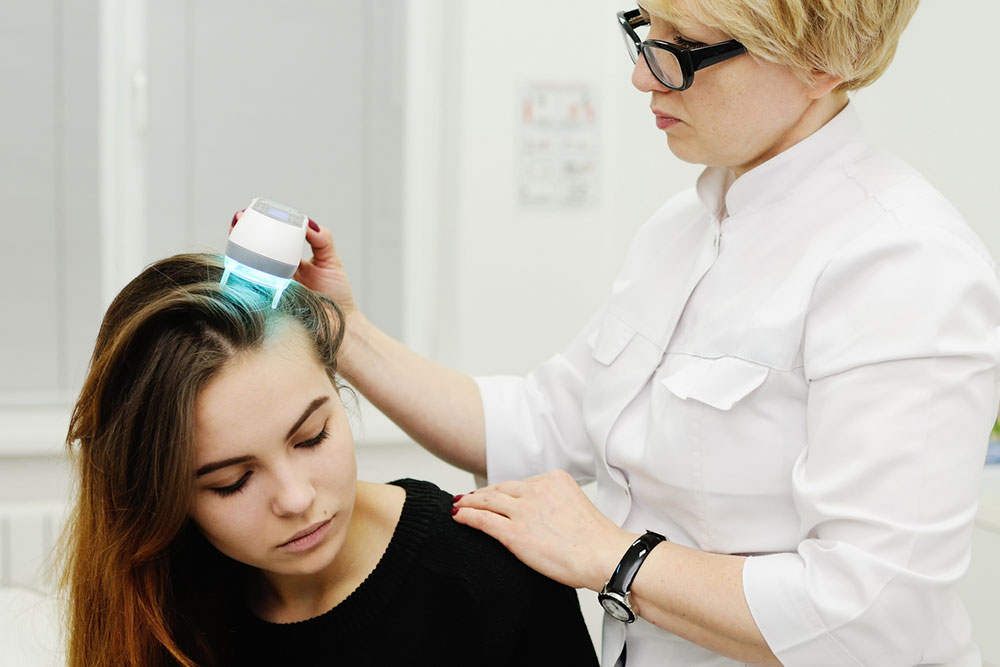
Phototherapy involves exposing affected skin to controlled ultraviolet (UV) light, primarily UVB. This method has proven effective in reducing inflammation and slowing down cell proliferation. Procedures like narrowband UVB therapy and excimer laser treatments are commonly employed for moderate to severe psoriasis cases. Regular sessions under medical supervision yield the best results.
Systemic treatments include oral or injectable medications aimed at suppressing the immune response. Drugs like cyclosporine, methotrexate, and newer biologics targeting specific immune pathways (e.g., TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors) are prescribed for extensive or resistant psoriasis. These medications can provide significant symptom relief but require careful monitoring for side effects.
Natural and Alternative Remedies are becoming increasingly popular among patients seeking complementary approaches. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil may help reduce inflammation. Aloe vera gel can soothe irritated skin, while maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including stress management, proper skin hydration, and avoiding known triggers, plays a vital role in disease control.
Consulting a dermatologist is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan. New research continues to improve understanding and management of psoriasis, offering hope for more effective therapies in the future.