Comprehensive Guide to Managing Adult Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
This comprehensive guide provides effective strategies for managing adult type 2 diabetes through lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and technology tools. It emphasizes the importance of diet, exercise, foot care, stress management, and regular monitoring to help patients control blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Learn practical tips for maintaining health and improving quality of life with expert insights into comprehensive diabetes management.
Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Adult Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a widespread chronic condition that affects millions of adults across the globe. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels. This impairment causes elevated sugar levels in the bloodstream, which can lead to severe health complications if not properly managed. Effective management requires a multifaceted approach that combines medical treatment with lifestyle modifications. In this detailed guide, we will explore various strategies to control and manage adult type 2 diabetes effectively, helping individuals lead healthier lives and prevent serious complications.
Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the foundational steps in managing type 2 diabetes. Obesity and excess weight are significant risk factors that contribute to insulin resistance. Engaging in regular physical activity such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling helps improve insulin sensitivity and aids in blood glucose regulation. The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week complemented by resistance training exercises twice a week for optimal results. Incorporating these physical activities into daily routines can greatly impact blood sugar control and overall health.
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes. A balanced diet rich in high-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, supports stable blood glucose levels. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel, help reduce inflammation and improve cardiovascular health—crucial given the increased risk of heart disease among diabetics. Monitoring carbohydrate intake is essential; choosing complex carbs over simple sugars prevents rapid spikes in blood glucose. Limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive alcohol consumption further aids in maintaining optimal blood sugar levels.
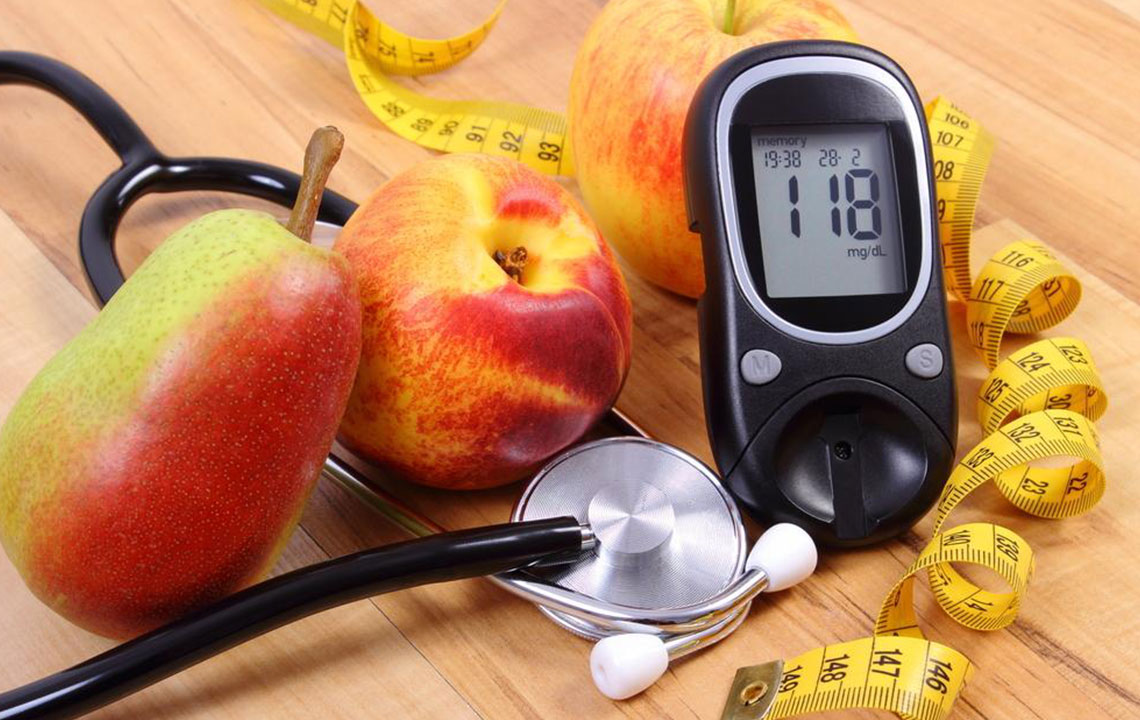
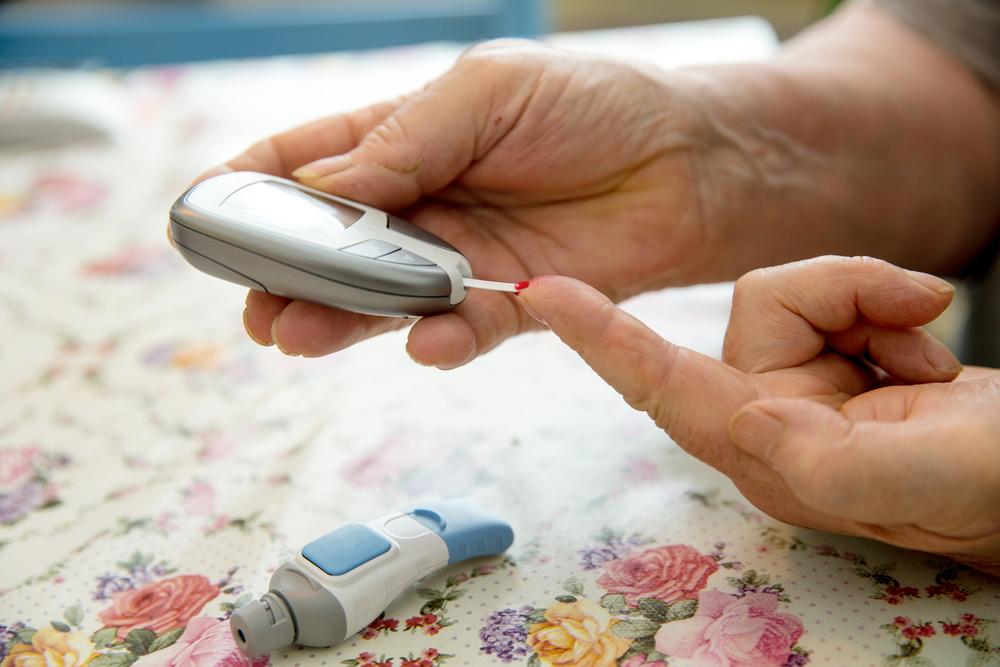
Regular blood glucose monitoring allows individuals to understand how their body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. Using a glucometer daily provides immediate feedback, aiding in making informed lifestyle choices. Additionally, HbA1c tests every three to six months offer insights into long-term blood glucose control. This data enables healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans effectively and ensure target ranges are maintained.
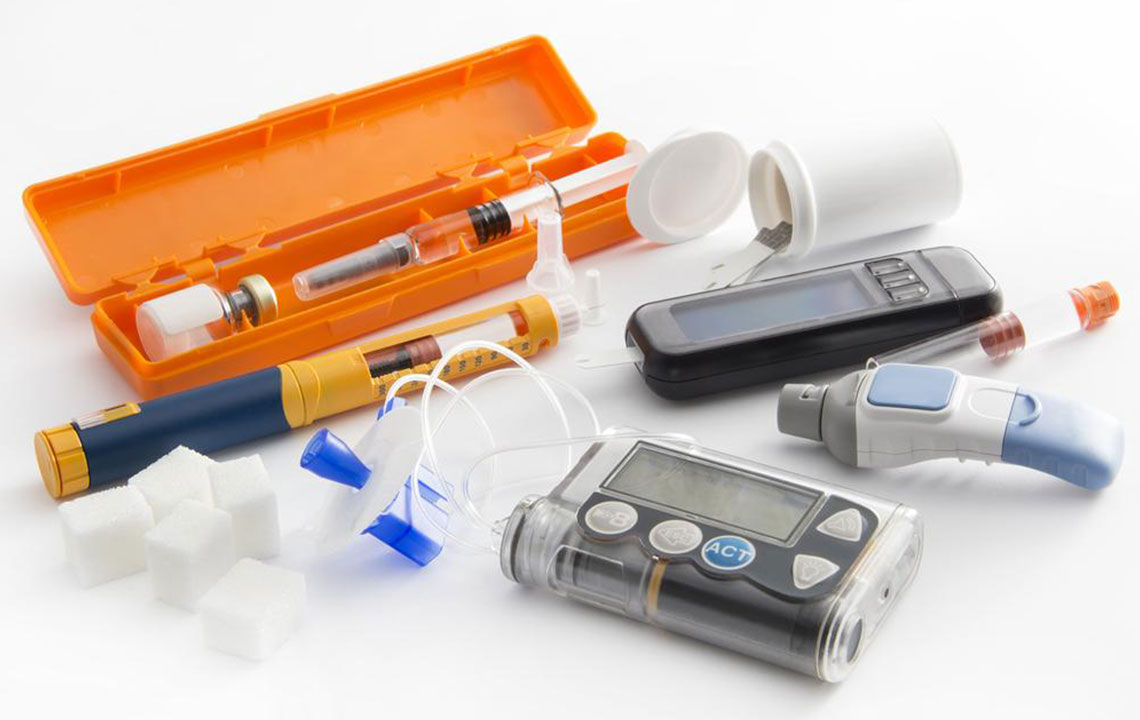
Besides diet and exercise, medication adherence is critical for many patients. Oral hypoglycemic agents, insulin therapies, and other medications prescribed by physicians help manage blood glucose levels when lifestyle modifications alone aren’t sufficient. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions meticulously, report any side effects, and regularly attend check-ups to optimize treatment efficacy.
Foot care is an often overlooked aspect of diabetes management, yet it is vital. High blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage and poor circulation, increasing the risk of foot ulcers and infections. Daily foot inspections, proper hygiene, and moisturizing prevent skin dryness and cracking. Wearing comfortable, well-fitting shoes—preferably diabetic-friendly footwear—reduces injury risk. Regular podiatric examinations are recommended to detect early signs of complications and provide professional care accordingly.
Managing stress and ensuring mental health are essential components. Chronic stress triggers physical responses that can raise blood sugar levels. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and adequate sleep can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being. Support from family, friends, or diabetes support groups provides emotional encouragement, which is vital for long-term disease management.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle also involves avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake, both of which significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular complications and worsen blood sugar control. Quitting smoking can improve circulation and reduce the risk of peripheral neuropathy and other diabetic complications. Limiting alcohol consumption is advisable because alcohol can cause unpredictable blood sugar fluctuations and add extra caloric intake, which may lead to weight gain.
Education and continuous learning about diabetes are fundamental. Patients should work closely with healthcare providers to understand their condition, treatment options, and the importance of lifestyle adjustments. Staying informed empowers individuals to make healthier choices, adhere to therapy, and recognize early warning signs of complications like hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Technology also offers innovative solutions for better blood sugar management. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) and mobile health applications provide real-time tracking and data insights, empowering patients to maintain better control. Telemedicine services enable easier communication with healthcare professionals, especially for those with limited access to clinics.
In conclusion, managing adult type 2 diabetes requires a comprehensive, disciplined approach that integrates dietary management, physical activity, medication, regular monitoring, and mental health care. By implementing these strategies consistently and working in close collaboration with healthcare providers, individuals can not only control their blood sugar levels but also significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications. With proper management, patients can enjoy a good quality of life and maintain their independence and vitality for years to come.