Comprehensive Dietary Guidelines for Managing Lupus: Foods to Avoid for Better Symptom Control
Learn comprehensive dietary strategies for managing lupus effectively. Discover which foods to avoid—like alfalfa sprouts, garlic, and foods high in unhealthy fats—to reduce inflammation and prevent flare-ups. Incorporate lifestyle tips and medical advice for optimal health management in lupus patients.

Comprehensive Dietary Guidelines for Managing Lupus: Foods to Avoid for Better Symptom Control
Lupus, medically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a persistent and often unpredictable autoimmune disease. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly targets the body’s own tissues, leading to widespread inflammation and tissue damage across multiple organs. The clinical manifestations of lupus are highly variable, ranging from mild symptoms such as fatigue and skin rashes to severe complications affecting the kidneys, heart, and lungs. Because of its variable nature, diagnosing lupus can be challenging, often requiring extensive testing and differential diagnosis.
While medication remains the cornerstone of lupus treatment, lifestyle modifications—particularly dietary choices—play a crucial role in managing symptoms and reducing flare-ups. Proper nutrition can help bolster the immune system, reduce inflammation, and support overall health, thus improving quality of life for lupus patients. Identifying and avoiding certain foods that may trigger or worsen symptoms is essential in a comprehensive management plan.
Key Foods to Avoid in Lupus Dietary Management
Knowing which foods can exacerbate lupus symptoms helps patients make informed choices that help prevent flare-ups and maintain stability. Below is an in-depth look into specific foods and ingredients that should be limited or avoided entirely to optimize health outcomes in lupus management.
Alfalfa Sprouts
Alfalfa sprouts are a popular ingredient in salads, sandwiches, and healthy dishes. However, they contain a compound called L-canavanine, which has been linked to stimulating immune responses. For individuals with autoimmune conditions like lupus, this can be problematic. L-canavanine may trigger inflammation and potentially worsen symptoms by activating immune pathways unnecessarily. Therefore, lupus patients are advised to avoid consuming alfalfa in any form—whether raw, cooked, or as a garnish—until further notice. Eliminating alfalfa sprouts from your diet can help in reducing the risk of flare-ups related to immune system overactivation.
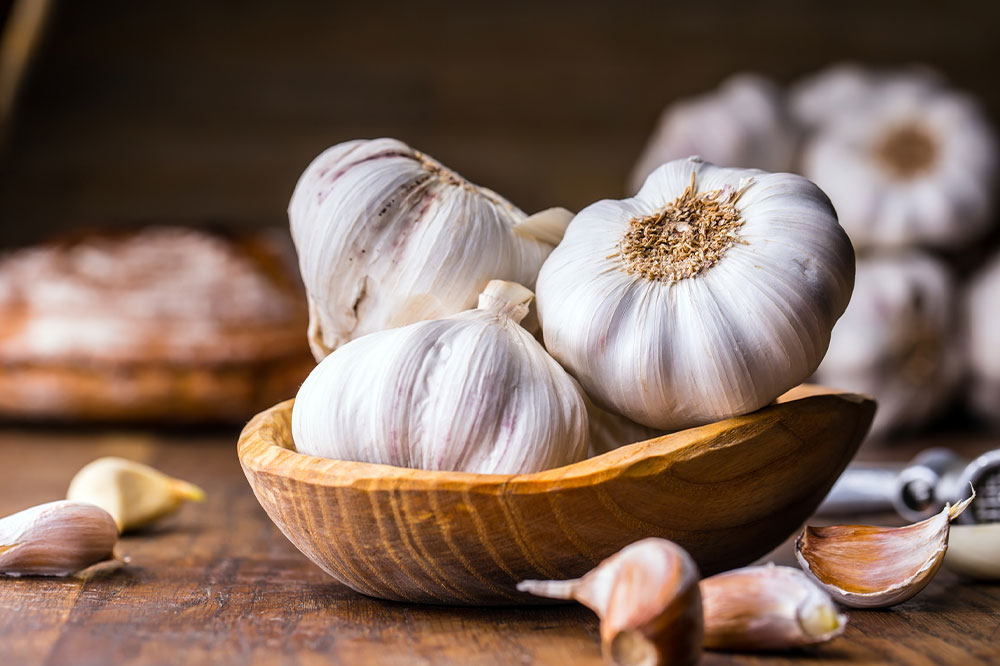
Garlic and Other Alliums
Garlic is widely celebrated for its ability to enhance immune function, reduce inflammation, and provide cardiovascular benefits. However, in lupus and other autoimmune diseases, immune enhancement can backfire. Excessive garlic intake may lead to immune overactivation, increasing inflammation and potentially triggering disease flare-ups. As a result, lupus patients should enjoy garlic in moderation—small amounts used as flavoring are generally acceptable, but large quantities or supplement form should be avoided unless approved by a healthcare professional. Being mindful of garlic consumption helps balance its health benefits without aggravating autoimmune symptoms.
Foods Rich in Saturated and Trans Fats
Dietary fats play a significant role in systemic inflammation and cardiovascular health. Foods high in saturated fats include fatty cuts of red meat, full-fat dairy products, and certain fried foods. Trans fats, often found in commercially baked goods, margarine, and processed snacks, are particularly harmful as they promote inflammation and increase bad cholesterol levels. For lupus patients, who already face a heightened risk of cardiovascular disease, reducing intake of saturated and trans fats is essential. Replacing these with healthier fats like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats—found in olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish—can help decrease inflammation and support heart health.
Echinacea and Immune-Boosting Supplements
Echinacea is a popular herbal supplement used to boost immune function and ward off infections. While this may seem beneficial, lupus patients with an overactive immune system should exercise caution. Echinacea can stimulate immune responses, which may inadvertently worsen inflammation and contribute to disease flares. Because supplements are not always well-regulated and may contain multiple active ingredients, it is crucial that lupus patients consult their healthcare providers before starting echinacea or any other immune-boosting supplement. Proper medical guidance ensures safe use tailored to individual health statuses.
Additional Strategies for Managing Lupus
Beyond diet, managing lupus effectively involves comprehensive approaches such as medication adherence, regular medical check-ups, sun protection, and lifestyle modifications. Medications like corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and antimalarials are often prescribed to control active disease and prevent organ damage. Complementing these with dietary adjustments enhances overall management. Importantly, each individual's condition is unique; therefore, personalized plans created in consultation with healthcare providers yield the best outcomes.
In conclusion, while medications are vital in controlling lupus, understanding dietary triggers and avoiding problematic foods can significantly improve symptom stability. Maintaining a balanced diet tailored to your condition, along with medical treatment, sun protection, and regular exercise, empowers lupus patients to lead healthier, more active lives with fewer flare-ups.