Effective Strategies for Managing and Treating Type 2 Diabetes
This comprehensive article explores effective strategies for managing and treating type 2 diabetes. It covers causes, symptoms, crucial diagnostic tests, and holistic treatment approaches including diet, exercise, medication, and monitoring. Early detection and ongoing management are emphasized as key to preventing serious complications and maintaining a healthy, balanced life. Whether you are newly diagnosed or seeking to improve your current management plan, this detailed guide provides valuable insights to help you take control of your health and well-being.
Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is one of the most prevalent chronic health conditions worldwide. It affects millions of adults and increasingly impacts younger populations due to lifestyle changes. Proper management and treatment can restore health, reduce risks of severe complications, and sometimes even reverse the condition when detected early. This extensive guide aims to offer detailed insights into understanding the disease, methods for diagnosis, and effective treatment options to help individuals take control of their health.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Risks
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body's cells become resistant to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Over time, the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to overcome this resistance, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. The condition is closely linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, obesity, and genetic predisposition. Symptoms often develop gradually and can be subtle, which is why early detection is crucial.
Common signs of type 2 diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing cuts or wounds, and recurrent infections. If left unmanaged, the disease can lead to severe complications like cardiovascular disease, stroke, kidney failure, nerve damage (neuropathy), and vision impairment, including blindness. Recognizing these symptoms and undergoing regular screening can prevent serious health issues.
Diagnostic Tests for Type 2 Diabetes
Accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective treatment. Several blood tests are employed by healthcare professionals to confirm the presence of diabetes and to assess its severity:
A1C Test: This test measures the percentage of hemoglobin proteins that are glycated, providing an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher confirms diabetes. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, a condition that increases the risk of developing full-blown diabetes. The A1C test does not require fasting, making it convenient for routine screening.
Fasting Blood Sugar Test: This test involves fasting for at least 8 hours before blood sample collection. A fasting blood sugar of 126 mg/dL or higher signifies diabetes. Pre-diabetes is indicated by levels between 100-125 mg/dL, and levels below 100 mg/dL are considered normal.
Random Blood Glucose Test: This test can be administered at any time, regardless of meal times, especially useful when symptoms are evident. A reading of 200 mg/dL or more, combined with symptoms, confirms diabetes. It's particularly beneficial for patients presenting with nausea, vomiting, or sudden symptoms.
Additional tests like the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) can provide further clarity, especially in ambiguous cases. Once diagnosis is confirmed, comprehensive management strategies are implemented to control blood sugar levels.
Effective Treatment options for Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes involves a multifaceted approach that combines lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. Early intervention is essential in preventing complications and maintaining quality of life.
Adopting a Healthy Diet: Nutrition plays a pivotal role. Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Prioritize low-glycemic index foods that help maintain steady blood sugar levels. High dietary fiber intake is associated with improved insulin sensitivity and better glycemic control. Consulting with a registered dietitian can help develop an individualized meal plan that aligns with personal preferences and medical needs.
Engaging in Regular Physical Activity: Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, promotes weight loss, and improves cardiovascular health. Incorporate a variety of activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, yoga, and strength training into your routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week, complemented by muscle-strengthening exercises twice a week. Staying physically active is one of the most effective ways to improve blood sugar control.
Medication and Insulin Therapy: Depending on the severity of the condition, healthcare providers may prescribe oral hypoglycemics like metformin, SGLT2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, or insulin therapy. Medications are tailored to individual needs to help achieve target blood glucose levels. It’s important to adhere to prescribed regimens and regularly review treatment plans with your healthcare team.
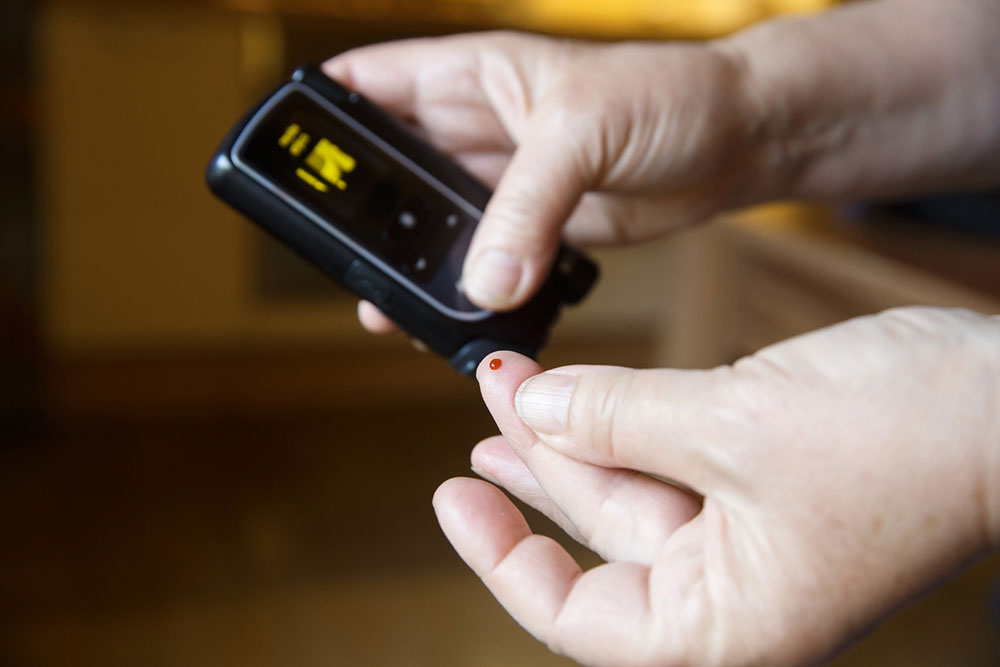
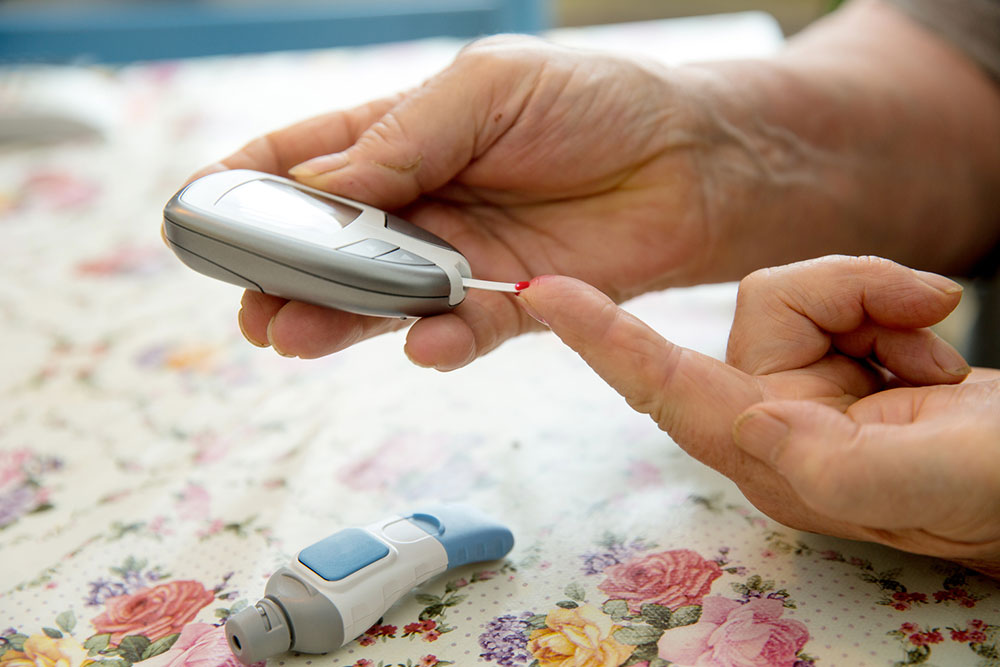
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose helps reflect the effectiveness of the treatment plan. Using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor, patients can observe how different foods, activities, medications, and stress impact their blood sugar. Keeping a record assists healthcare professionals in making necessary adjustments and reinforces awareness of daily health habits.
Beyond these strategies, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption are essential to maximizing treatment success. With early detection, continuous management, and lifestyle discipline, individuals with type 2 diabetes can lead full, healthy lives despite their diagnosis.