Effective Strategies and Treatments for Retinal Tears and Detachment
This comprehensive article explains the causes, symptoms, and advanced treatment options for retinal tears and detachment. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and covers modern surgical procedures like laser therapy, scleral buckling, vitrectomy, and pneumatic retinopexy. With detailed insights into symptoms and management techniques, it provides valuable guidance for anyone looking to understand retinal health and treatment options. Early intervention is crucial to prevent permanent vision loss, making this an essential read for those at risk or seeking to learn more about retinal disorders.

Understanding and Managing Retinal Tears and Detachment
The retina is a vital component of the eye, responsible for capturing light and converting it into neural signals that the brain interprets as visual images. This delicate layer of tissue is an extension of the central nervous system (CNS) and is situated at the back of the eye. Unlike other eye structures, the retina is visible externally, making its health crucial for overall vision. It contains specialized cells called cones and rods, which enable us to perceive color and function effectively in low-light conditions. Proper functioning of these cells depends on the integrity of the retina’s structure and the surrounding vitreous gel that fills the eye’s interior.
Maintaining retinal health is essential to preserve vision, but various issues can compromise its structure. Problems such as degeneration, trauma, or structural abnormalities can lead to conditions like retinal tears, detachment, and diabetic retinopathy. Of these, retinal tears are quite common and can be painless but serious if left untreated. They typically occur when the vitreous gel inside the eye contracts or shrinks, pulling on the retina and creating a tear. This sudden event often presents with noticeable symptoms, signaling the need for prompt medical attention.
Symptoms of retinal issues frequently include an increase in floaters—small specks or cobweb-like shadows drifting through your field of vision—and flashes of light, often described as bright sparks or lightning streaks. These signs indicate that the vitreous gel is pulling on the retina and may be causing or leading to tears. Other warning signs are peripheral shadows or curtain-like darkening across the side of vision, blurred vision, or a sudden increase in floaters. Recognizing these early symptoms is crucial to preventing further complications such as retinal detachment, which can cause permanent vision loss if not treated promptly.
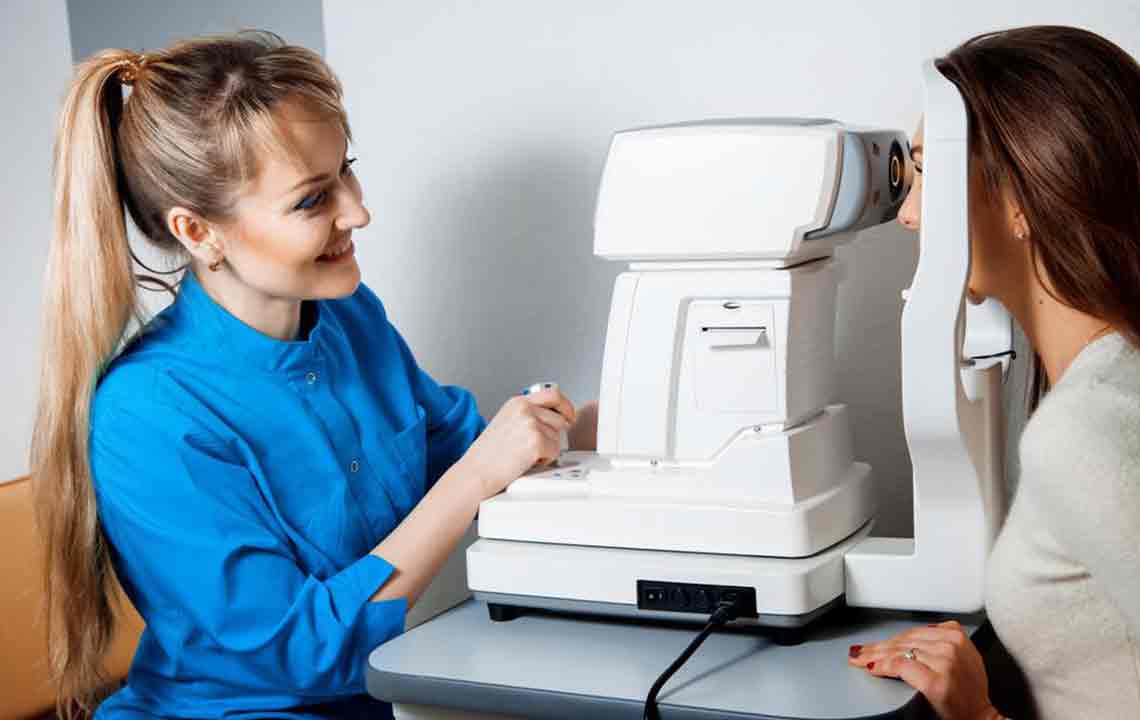
When a retinal tear occurs, immediate treatment is vital to prevent progression to retinal detachment. The primary goal of treatment is to seal the tear and prevent fluid from passing through, which could lift the retina away from its underlying tissue. Several advanced procedures have been devised to accomplish this, each suited to specific conditions and severity levels.
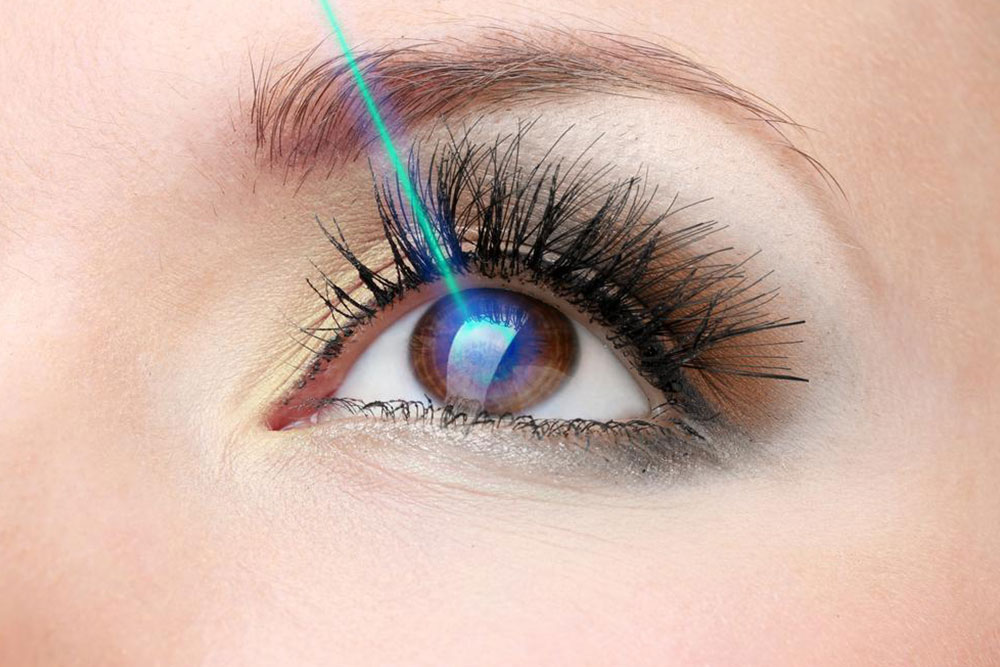
The most common treatments include laser photocoagulation and cryopexy. Laser photocoagulation uses focused laser energy to create controlled scars around the tear, sealing it and preventing fluids from infiltrating behind the retina. Cryopexy employs freezing temperatures via a special probe applied externally to induce scarring and closure of the tear. Both methods are minimally invasive and highly effective when performed early.
For more complex cases, surgical procedures such as scleral buckling are often recommended. In this procedure, a flexible silicone band is placed around the outer part of the eyeball, reducing the traction exerted on the retina and supporting reattachment. This technique has been a mainstay in retinal detachment repair for decades. Another advanced option is vitrectomy surgery, where the vitreous gel is carefully removed and replaced with a gas bubble, silicone oil, or a combination thereof. This internal approach allows the surgeon to directly access and repair retinal tears and detachments, often with excellent success rates.
Pneumatic retinopexy is another minimally invasive procedure where a gas bubble is injected into the vitreous cavity to tamponade the retina back into its proper position. Often combined with laser or cryotherapy to secure the retina, this method is suitable for selected cases of detachment with tears confined to certain regions. Postoperative positioning of the patient is critical, as keeping the gas bubble in contact with the tear helps facilitate repair.
In cases where fluid has accumulated behind the retina—causing it to lift or detach—prompt drainage may be necessary. Techniques involve creating a small incision or a controlled tear to allow the fluid to escape, restoring proper placement of the retina. The success of these interventions heavily depends on early diagnosis, appropriate surgical technique, and postoperative care, including careful monitoring for scar tissue formation, which may impair vision healing.
While most procedures yield positive outcomes with restored vision, it is essential for patients to follow their ophthalmologist’s post-treatment instructions diligently. Regular follow-up appointments ensure that the retina remains attached and healthy. Over time, some patients may experience scar tissue or proliferative vitreoretinopathy, requiring additional interventions. Nevertheless, advances in retinal surgery continue to improve success rates and patient prognosis, making early detection and treatment more effective than ever.