In-Depth Guide to Cataract Removal Surgery: Procedures, Benefits, and Recovery
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth overview of cataract removal surgery, detailing the procedure, benefits, preparation tips, and post-surgery care. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and explains how advancements in technology have improved outcomes. Patients can better understand what to expect, how to prepare, and the recovery process, making informed decisions about their eye health and vision correction options.

Comprehensive Overview of Cataract Surgery and What to Expect
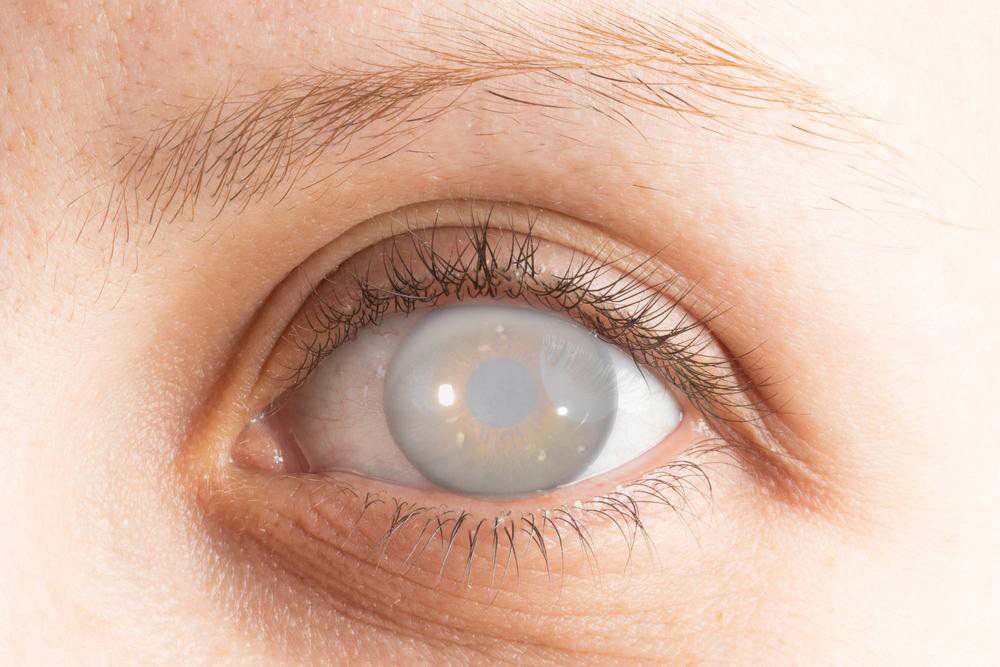
Cataracts are a common eye condition characterized by clouding of the eye's natural lens, leading to significant vision impairment that cannot be corrected with standard glasses. This condition tends to develop gradually over time, affecting millions worldwide, especially as people age. The most reliable and effective treatment for restoring clear vision is cataract removal surgery, a procedure that has evolved significantly with technological advances to ensure safety, efficiency, and quicker recovery.
Cataracts typically develop in individuals over the age of 50, with the risk increasing as age advances. By the time individuals reach 80, the majority have experienced some degree of cataract development. Early detection is crucial because timely intervention can prevent the progression of visual deterioration. Modern diagnostic tools allow ophthalmologists to identify cataracts early, enabling physicians to recommend the right course of action based on the size and impact of the cataract. The cost of the procedure varies depending on the surgical method used, the healthcare facility, and the geographic region, but innovations have made surgery more accessible and affordable than ever before.
Reasons to Consider Cataract Surgery
While small or early-stage cataracts might not necessitate immediate surgery, and vision can often be corrected temporarily with prescription glasses, magnifiers, or enhanced lighting, the progression of the condition typically impairs daily activities over time. Bright lighting can sometimes help with visual clarity, but as the clouding thickens, vision becomes increasingly blurry, and light sensitivity increases, making activities like driving, reading, or recognizing faces difficult.
At this advanced stage, cataract removal becomes the most effective way to regain clear eyesight. When assessing whether to undergo surgery, ophthalmologists consider the extent of vision impairment and how much it interferes with your quality of life. The advantages of surgery generally outweigh the risks or costs involved. Moreover, the procedure boasts quick recovery times, with most patients noticing improved vision within a few days post-operation.
Cataract Surgery Procedure Explained
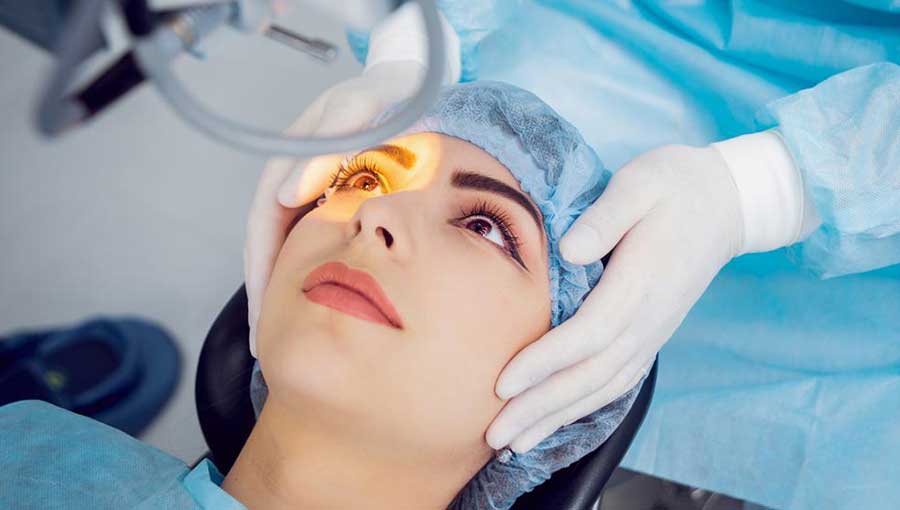
The procedure involves removing the cloudy natural lens of the eye and replacing it with a synthetic intraocular lens (IOL). This lens is designed to restore normal vision and is tailored to meet the patient’s specific needs. The surgery is typically performed on an outpatient basis, meaning you can go home the same day.
Timing and Healing Process
If you experience symptoms such as glare, halos, or noticeable decline in visual clarity, it is advisable to undergo testing to confirm the presence of cataracts and determine the right timing for surgery. The operation usually lasts around 15 minutes, during which the ophthalmologist uses either traditional ultrasound or laser-assisted techniques to break up and remove the clouded lens. Most patients report improved clarity of vision shortly after the procedure, with complete recovery typically within a month.
Step-by-Step Surgical Details
During surgery, the doctor makes a tiny incision in the eye and gently removes the natural lens. The artificial lens is inserted in its place, often behind the iris, without the need for stitches as the incisions are self-sealing. Post-surgery, the eye is covered with a protective shield to prevent accidental injury or pressure. Recent advancements in laser technology enable surgeons to perform highly precise incisions, reducing trauma and improving outcomes compared to traditional methods.
Preparation for Surgery
Preparation is straightforward but crucial. Patients are advised to consult with their ophthalmologist about any questions before surgery. About a week prior, eye measurements are taken meticulously to determine the appropriate lens power and size. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins, particularly vitamin E and antioxidants, supports eye health and healing. It’s vital to refrain from eating or drinking anything 12 hours before the procedure. Confirming insurance coverage beforehand can help manage out-of-pocket expenses and avoid surprises.
Postoperative Expectations and Care
The recovery process is generally smooth, with minimal complications. Common temporary side effects include mild soreness, light sensitivity, and slight swelling or bruising around the eye. Serious complications such as infection, bleeding, or increased intraocular pressure are rare but require prompt medical attention. In the initial days following surgery, patients are prescribed antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops to prevent infection and facilitate healing.
It is important to avoid touching or pressing on the operated eye, wear protective eye gear especially when outdoors, and steer clear of strenuous activities. Bright lights should be avoided, and sunglasses are recommended to protect the eyes from glare. Rest and proper eye hygiene accelerate healing. Most patients notice significant visual improvement within the first few days, with full stabilization occurring over 8 weeks. The success rate exceeds 90%, and many patients find that they no longer need glasses for distance vision, enjoying clearer, sharper sight after the procedure.