Comprehensive Insights into Insulin Pump Therapy: Benefits and Drawbacks
Insulin pump therapy offers a modern approach to diabetes management, providing consistent insulin delivery, personalized dosing, and lifestyle flexibility. While it involves higher costs and certain challenges such as site maintenance and monitoring, its benefits often outweigh drawbacks. Consulting healthcare providers can help determine if this technology suits individual needs. This comprehensive overview covers the key advantages and disadvantages, helping patients make informed decisions for better blood sugar control and quality of life.
Understanding the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using an Insulin Pump for Diabetes Management
Managing diabetes effectively requires precise control of blood glucose levels, and insulin pump therapy has emerged as a sophisticated solution that offers multiple advantages over traditional insulin injections. An insulin pump is a small, portable, computerized device designed to deliver insulin continuously throughout the day and night, mimicking natural pancreatic function more closely. As its popularity continues to rise among individuals with diabetes, understanding its benefits and potential drawbacks becomes crucial for making informed treatment decisions.
Advantages of Insulin Pump Therapy
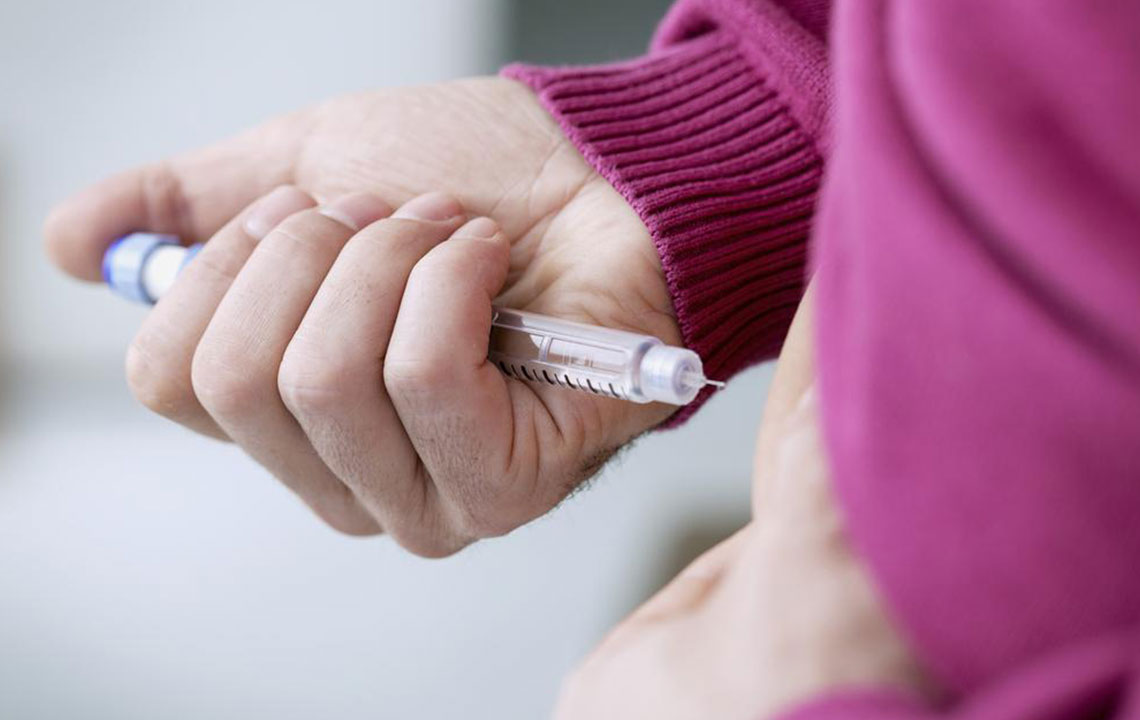
Consistent Insulin Delivery: The primary benefit of an insulin pump is its ability to administer a steady flow of insulin, removing the inconvenience of multiple daily injections required with insulin pens or syringes. This precise delivery enhances blood sugar regulation and comfort.
The pump's tubing connects directly to the body via a catheter inserted under the skin, allowing users to receive insulin on demand without the need for injections at every meal or snack.
Personalized Basal Rates: Users can modify basal insulin rates to match their individual metabolic needs, lifestyle, and daily routines. Adjustments can be made easily to accommodate changes such as exercise, illness, or sleep patterns, providing a tailored approach to diabetes management.
In addition to basal rate adjustments, insulin pump technology allows for bolus doses—larger amounts administered at mealtime to cover carbohydrate intake. If glycemic control needs fluctuate during the day, the pump’s settings can be instantaneously modified, providing flexibility and precision. This feature is especially advantageous during special occasions or unexpected situations where dietary routines might change.
Enhanced Lifestyle and Reduced Complication Risks
One of the most appreciated advantages of insulin pump therapy is the enhanced freedom it offers in daily life. With more control over insulin dosing, individuals can engage in activities like exercising, social gatherings, or travel without the constant need to plan for injections.
For example, indulging in desserts or skipping a meal temporarily becomes easier because insulin doses can be finely adjusted in real-time, reducing the risk of significant blood sugar swings.
Using an insulin pump can significantly lower the risk of dangerous diabetes-related complications, such as hypoglycemia (a condition of dangerously low blood sugar), which remains a concern with less precise dosing methods.
Challenges and Limitations of Insulin Pump Therapy
Despite its many advantages, insulin pump therapy does have some limitations. Firstly, pumps are incompatible with long-acting insulins like Lantus or Levemir, which means users must rely solely on short-acting or rapid-acting insulins.
Frequent blood sugar monitoring is essential to ensure the pump delivers the correct insulin dosage. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems can be integrated to facilitate this process, but it adds to the overall cost and complexity.
The financial aspect is a significant consideration; the initial investment for the device, along with ongoing supplies and maintenance, tends to be higher than traditional insulin injections, which may be prohibitive for some patients.
Some users may feel self-conscious about wearing the pump, especially if the device or its tubing is visible to others. This can impact social interactions and comfort levels.
Inserting and maintaining the catheter can cause discomfort, skin irritation, or infections if proper hygiene isn’t maintained. Regular site changes and skin care are necessary to minimize these risks.
While insulin pump therapy offers substantial benefits in diabetes management, it’s important to assess individual needs, lifestyle, and medical conditions before opting for this advanced treatment option. Consulting healthcare professionals specializing in diabetes care can provide personalized advice and help determine if an insulin pump aligns with your health goals.
In conclusion, insulin pump therapy represents a significant advancement in diabetes treatment, offering enhanced control, flexibility, and potential for reducing complications. However, it requires careful consideration of its limitations, costs, and ongoing management to ensure optimal benefits. With proper medical guidance, many individuals with diabetes can experience improved quality of life through this innovative approach.