Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Symptoms and Causes of Cataracts
This comprehensive guide explores the key signs, symptoms, and causes of cataracts. It emphasizes early detection, risk factors such as UV exposure and diabetes, and effective treatments like surgery. By understanding these aspects, individuals can take proactive steps to preserve their vision and prevent vision loss from cataracts, which primarily affect older adults but can occur at any age due to various factors. Regular eye exams and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing this common eye condition, ensuring better visual health for life.
Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Symptoms and Causes of Cataracts
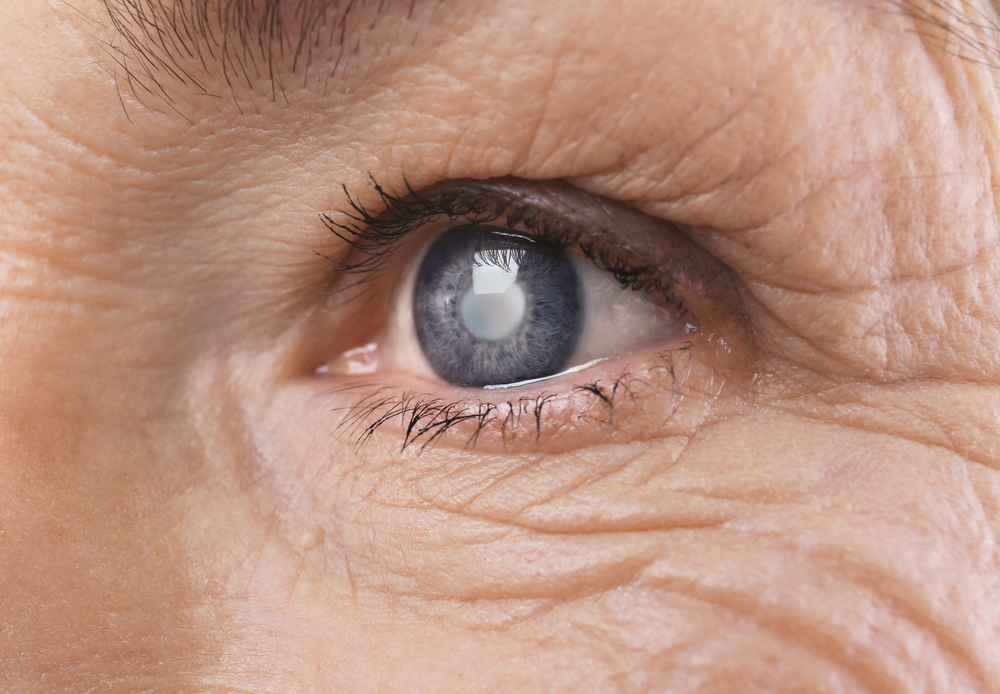
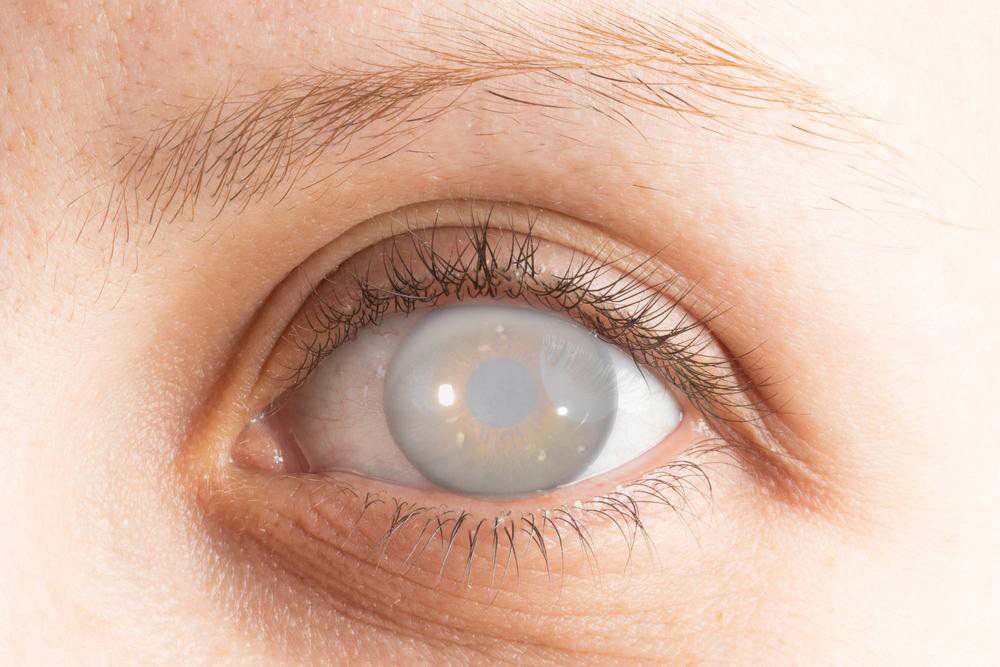
Cataracts are a common eye condition characterized by the gradual clouding of the eye’s natural lens, which can lead to significant visual impairment if left untreated. They develop when proteins inside the lens begin to thicken and clump together, creating a cloudy or opaque area that hampers light transmission to the retina. This process typically occurs slowly over time, and early-stage symptoms are often subtle, making early detection important for preserving vision.
This condition predominantly affects older adults, especially those over the age of 60, but it is not exclusive to the elderly. Younger individuals can also experience cataracts due to various risk factors such as prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, eye injuries, certain medical conditions like diabetes, use of specific medications, and genetic predispositions. Understanding the signs and causes of cataracts enables individuals to seek timely diagnosis and treatment, significantly improving quality of life.
In the early stages, managing cataracts might involve adjusting lighting conditions, using prescription glasses, or other non-invasive measures. However, as the condition advances, surgical removal of the cloudy lens becomes the most effective treatment, often restoring clear vision completely. This comprehensive guide explores the key symptoms to watch for, risk factors contributing to cataract development, and the latest treatment approaches to help you stay informed and proactive about eye health.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Cataracts
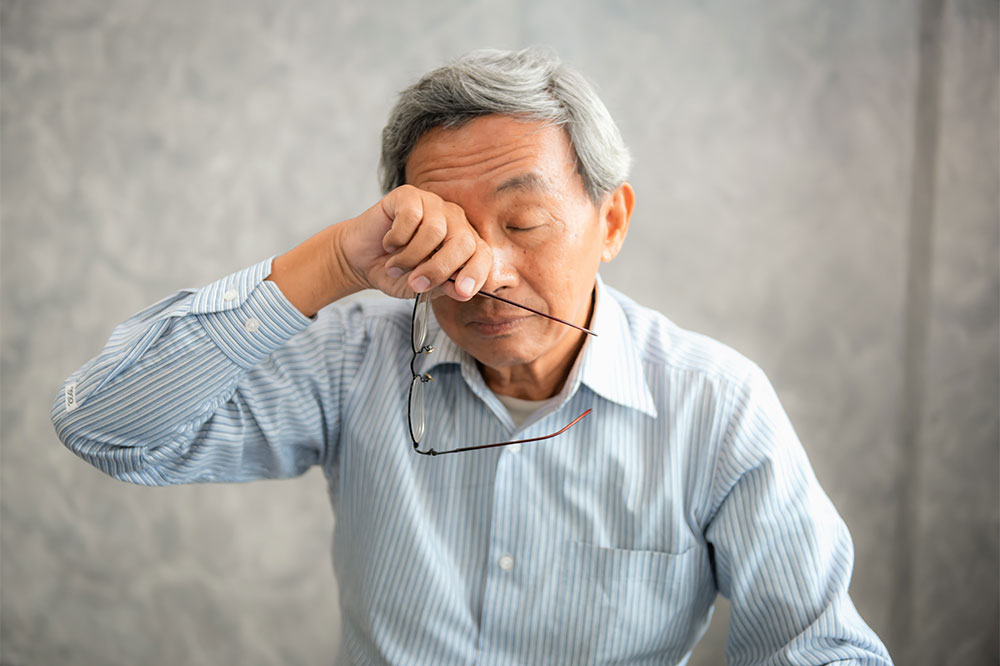
Blurry or Cloudy Vision – One of the most typical early indicators is a gradual clouding of vision. People often notice that their sight becomes blurry or foggy, similar to looking through a dirty window. This symptom tends to worsen over time, affecting daily activities like reading, watching TV, or recognizing faces. The clouding results from the lens becoming less transparent, obstructing clear images from reaching the retina.
Difficulty Seeing at Night – Night vision impairment is common among individuals with cataracts. Activities like driving after sunset or walking in dimly lit environments become challenging due to reduced visual acuity, glare, and light scattering caused by the cloudy lens.
Frequent Changes in Prescription – As cataracts develop, the refractive properties of the eye change, necessitating regular updates to glasses or contact lens prescriptions. Patients may notice that their vision fluctuates more frequently, which can be frustrating and indicates progressive lens clouding.
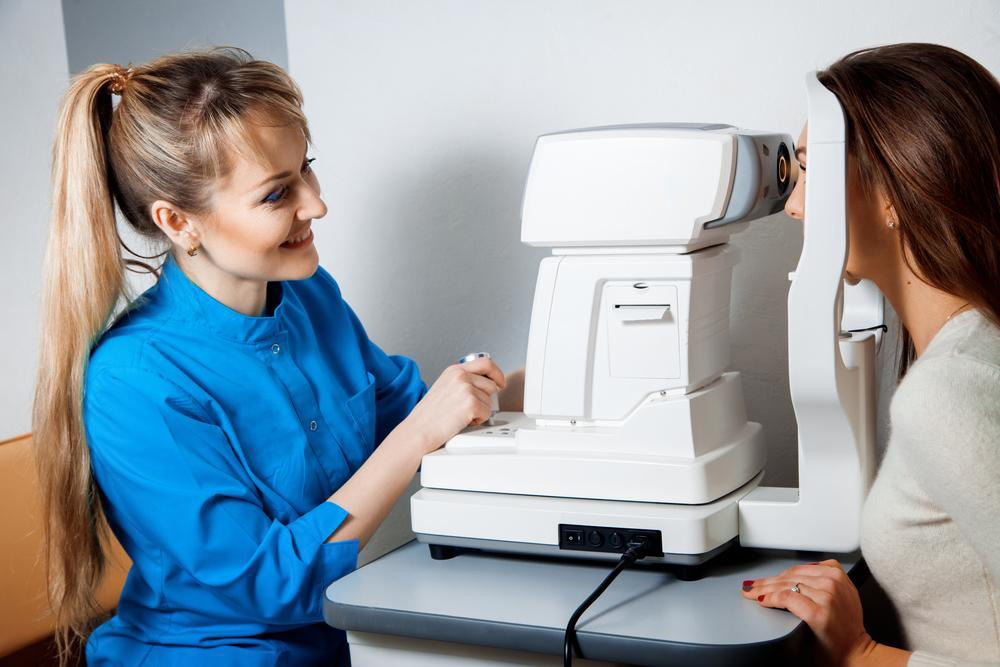
Patients experiencing these symptoms should schedule an eye examination with an ophthalmologist or optometrist for accurate diagnosis. Early detection can lead to better management and timely intervention.
Light Sensitivity and Discomfort – Increased sensitivity to bright lights or glare, particularly during the day or under direct sunlight, can be an early warning sign. Bright lights may cause discomfort or visual halos, signifying lens aging or clouding.
Halos and Glare Around Lights – Halos or rings appearing around lights, especially at night, are common in cataract progression. These are caused by light scattering through the cloudy lens, creating optical illusions that can impair night-time navigation.
Double Vision and Multiple Images – In some cases, individuals may perceive double images or experience multiple overlapping images due to irregularities in light refraction caused by lens opacity.
Yellowing of Vision – The lens may develop a yellow or brownish tint as proteins degenerate, affecting the perception of colors and contrast. This yellowing reduces the ability to distinguish between subtle shades and diminishes overall visual clarity.
It is crucial to recognize these signs early, as they can significantly impair daily functioning and safety. While aging remains the primary cause of cataracts, several external factors influence their development and progression.
Risk factors include:
Prolonged ultraviolet (UV) light exposure from the sun without proper eye protection
Diabetes mellitus and poor blood sugar control
Eye injuries or trauma
Long-term use of steroid medications
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
Genetic predisposition or familial history of cataracts
Radiation exposure
Although complete prevention of cataracts may not be possible, modifying certain lifestyle factors and adopting protective measures can delay their onset or slow their progression. Wearing UV-protective sunglasses, managing blood sugar levels effectively, avoiding smoking, and regular eye check-ups are essential steps in preserving eye health.
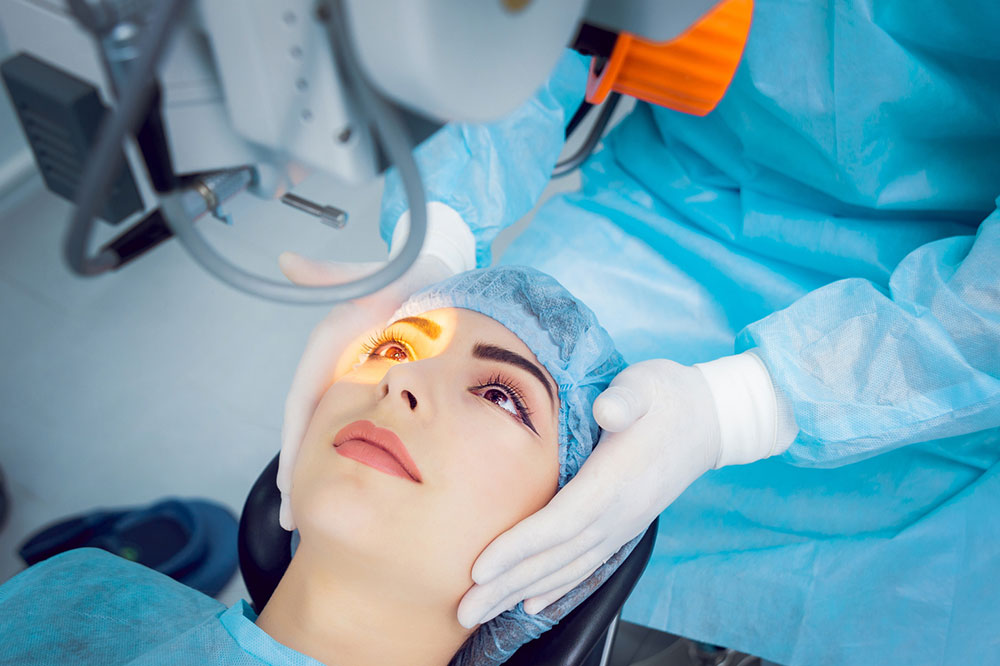
When cataracts interfere with daily activities or significantly impair vision, surgical removal remains the most effective treatment. The procedure typically involves removing the clouded natural lens and replacing it with a clear artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Advances in surgical techniques have made the procedure safe, quick, and highly effective, with a high success rate in restoring vision.
In conclusion, understanding the signs and causes of cataracts empowers individuals to seek early diagnosis and intervention. Regular eye exams, protective measures, and timely surgery when necessary can ensure a better quality of life and maintain good eyesight well into old age.