Comprehensive Guide to How Diabetes Impacts Foot Health and Alleviates Pain
Diabetes can significantly impact foot health through nerve damage and poor circulation, leading to ulcers, infections, and pain. Proper management, regular foot care, and medical intervention are essential for preventing complications. This comprehensive guide highlights the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures for foot problems in diabetics, emphasizing the importance of early detection and lifestyle modifications to maintain foot health and reduce discomfort.

Understanding the Comprehensive Impact of Diabetes on Foot Health and Pain Management
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that, if not properly managed, can lead to a myriad of health complications. One of the most common yet often overlooked issues faced by individuals with diabetes is foot problems. These issues include persistent discomfort, formation of ulcers, calluses, infections, and even severe tissue damage. Many patients wonder what causes these distressing symptoms. The root cause is frequently undiagnosed or poorly controlled diabetes that leads to elevated blood sugar levels. Elevated glucose damages blood vessels and nerves over time, resulting in compromised blood flow and nerve function in the feet. These changes make foot injuries more likely and slower to heal, increasing the risk of severe complications. Recognizing and understanding how diabetes influences foot health is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
What Causes Foot Pain in People with Diabetes?
Diabetes contributes primarily to two major conditions that directly impair foot health:
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy – This is a form of nerve damage caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels. It results in numbness, tingling, burning sensations, and decreased sensation in the feet. When nerves are damaged, individuals may not notice minor injuries or cuts, leading to untreated wounds that become infected or develop ulcers. Over time, neuropathy can cause deformities like hammer toes or Charcot foot, increasing vulnerability to injuries.
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) – PVD involves the hardening and narrowing of peripheral arteries, especially in the legs and feet. Poor circulation caused by PVD reduces oxygen and nutrient delivery to tissues, impairing the body's ability to heal wounds. This can lead to persistent ulcers, gangrene, and in severe cases, tissue death. Both neuropathy and vascular disease often coexist, compounding the severity of foot problems in diabetics.
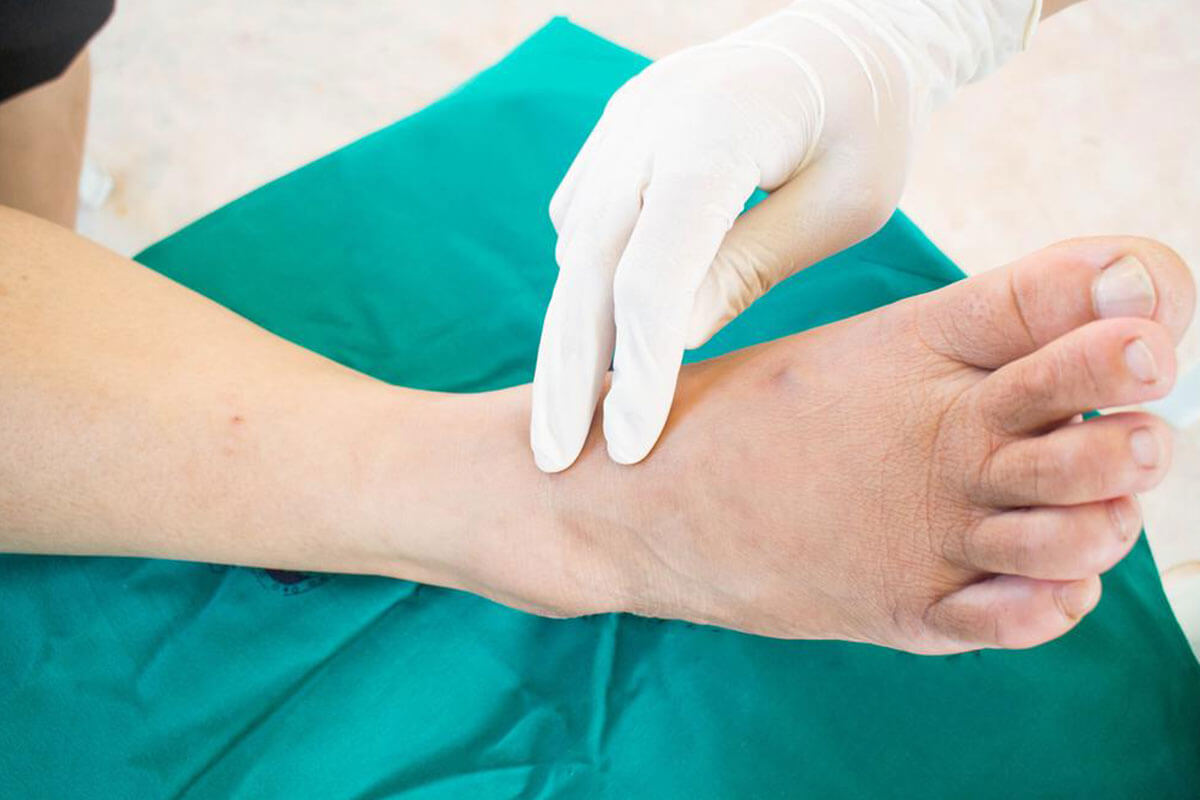
Research indicates that nearly 80% of diabetic patients experience some form of foot complication during their lives. These issues can range from minor calluses to life-threatening infections. The importance of meticulous foot care cannot be overstated, as early detection and management can prevent many serious outcomes.
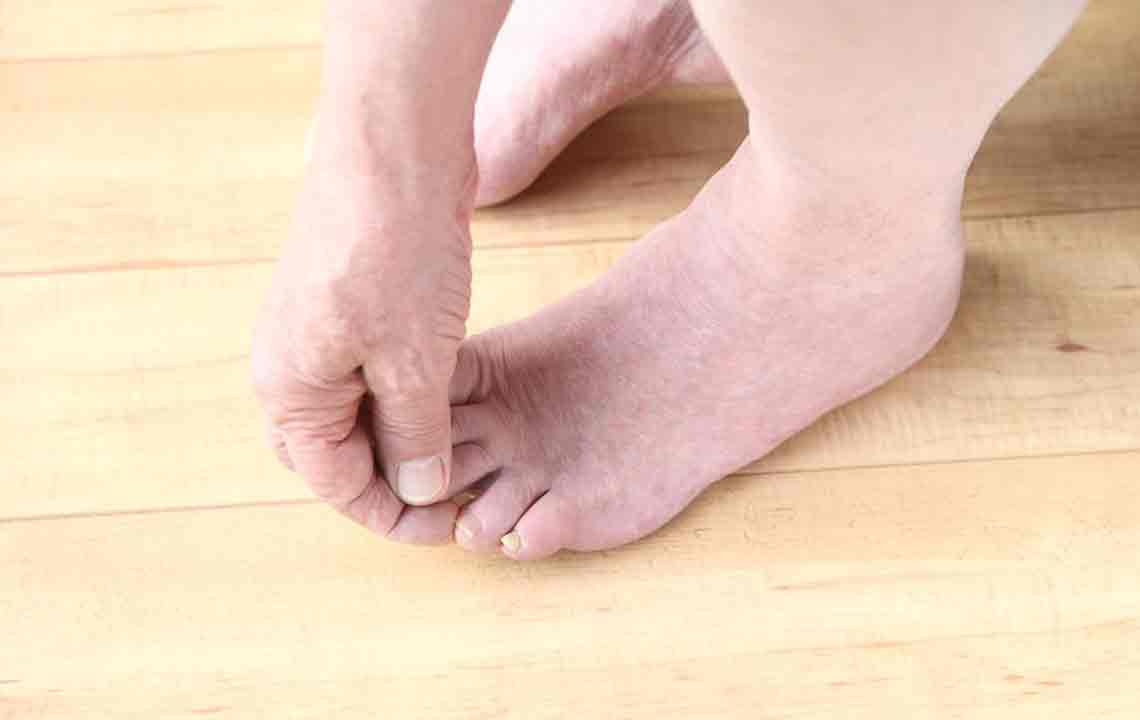
Common symptoms of diabetic foot problems include numbness, tingling sensations, sharp shooting pains, and increased pain at night, which can disrupt sleep patterns. While various treatments help to reduce symptoms and prevent progression, complete elimination of pain may not always be achievable. Therefore, proactive measures are essential to minimize risks and enhance quality of life.
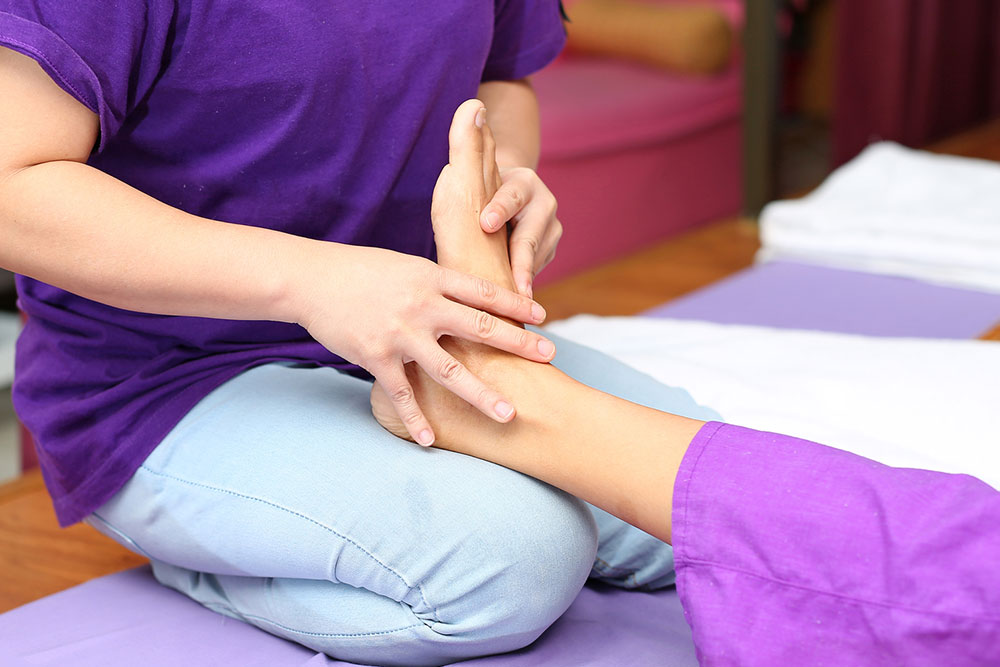
What Can You Do to Protect Your Feet?
Effective management of blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and lifestyle adjustments is fundamental. Regular foot examinations, daily inspection of your feet, proper footwear, and hygiene practices are critical in early detection of problems. Engaging in low-impact exercises can improve circulation, while therapies such as acupuncture have shown promise in alleviating neuropathy-related discomfort. Consulting healthcare professionals, including podiatrists and endocrinologists, ensures personalized care tailored to your needs. Educating yourself about diabetic foot health empowers you to take early action and prevent serious complications.