Comprehensive Guide to Cataract Removal Surgery: What Patients Need to Know
This comprehensive guide covers everything patients need to know about cataract removal surgery, including preparation, procedure details, recovery tips, costs, and insurance options. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and professional care to restore clear vision and improve quality of life. Understand the different surgical techniques, recovery process, and financial considerations to make informed decisions and ensure optimal outcomes. Cataract surgery is safe and highly effective, offering a renewed clarity of vision for millions worldwide.
Comprehensive Guide to Cataract Removal Surgery: What Patients Need to Know
Understanding the cataract removal procedure and essential information for patients
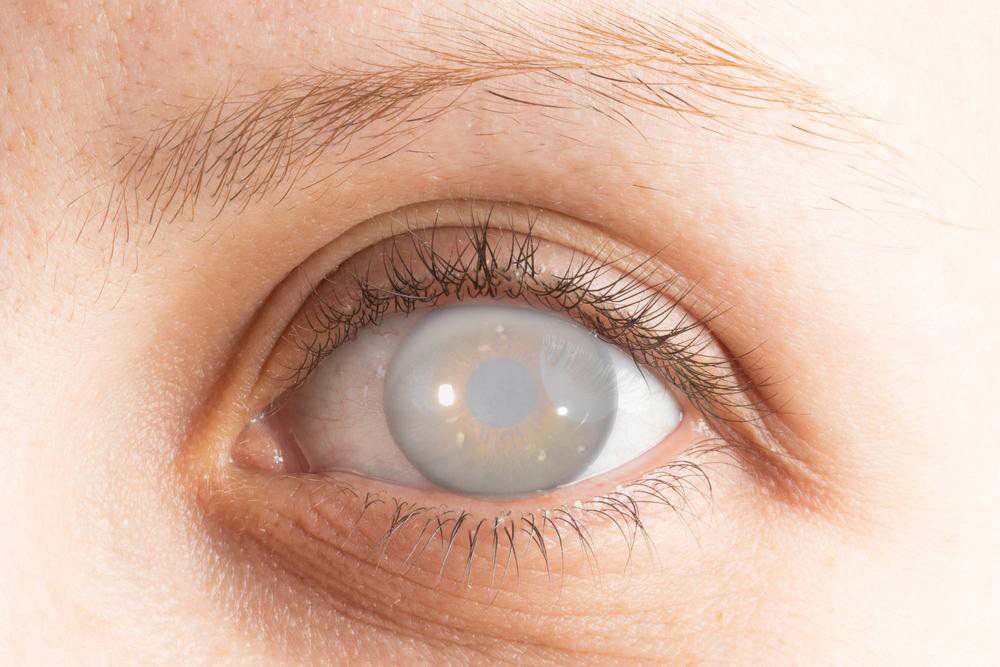
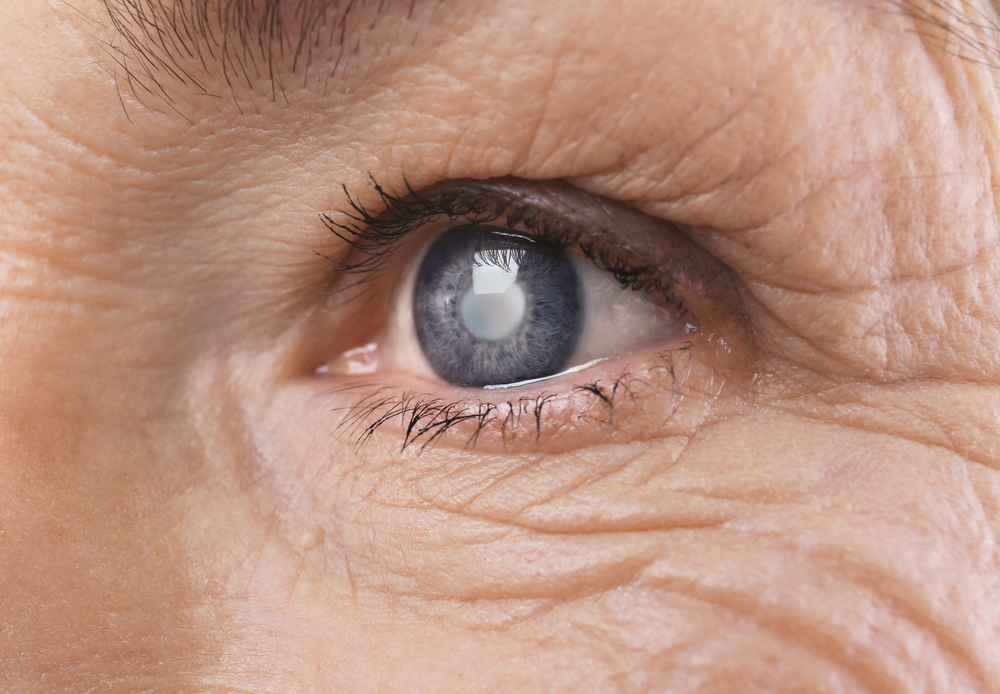
Cataracts are among the most common age-related eye conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people. This condition is characterized by a gradual clouding of the natural lens inside the eye, leading to blurred vision and, if untreated, progressive vision loss. Recognizing the symptoms early and knowing the treatment options available can significantly enhance quality of life. For many, especially as vision deteriorates and daily activities become challenging, cataract surgery offers a safe and highly effective solution. This comprehensive guide aims to provide detailed insights into what patients should know about the procedure, preparation, recovery, costs, and insurance coverage.
Understanding cataracts and when to consider surgery
Cataracts develop slowly over time, often imperceptible in early stages. Common symptoms include blurred vision, difficulty seeing at night, sensitivity to light and glare, frequent changes in prescription eyeglasses, and sometimes a need to increase brightness for reading. If left untreated, cataracts can lead to significant vision impairment and even blindness. When these symptoms start impacting daily life—reading, driving, recognizing faces—it's time to consult an ophthalmologist.
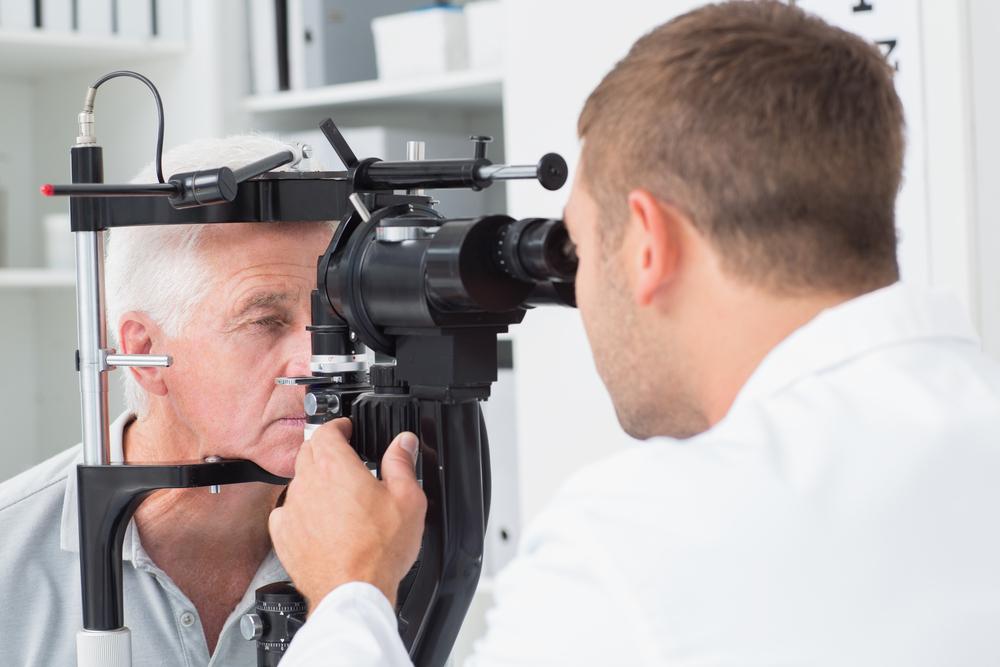
Once diagnosed, the ophthalmologist evaluates the severity of the cataract and discusses whether surgical intervention is necessary. Nowadays, cataract removal is the most effective way to restore clear vision and improve overall eye health.
Preoperative preparations for cataract surgery
Preparation is crucial to ensure a smooth procedure and speedy recovery. Prior to surgery, your eye specialist will provide specific instructions, which typically include:
Conducting diagnostic tests such as ultrasounds to determine the eye's shape, size, and the precise location for the artificial intraocular lens (IOL). This step helps in customizing the lens for optimal visual results.
Discontinuing medications that increase bleeding risk, such as blood thinners, as advised by your doctor.
Applying prescribed antibiotic eye drops several days before surgery to reduce the risk of postoperative infection.
Fasting for at least 12 hours prior to the procedure, depending on your doctor's instructions, especially if sedation or general anesthesia is planned.
Arranging transportation to and from the surgical center, as the outpatient procedure typically does not require overnight hospitalization.
Details of the cataract removal procedure
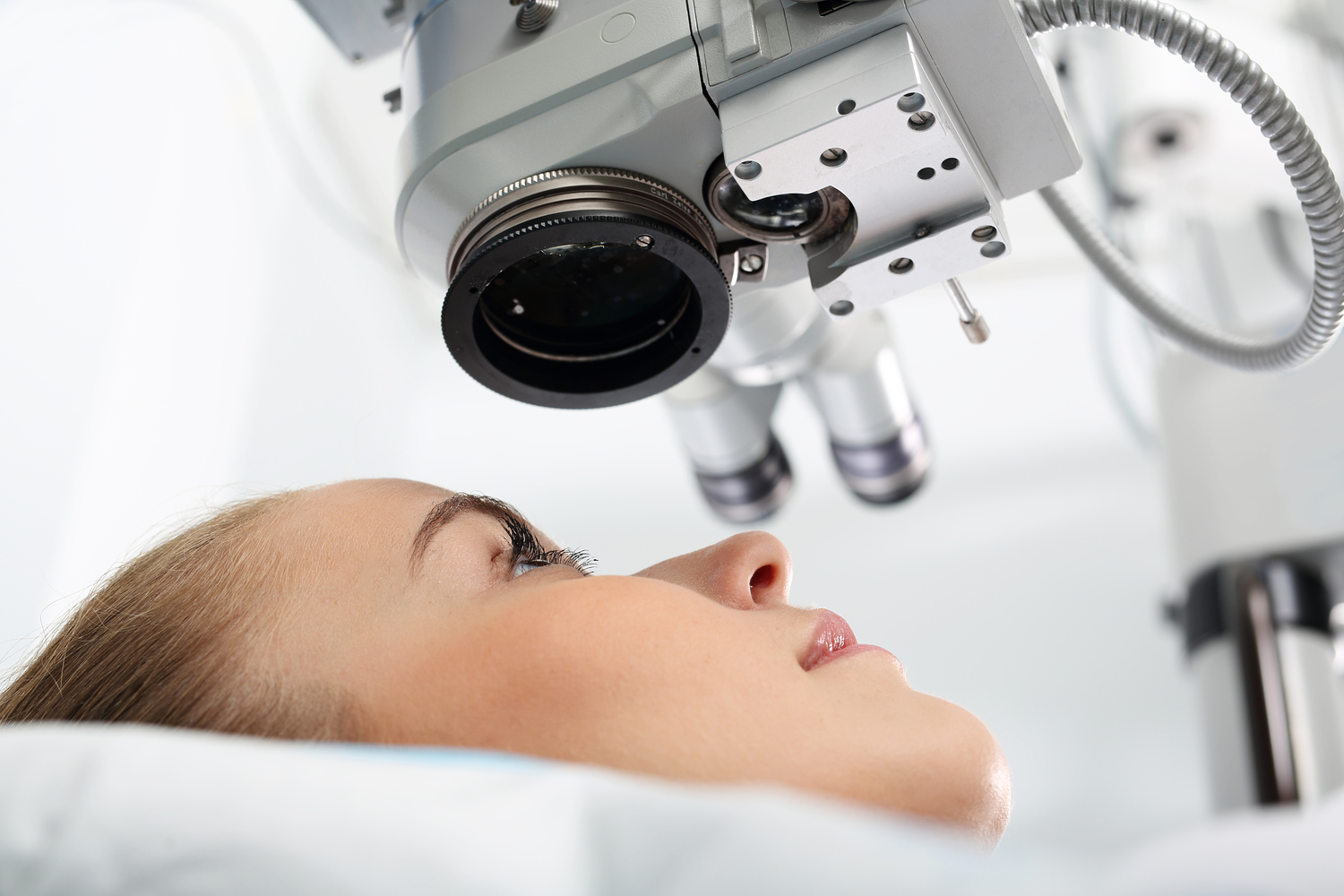
Cataract surgery is one of the most common and safe ophthalmic procedures performed worldwide. The operation usually lasts less than 30 minutes to an hour and is performed under local anesthesia with sedation in most cases. The process involves several well-established steps:
First, the eye is numbed using topical anesthesia, typically in the form of eye drops, accompanied by dilation to provide a clear view of the eye's interior. Some patients may receive light sedation to help them relax.
During surgery, the surgeon makes a tiny incision—about 2-3 millimeters—on the cornea, the eye's outermost transparent layer. Using advanced techniques, the cloudy natural lens is either emulsified with ultrasound waves (phacoemulsification) or softened with laser technology. The broken-up lens fragments are then gently suctioned out through the small incision. The surgeon then precisely implants a synthetic intraocular lens (IOL) into the empty lens capsule. In some cases, if necessary, the natural lens may be removed without replacement, although this is less common.
Ophthalmologists utilize one of three main methods to perform the procedure:
Ultrasound-Assisted Phacoemulsification: Using ultrasonic waves to break up the cloudy lens for easy removal and replacement.
Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery: Employing femtosecond laser technology to soften and expertly remove the cataract, offering potentially greater precision.
Extracapsular Cataract Extraction: A traditional method involving a larger incision—typically reserved for complex cases where other techniques are unsuitable.
After the lens replacement, the incisions are self-sealing or may be closed with tiny sutures. The entire process is minimally invasive, resulting in minimal discomfort and rapid recovery.
Recovery and postoperative care
Recovery from cataract surgery is typically swift, with most patients experiencing improved vision within a few days. Complete healing generally takes about eight weeks, during which proper postoperative care is vital. Common minor side effects include mild itching, a sensation of grittiness, and slight redness. These symptoms usually resolve quickly with prescribed eye drops and eye protection.
Patients are advised to use anti-inflammatory and antibiotic eye drops as prescribed to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. Wearing an eye patch or shield might be recommended immediately after surgery to protect the eye, especially overnight.
It is important to monitor for symptoms that warrant immediate medical attention, such as severe pain, sudden loss of vision, increasing redness, or flashes of light. Regular follow-up visits ensure proper healing and help the surgeon assess the success of the surgery.
Cost considerations and insurance coverage
The cost of cataract surgery varies based on factors like geographic location, the complexity of the case, and the technology used. On average, the total expense per eye is approximately $3,500, with laser-assisted procedures tending to be more expensive than traditional methods. Although many insurance plans, including Medicare and private insurance, generally cover essential cataract surgery, coverage for advanced techniques or premium lenses might vary. Patients should verify their insurance benefits before proceeding with surgery.
Additional expenses might include preoperative diagnostic tests, postoperative follow-up appointments, specialized intraocular lenses, and prescription eyeglasses following surgery. Always consult with your healthcare provider and insurance company to understand what costs are covered and what out-of-pocket expenses you should anticipate.
Proper planning and communication with your healthcare team can help streamline the process and reduce surprises, ensuring a successful surgical outcome.
In conclusion, cataract removal surgery is a safe, effective, and widely performed procedure that restores clear vision and enhances quality of life. With proper preparation, skilled surgical intervention, and diligent postoperative care, patients can enjoy long-lasting results and improved visual health.