Comprehensive Guide to Cataracts: Causes, Types, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Solutions
This comprehensive article covers all aspects of cataracts, including causes, types, symptoms, and effective treatments. It highlights the importance of early detection and modern surgical options to restore vision, making it a valuable resource for anyone concerned about eye health and aging-related vision problems.

Understanding Cataracts: Causes, Variations, Signs, and Treatments
Cataracts are a prevalent eye condition primarily linked to aging, which gradually cloud the lens of the eye, leading to blurred vision and impacting daily life. They are among the leading causes of vision impairment worldwide and significantly affect quality of life if left untreated. This in-depth guide explores everything you need to know about cataracts, from their causes and different types to symptoms and available treatment options, including the latest advancements in surgical procedures.
What is a cataract?
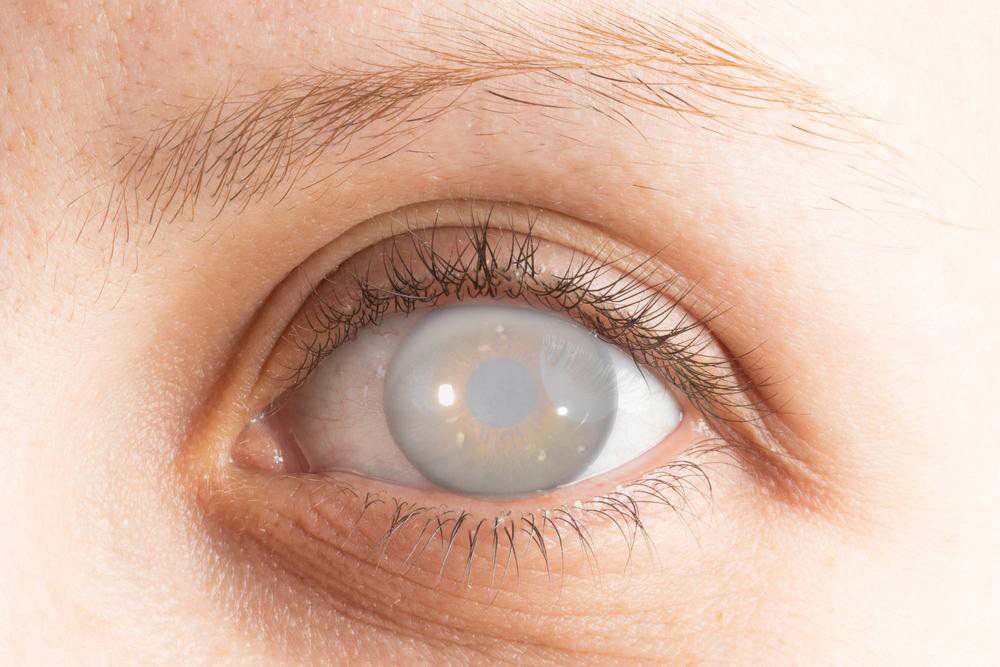
In a healthy eye, the crystalline lens located behind the iris and pupil functions like the lens of a camera, focusing light onto the retina for clear vision. However, when proteins within this lens begin to clump together and form cloudy areas, a cataract develops. As the cataract progresses, it obstructs the passage of light, resulting in vision deterioration. The development of cataracts is usually gradual, often starting unnoticed but eventually leading to significant visual impairment if not addressed.
Causes of cataracts
Natural Aging Process: Age-related changes in the lens proteins lead to clouding over time, making age the most significant risk factor.
Health Conditions: Diseases like diabetes significantly increase the risk of cataract formation. Additionally, conditions such as glaucoma can contribute to lens changes.
Genetic Factors: Hereditary traits can predispose individuals to develop cataracts at an earlier age or have more severe forms.
Medications: Long-term use of steroid medications can cause cataracts as a side effect.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight, smoking, excessive alcohol intake, obesity, and hypertension have all been linked to higher incidences of cataracts.
Types of Cataracts
Nuclear Cataracts: These form in the central nucleus of the lens and are often associated with aging. They initially cause difficulty in reading or seeing in low light but tend to progress slowly.
Cortical Cataracts: Occur at the edges of the lens and spread inward in spoke-like patterns, creating glare and light sensitivity issues.
Sub-capsular Cataracts: Develop at the back of the lens, often more rapidly, and are common in individuals with diabetes or those taking high-dose steroids.
Traumatic Cataracts: Result from trauma or injuries to the eye, often appearing months or years after the injury.
Congenital Cataracts: Present at birth, caused by genetic mutations or infections during pregnancy, affecting infants and young children.
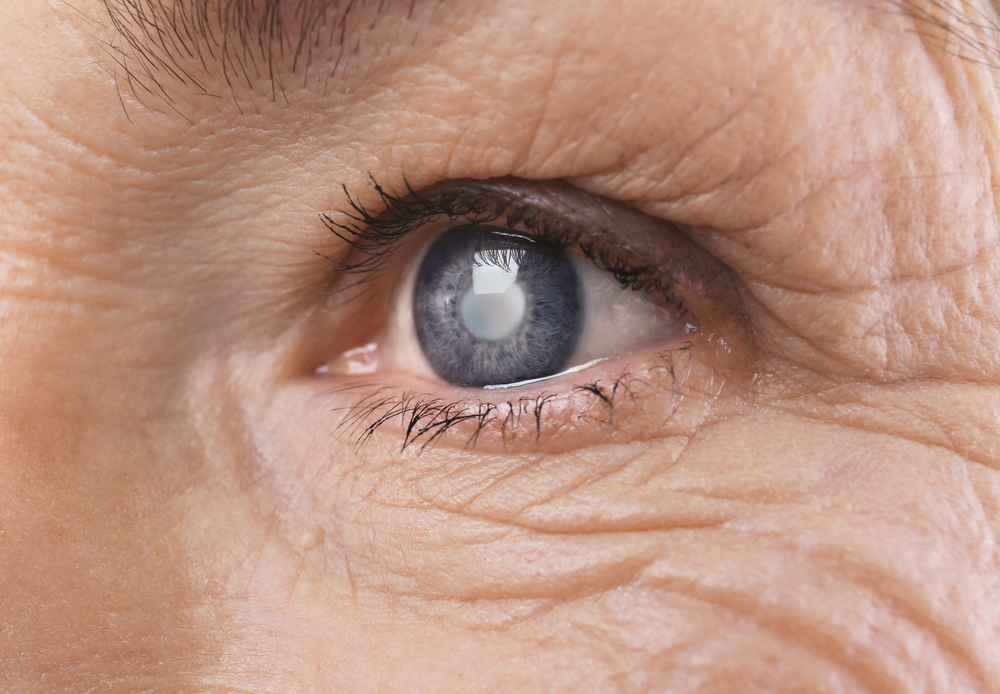
Signs and Symptoms of Cataracts
Progressive blurred or cloudy vision, which worsens over time
Difficulty seeing clearly at night or in dim lighting conditions
Increased reliance on brighter lighting for reading and daily activities
Sensitivity to light and glare, making halos around lights more prominent
Seeing double images or ghosting effects in one eye
Colors appearing less vibrant or more faded
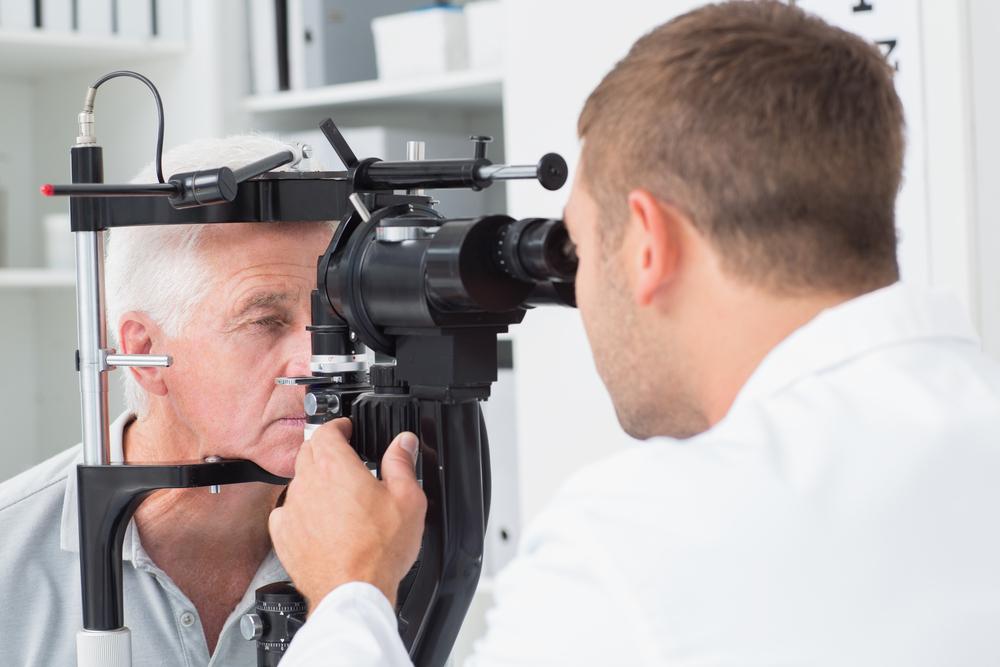
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
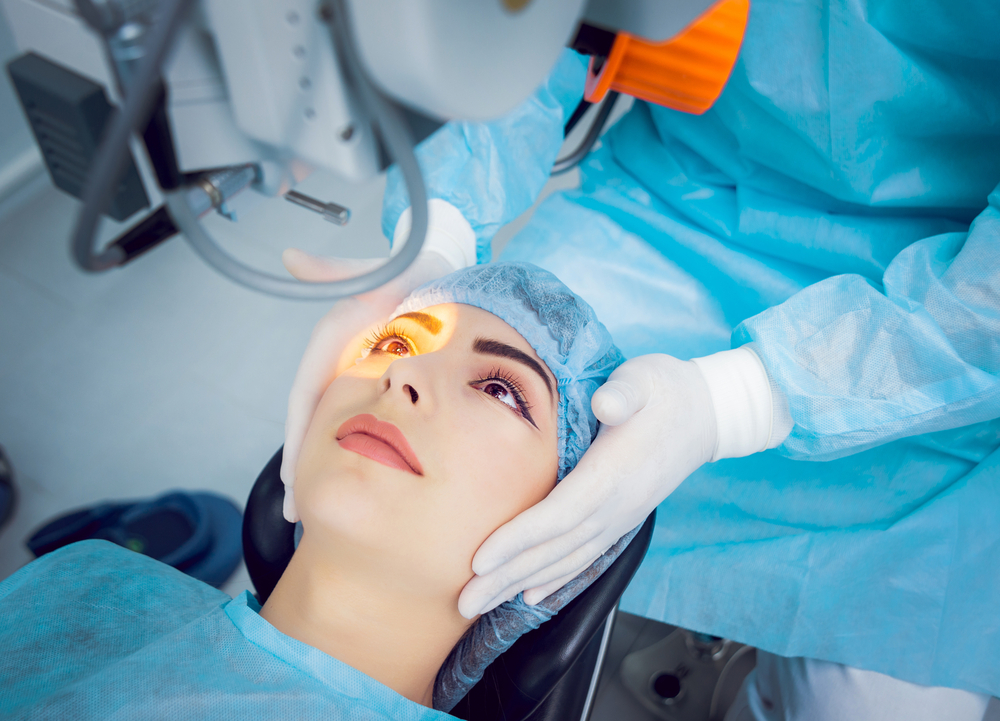
During the early stages, mild vision changes can often be corrected with prescription glasses or magnifying lenses. However, as the cataract advances, these measures may become ineffective. The most definitive treatment for cataracts is surgical removal of the cloudy lens, replaced with a clear artificial intraocular lens (IOL). This outpatient procedure is highly successful and offers rapid recovery, restoring clear vision and improving quality of life. Advances in laser-assisted surgery and premium IOL options have further enhanced outcomes and patient satisfaction.