Comprehensive Guide to Cataract Prevention and Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores the latest strategies for managing cataracts, including lifestyle adjustments, advanced intraocular lens technology, and modern surgical options like laser-assisted procedures. It emphasizes personalized treatment plans, postoperative care, and preventive measures to improve patient outcomes and restore clear vision effectively.
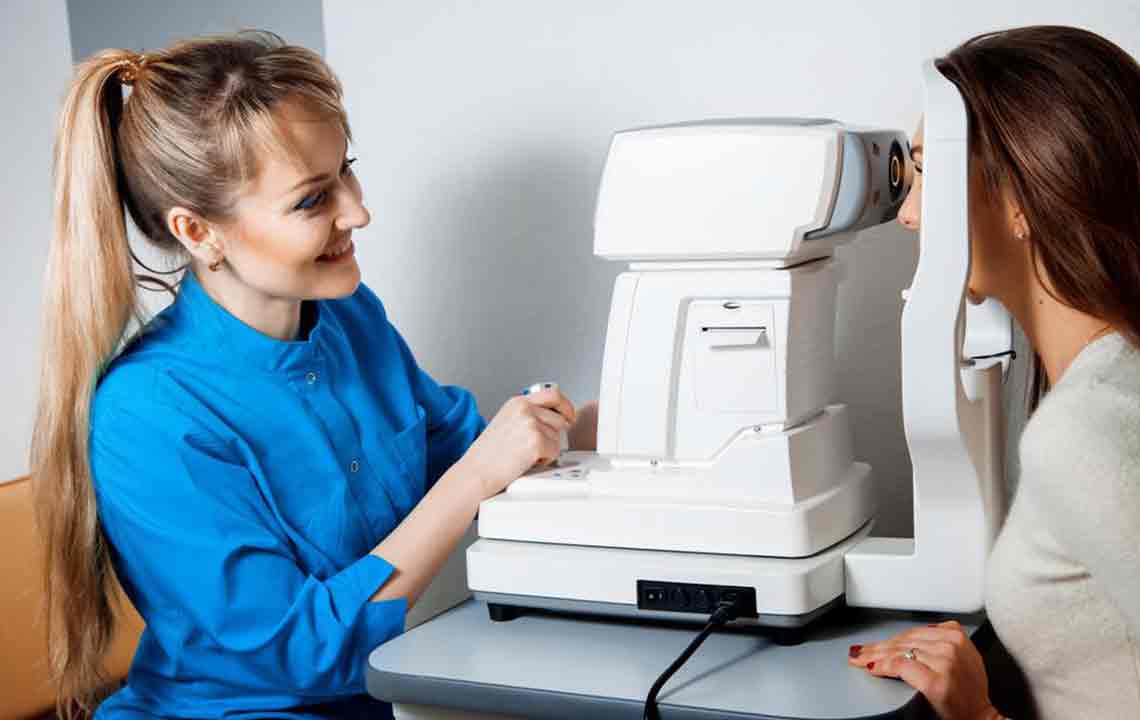

Effective Approaches for Managing Cataracts
Cataracts develop when the natural lens of the eye becomes cloudy due to the accumulation of proteins, leading to deteriorated vision quality. This condition can significantly affect daily life, causing blurriness, difficulty in seeing clearly, and challenges in performing routine activities like reading, driving, and recognizing faces.
Typically, cataracts form in one eye but are non-contagious and cannot spread from one eye to another. They are among the primary causes of loss of vision worldwide, particularly impacting individuals aged 55 and above as part of the natural aging process. Other risk factors include genetic predisposition, exposure to ultraviolet light, poor nutrition, and certain medical conditions like diabetes.
While early-stage cataracts may be managed with non-invasive methods, the progression of this condition often necessitates active treatment to restore vision. Understanding the various management options—including lifestyle adjustments, medical procedures, and surgical interventions—is essential for effective care.
Strategies for Cataract Treatment and Management
Choosing the appropriate treatment depends on the severity of the cataract, the patient’s overall health, and specific needs. Below is a comprehensive overview of available options:
Use of Corrective Eyewear for Early-Stage Cataracts
For mild cases, specially designed thick lenses or magnifiers can temporarily enhance vision. These glasses are easy to use, cost-effective, and serve as an initial remedy for visual impairment caused by early cataracts. Although they do not halt progression, they provide significant visual aid during the early stages.
Environmental and Lifestyle Adjustments
Adapting your surroundings can substantially improve your quality of life with cataracts. This includes using soft, glare-free lighting indoors, minimizing reflections from screens and windows, and employing low-vision assistive devices such as handheld magnifiers, digital screen enlargers, or specialized reading glasses. Modern technologies like electronic magnification and assistive apps are also effective tools for people with impaired vision.
Advanced Lens Technologies: Multi-Focal Intraocular Lenses
In cases requiring surgical intervention, intraocular lenses (IOLs) can be implanted to replace the clouded natural lens. Multi-focal IOLs are designed to provide clear vision at multiple distances—near, intermediate, and far—emulating the function of bifocal or multifocal glasses. This technology significantly reduces dependency on glasses post-surgery and enhances overall visual performance.
Surgical Procedures for Cataract Removal
When cataracts impair daily functioning and quality of life, surgical treatment is often the most effective solution. Several surgical options are available, tailored to individual needs:
Phacoemulsification (Ultrasound-Assisted Surgery): This minimally invasive technique uses ultrasonic waves to break up the cloudy lens into tiny fragments, which are then gently removed through a small incision. Post-removal, an artificial intraocular lens is implanted. The procedure is quick, typically performed on an outpatient basis, and boasts high success rates.
Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery: This advanced method employs femtosecond lasers to make precise incisions, fragment the lens more efficiently, and correct astigmatism if present. It offers increased accuracy and potentially faster recovery.
Extracapsular Cataract Extraction: A more traditional surgical approach, mainly used in cases with advanced cataracts or certain complexities. It involves removing the lens in one piece through a larger incision, with subsequent lens implantation.
Postoperative care is crucial for optimal recovery and includes prompt management of complications and routine follow-up appointments. Common postoperative considerations involve managing swelling, preventing infection, and monitoring for secondary cataracts or other eye issues.
Dietary and Lifestyle Considerations in Cataract Management
Nutrition plays a role in eye health. Consuming foods rich in antioxidants—such as leafy greens, berries, and citrus fruits—may help slow cataract progression. Limiting intake of high-protein foods like red meats and dairy could potentially reduce protein deposits in the eye. Additionally, protecting your eyes from excessive UV exposure with sunglasses and maintaining overall health with regular exercise and medical checkups can have beneficial effects.
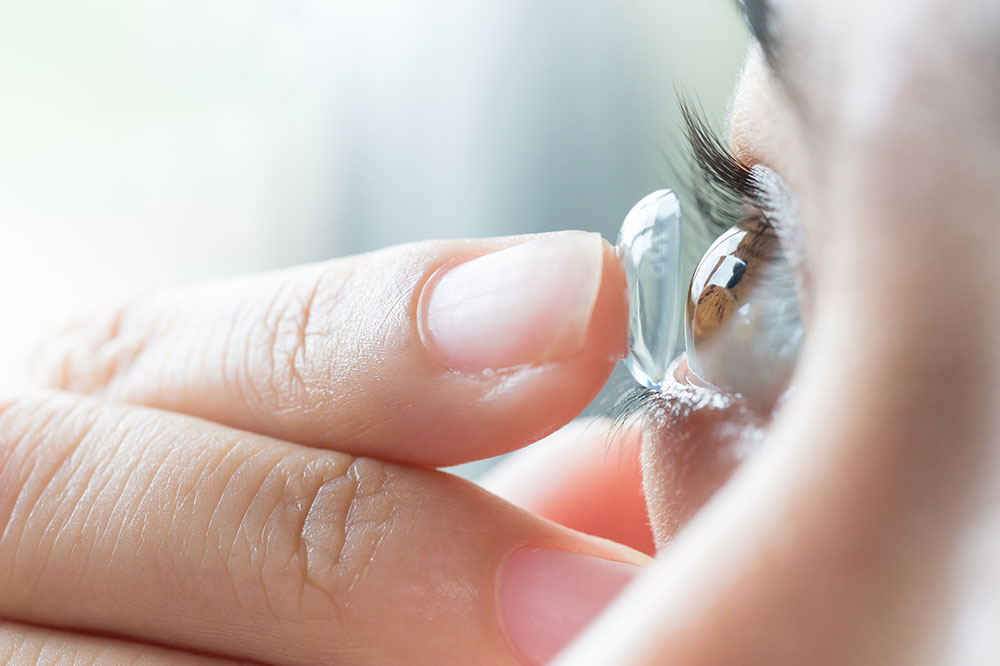
Prescription Eyewear as a Non-Invasive Solution
Custom-designed glasses with specialized lenses continue to be an effective, non-surgical option for managing early to moderate cataracts. These optical aids can significantly improve vision quality and are easy to use, making them a preferred choice for many patients.
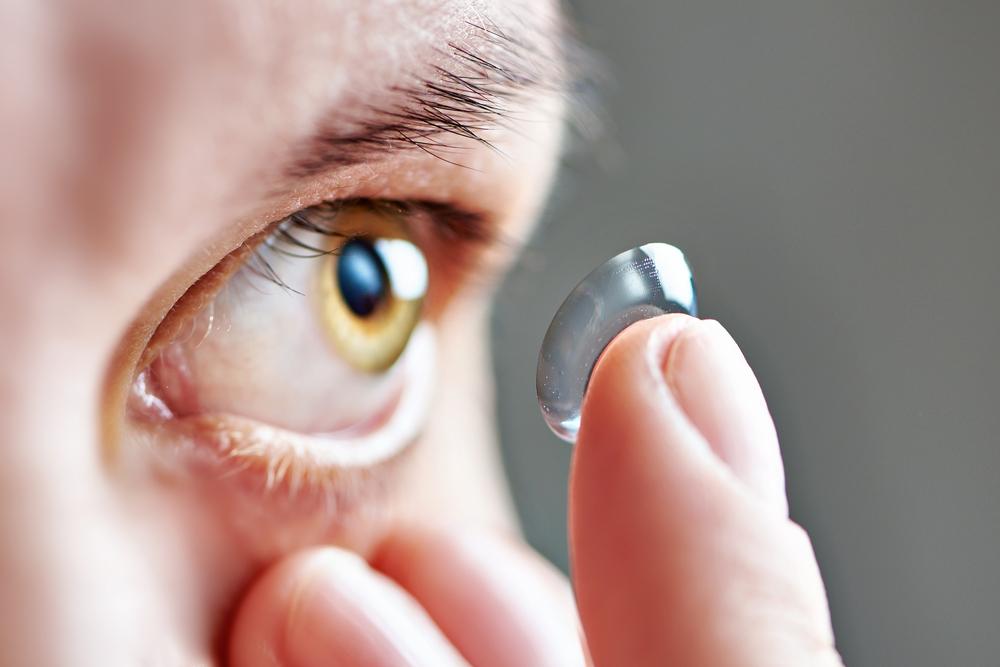
Implantable Intraocular Lenses for Long-Term Vision Restoration
Implanting modern intraocular lenses is a common and highly successful treatment for cataracts. The selection of appropriate IOLs should be discussed thoroughly with your ophthalmologist, taking into consideration your visual needs, lifestyle, and eye health conditions.
Surgical Innovations: Ultrasound and Laser Technologies
Advances in surgical technology, including phacoemulsification and femtosecond laser-assisted techniques, have revolutionized cataract treatment. These methods offer high precision, minimal tissue trauma, and quicker recovery times. In some cases, laser surgery can address residual lens opacities or secondary cataracts that may develop months or years after the initial operation.
Traditional Techniques: Extracapsular Extraction
Although less common today, this approach involves removing the lens in one piece via a larger incision, and it remains relevant for specific complicated cases or in regions with limited access to newer technology.
Postoperative Precautions and Monitoring
Report any sudden loss of vision or vision worsening
Seek medical advice if experiencing significant discomfort, persistent redness, or abnormal discharge
Monitor for flashes of light or shadowy areas in your vision
Attend scheduled follow-up visits for comprehensive eye examinations
Additional Factors Influencing Treatment Decisions
Age, lifestyle, underlying health conditions, and the presence of other eye disorders influence the choice between non-invasive and surgical options. Mild cataracts may be managed with lifestyle modifications and optical correction, while more advanced cases typically require surgery for optimal results. In cases involving both eyes, procedures are usually staged to allow for proper healing. It’s common to experience some temporary side effects such as swelling and blurred vision following surgery. Over time, prescriptions may need adjustments based on post-surgical outcomes, and diligent follow-up is essential.