Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Diabetic Foot Problems
This comprehensive guide covers the causes, symptoms, preventive measures, and treatment options for diabetic foot complications. Emphasizing daily foot care, blood sugar control, and early medical intervention, it aims to help diabetics prevent severe issues like ulcers and amputations. With practical tips and medical insights, readers learn how to maintain foot health and avoid serious complications, ensuring a better quality of life. Routine check-ups, proper footwear, and vigilant care are essential components in managing diabetic foot problems effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Diabetic Foot Problems
Diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, is known to affect various organs and systems within the human body. While typically associated with blood complications, one of the most common yet serious complications is diabetic foot issues. Foot problems related to diabetes can range from minor discomfort to severe ulcers, infections, and even the need for limb amputation. Understanding the causes, implementing effective care strategies, and adopting preventive measures are crucial steps in safeguarding foot health for diabetics.
One of the key issues in diabetic foot health is poor blood circulation, mainly affecting areas such as the toes and the ball of the foot. Reduced blood flow deprives tissues of essential nutrients and oxygen, making the skin more prone to injury and slower to heal. Additionally, peripheral neuropathy caused by nerve damage results in numbness or loss of sensation, meaning diabetics may not notice injuries until they worsen. These injuries often begin as small blisters or calluses but can escalate into ulcers or infected wounds if not treated promptly.
Chronic high blood sugar levels can lead to skin dryness, cracking, and irritation, further increasing susceptibility to infections. When bacteria or fungi invade compromised skin, infections can occur, potentially spreading to underlying tissues and bones. Severe infections can be challenging to treat and may necessitate surgical intervention or amputation to prevent the spread of infection or systemic complications.
Common symptoms of diabetic foot complications include:
Swelling and redness around the affected area
Unexplained discharge or foul odor
Persistent ulcers or open sores
Changes in skin color or texture
Painless injuries due to nerve damage
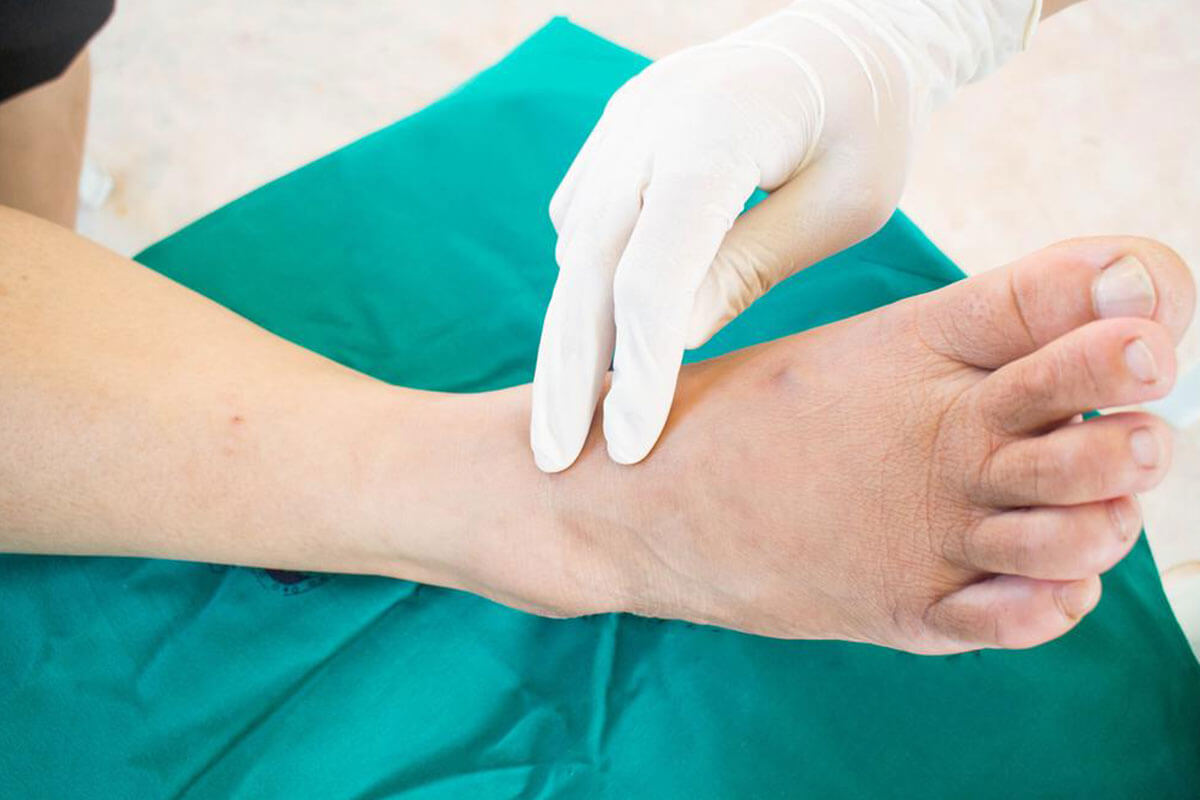
Because some foot problems may not exhibit obvious signs, regular foot examinations are vital for early detection and treatment. High-risk individuals, such as those with long-standing diabetes, poor glycemic control, or existing circulatory issues, should visit healthcare providers for routine assessments.
Effective Strategies for Preventing Diabetic Foot Problems
Preventive care is paramount in managing diabetic foot health. This involves a multifaceted approach focusing on blood sugar management, daily foot care, and appropriate footwear. Here are some essential practices to incorporate:
Control Blood Sugar Levels: Maintaining glycemic control through medication, diet, and exercise reduces the risk of nerve damage and circulatory problems.
Daily Foot Inspection: Examine your feet every day for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or any abnormalities. Use a mirror if necessary or ask for assistance.
Maintain Foot Hygiene: Wash feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap. Dry thoroughly, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections.
Moisturize: Apply a moisturizer to keep the skin supple, but avoid the areas between the toes to prevent fungal growth.
Wear Proper Footwear: Choose well-fitting shoes that do not cause pressure points or blisters. Use protective footwear in public places or rough terrains.
Avoid Prolonged Pressure: Limit sitting or standing for long periods, and take regular breaks to promote circulation.
Routine Medical Check-Ups: Schedule regular visits with a podiatrist or healthcare provider specializing in diabetic foot care for professional evaluations and early intervention.
Medical Treatments and Interventions
When foot problems occur despite preventive measures, medical intervention becomes necessary. The treatment plan depends on the severity and nature of the condition:
Specialized Footwear and Orthotics: Custom-made shoes and insoles help relieve pressure and accommodate deformities.
Wound Care: Proper cleaning, debridement (removal of dead tissue), and dressing of ulcers promote healing and prevent infection.
Infection Management: Antibiotics or antifungal medications are prescribed to treat infections effectively.
Surgical Procedures: In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary to correct deformities, resect infected tissues, or facilitate amputation to save the patient’s life.
Revascularization: Restoring blood flow through surgical or minimally invasive techniques improves healing capacity.
Maintaining Long-term Foot Health
Preventing diabetic foot complications requires long-term vigilance and lifestyle adjustments. Staying active, following medical advice diligently, and adopting healthy habits are essential. Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco or excessive alcohol consumption support circulatory health. Educating oneself about foot health and recognizing early warning signs empower diabetics to seek timely assistance. With comprehensive care and cautious management, many foot issues can be avoided, ensuring a better quality of life and mobility for diabetic patients.