Comprehensive Guide to Adult-Onset Type 2 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Prevention Strategies
This detailed guide explores adult-onset type 2 diabetes, covering its causes, symptoms, and practical prevention strategies. Emphasizing lifestyle modifications such as healthy eating, regular exercise, and stress management, the article provides comprehensive insights for reducing risk and managing the condition effectively. Early detection and proactive health habits are vital for preventing long-term complications and improving quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to Adult-Onset Type 2 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Prevention Strategies
Type 2 diabetes, often referred to as adult-onset diabetes, is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions worldwide. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels. This condition can lead to serious health complications if not detected early or managed appropriately. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the early signs, and implementing effective prevention strategies are crucial steps toward maintaining good health and preventing long-term complications.
In recent decades, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes has skyrocketed, partly driven by lifestyle and environmental factors. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune condition typically diagnosed in childhood, type 2 diabetes usually develops gradually in adults, although increasing cases are now seen in younger populations as well. The disease results mainly from complex interactions between genetic predisposition and modifiable lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, weight, and stress levels.
Understanding the Causes of Adult-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
While the exact mechanisms leading to type 2 diabetes are still being studied, several key factors have been identified as contributors to its development. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with studies showing that individuals with a family history of diabetes are at higher risk. However, genetics alone do not determine whether someone will develop the disease; environmental and lifestyle factors are equally important.
Obesity, especially central obesity or excess fat around the abdomen, is one of the most prominent risk factors. Excess fat tissue increases the body's insulin resistance, making it harder for cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. Inactivity or sedentary lifestyles further exacerbate this issue, as physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity. Poor dietary habits, such as high intake of refined sugars, processed foods, and unhealthy fats, contribute to weight gain and metabolic imbalance.
High-stress levels and chronic stress can also negatively influence blood sugar regulation by increasing cortisol levels, which promote glucose production in the liver. Additionally, certain medical conditions and hormonal disorders may predispose individuals to develop type 2 diabetes. Age is another factor; the risk increases with advancing years due to natural declines in metabolic efficiency, although lifestyle choices are often the primary modifiable factors.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Early detection of type 2 diabetes is vital to preventing complications. Common symptoms include frequent urination, persistent thirst, and increased hunger. Many individuals also experience fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing wounds, and unexplained weight loss despite normal or increased appetite. Some people remain asymptomatic for years, highlighting the importance of routine screening, especially if risk factors are present.
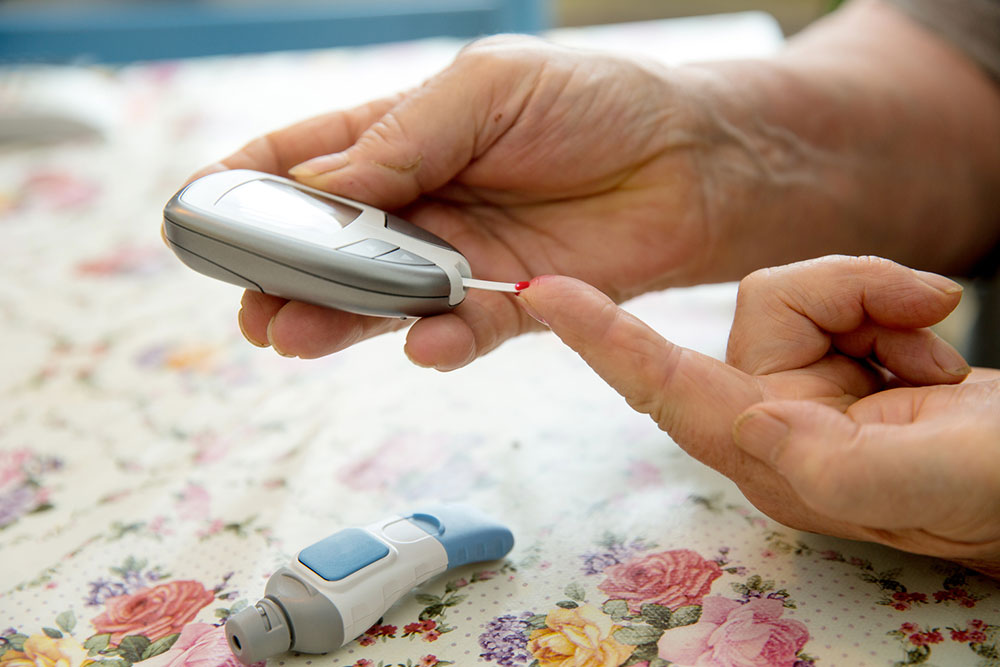
It's noteworthy that symptoms can develop gradually and may be mistaken for other ailments, which delays diagnosis. Health providers often recommend blood tests such as fasting plasma glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, or HbA1c to confirm the diagnosis.
Preventive Measures and Management Strategies
The good news is that type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed through lifestyle modifications. Maintaining a balanced diet that emphasizes whole grains, vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps stabilize blood sugar levels. Limiting intake of refined sugars, sugary beverages, and processed foods is essential.
Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, improves insulin sensitivity and aids weight management. Aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week is recommended. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial; even modest weight loss can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Stress management techniques, including mindfulness, meditation, and adequate sleep, support overall metabolic health. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption also contribute to better blood sugar control. For individuals with genetic predisposition or other risk factors, regular health screenings and proactive lifestyle changes form the cornerstone of prevention.
Managing and Controlling Type 2 Diabetes
For those diagnosed with diabetes, proper medical management is vital. This typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication to control blood glucose levels. Monitoring blood sugar regularly helps assess how well the management plan is working. In some cases, insulin therapy or other medications may be necessary.
Patients are encouraged to work closely with healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan. Weight management, dietary adjustments, and physical activity are integral components of effective control. Risk reduction for associated complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy is achievable with diligent management and regular medical check-ups.
Education about diabetes and its potential health impacts empowers patients to make informed choices and adopt healthier behaviors. Community support groups and diabetes education programs can provide valuable resources and emotional support during management and treatment.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Lifestyle Interventions
Early diagnosis of type 2 diabetes allows for prompt implementation of lifestyle interventions that can modify the disease course. Preventive strategies should be emphasized at community and policy levels to curb the rising incidence of this disease. Public awareness campaigns, screening programs, and health education are essential tools in combating the diabetes epidemic.
In conclusion, adult-onset type 2 diabetes is a complex condition influenced by a combination of genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Through a comprehensive understanding of its causes, early recognition of symptoms, and a commitment to healthy habits, individuals can significantly reduce their risk or effectively manage the disease. Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress, and seeking regular medical advice are the pillars of prevention and control. With proactive measures, it is possible to lead a healthy and fulfilling life despite the challenges posed by this chronic condition.