A Comprehensive Guide to Cataracts and Surgical Treatment Options
This comprehensive guide explores cataracts, their symptoms, management, and the role of surgery in restoring vision. It highlights when surgery becomes necessary, explains modern procedures like laser-assisted techniques, and discusses factors influencing treatment decisions. Understanding these aspects helps patients make informed choices about their eye health, emphasizing the safety, effectiveness, and advancements in cataract surgery. Early diagnosis and timely intervention can prevent severe vision loss, making awareness and consultation crucial for optimal eye care.
Understanding Cataracts: When is Surgery the Most Effective Solution?
Are you curious if surgical intervention is the most effective treatment for cataracts? Cataracts are a prevalent eye condition closely linked to aging, affecting millions worldwide. Recognized as one of the leading causes of vision impairment globally, understanding this condition and its management options is crucial, especially as the population ages. This article thoroughly explores what cataracts are, their symptoms, management strategies, and when surgery becomes the recommended course of action, helping you make informed decisions about your eye health.
When corrective glasses or contact lenses no longer provide adequate visual aid, cataract surgery becomes a viable and highly effective treatment option. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of cataracts, including their causes, symptoms, and available treatment methods, particularly focusing on surgical options. Whether you're diagnosed with cataracts or caring for someone with this condition, understanding when and why surgery is necessary can significantly influence treatment outcomes.
What Are Cataracts?
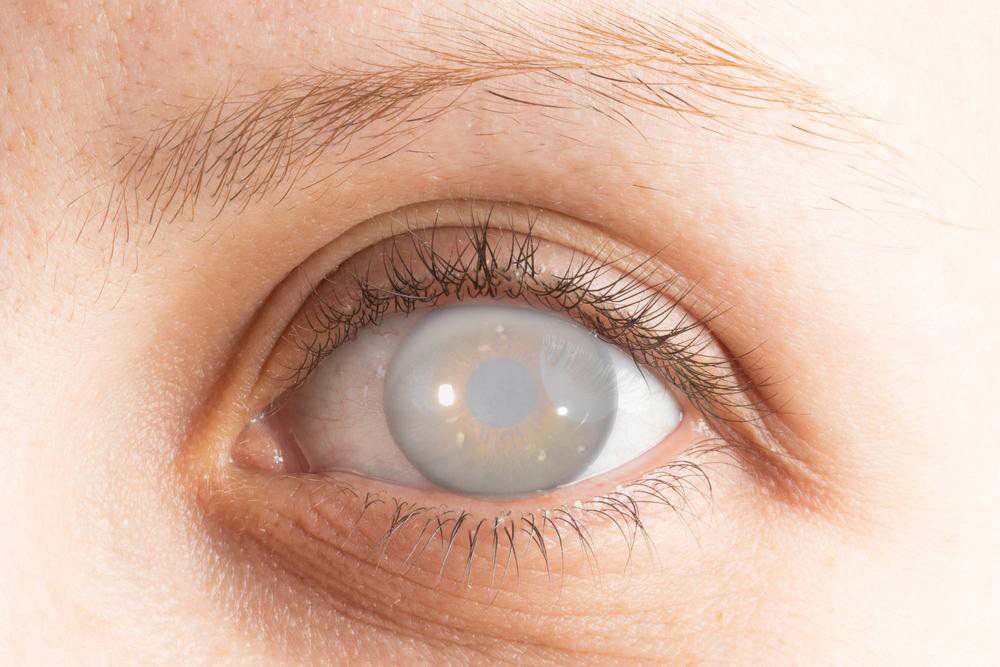
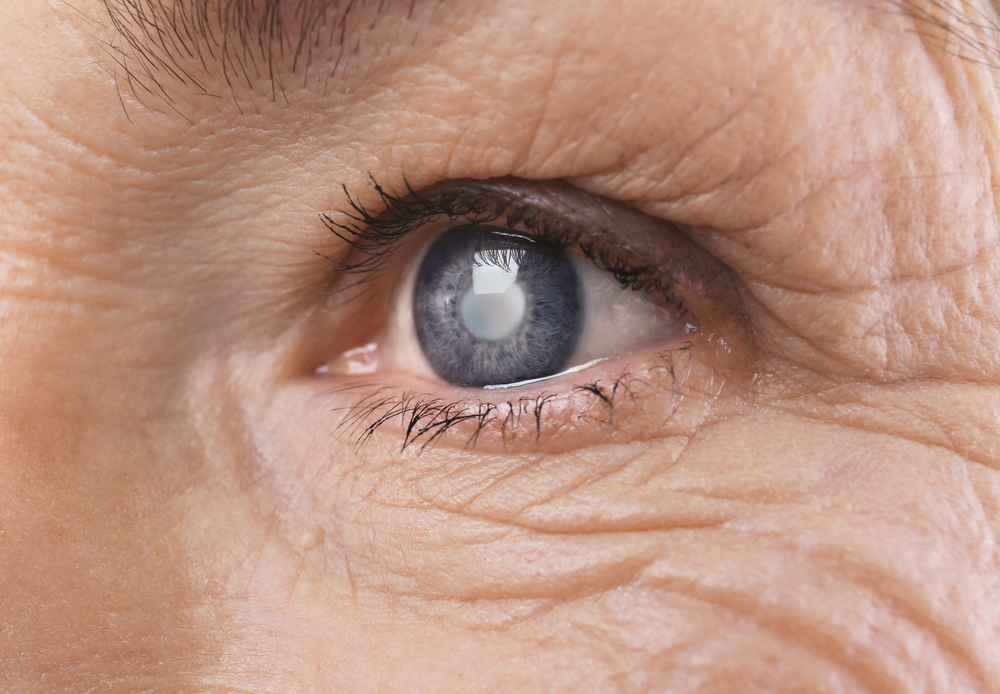
Despite the common nature of the term, many individuals are not fully aware of what cataracts entail, their symptoms, or treatment options. Gaining a clear understanding of these aspects is essential to managing and treating the condition effectively. Cataracts occur when the eye's natural lens, which is normally clear and essential for focusing light onto the retina, becomes clouded. This clouding results from protein build-up within the lens, often due to aging processes, but also impacted by other factors such as injury, certain medications, and health conditions.
The natural aging process causes the proteins in the lens to clump together, leading to gradual cloudiness. As the lens becomes more opaque, vision deteriorates, and the likelihood of requiring corrective measures or surgical intervention increases. Recognizing early signs of cataracts can help in timely treatment and prevent severe vision loss.
This clouding can significantly impair vision.
Signs and Symptoms of Cataracts
Recognizing the symptoms promptly can lead to better management of the condition. Common signs include blurred or cloudy vision, an increased sensitivity to light and glare, double vision in a single eye, difficulty seeing in low-light conditions, yellowing or fading of colors, and trouble seeing at night. Patients often report that they need brighter lighting and more focused help to read or perform visual tasks. Over time, these symptoms tend to worsen, reducing quality of life and independence.
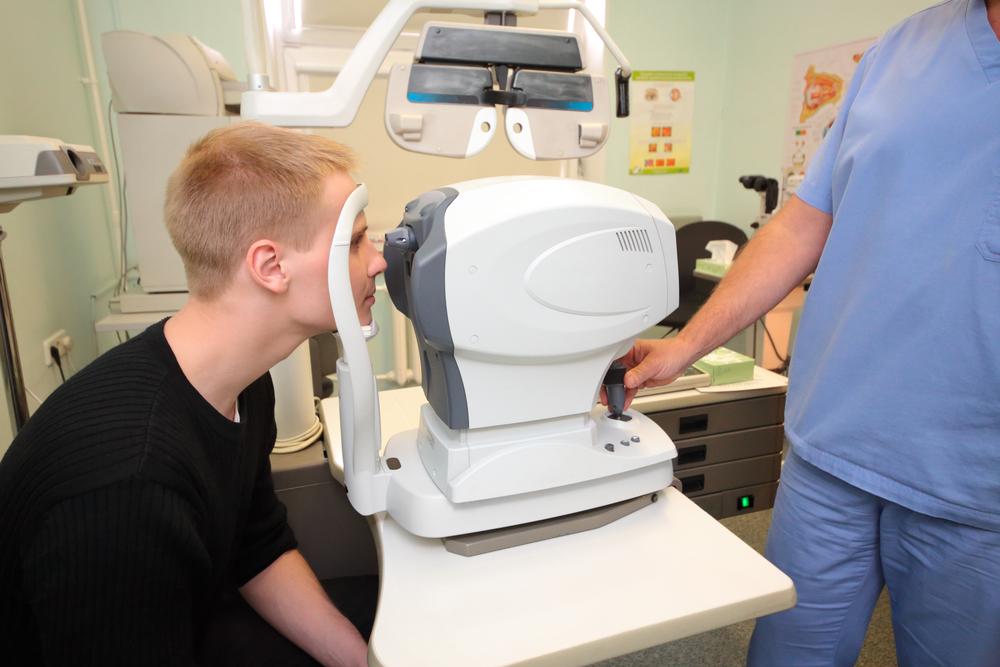
Early Management and Non-surgical Treatments
In the initial stages, conservative management such as corrective lenses, magnifiers, and improved lighting can help alleviate symptoms. For some, stronger bifocals or prescription contacts may suffice temporarily. Regular eye examinations are crucial for monitoring progression. However, as the cataract advances and these measures no longer provide sufficient relief, surgical intervention becomes the most effective option to restore normal vision.
Understanding Cataract Surgery
When cataracts significantly interfere with daily activities—such as reading, driving, or recognizing faces—surgery is generally recommended. Cataract surgery involves removing the clouded natural lens and replacing it with a clear, artificial intraocular lens (IOL). This procedure is one of the most common and successful eye surgeries worldwide.
Details of Cataract Surgery
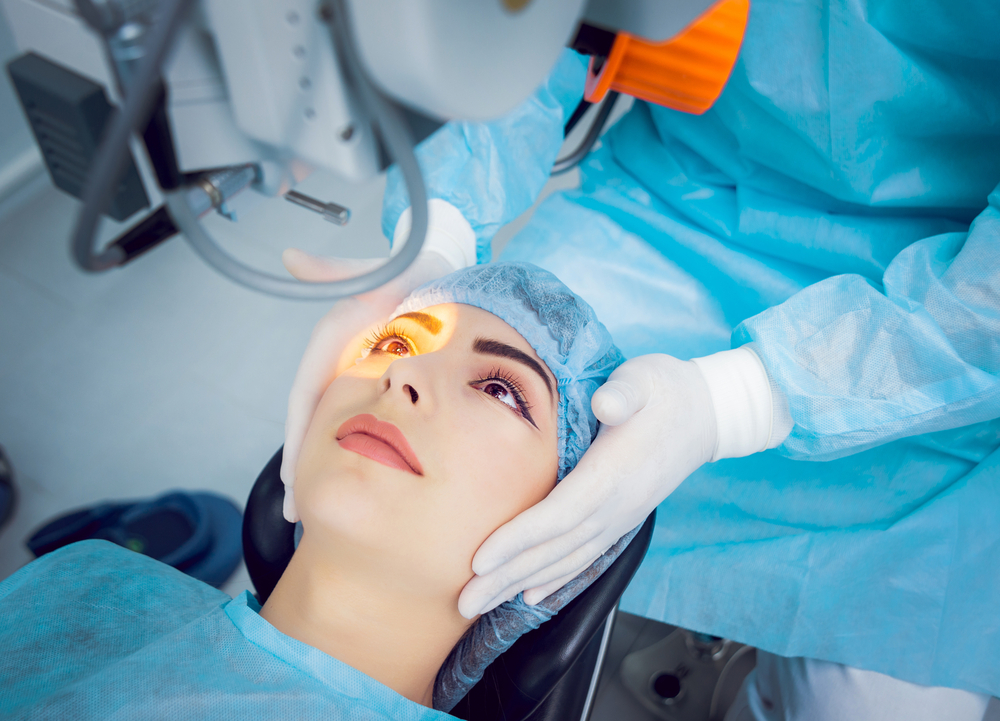
Typically performed on an outpatient basis, cataract surgery takes approximately 15 to 30 minutes. The procedure is usually conducted under local anesthesia, ensuring patient comfort without general sedation. Traditional methods use ultrasound technology, known as phacoemulsification, where high-frequency sound waves break the cloudy lens into tiny fragments, which are then aspirated out of the eye. The surgeon subsequently inserts the intraocular lens (IOL), which permanently replaces the natural lens, restoring clear vision.
In recent years, advancements in laser technology have enhanced the precision and safety of cataract surgery. Femtosecond laser systems perform key steps such as making incisions, creating the capsulotomy, and segmenting the lens with minimal manual intervention. Laser-assisted surgeries typically result in faster healing, reduced risk of complications, and improved visual outcomes. Despite these benefits, traditional ultrasound-based surgeries remain widely used and are often more cost-effective, making them accessible to a broad range of patients.
Surgery Effectiveness and Recovery
Cataract removal and lens replacement are among the safest surgical procedures with high success rates. The operation effectively restores visual clarity and often allows patients to reduce or eliminate the need for glasses for distance vision. Most patients experience postoperative improvement within days, with full recovery typically occurring within a few weeks. Minimal complications are associated with modern techniques, and ophthalmologists closely monitor the healing process to ensure optimal results.
Is Surgery the Right Choice for You?
Deciding whether to undergo cataract surgery depends on the severity of your symptoms and how much your daily life is impacted. While it is generally considered safe and effective, a consultation with an experienced eye specialist is essential for making an informed decision. Your ophthalmologist will assess the progression of your cataract, weigh the potential risks and benefits, and discuss the expected visual outcomes. It’s important to note that waiting too long can result in complications, so timely intervention is often advisable.
In conclusion, cataracts are a common condition associated with aging that can significantly impair vision if left untreated. While conservative measures can help in the early stages, surgery remains the most effective and reliable solution for restoring sight in advanced cases. Advances in laser technology and surgical techniques continue to improve outcomes, making cataract surgery a safe choice for most patients. Consulting an eye care professional is the best step to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.