Comprehensive Guide to Foot Care for Diabetic Patients: Prevention and Management Strategies
Learn essential strategies for maintaining foot health in diabetics. This comprehensive guide covers preventive care, proper footwear, blood sugar control, and when to seek medical help, aiming to reduce the risk of ulcers, infections, and amputations. Key tips for diabetic foot management are vital for preserving mobility and preventing serious complications.
Comprehensive Guide to Foot Care for Diabetic Patients: Prevention and Management Strategies
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by high blood sugar levels caused by insufficient insulin production or the body’s inability to effectively use insulin, diabetes has wide-ranging impacts on various organs and tissues. Among these, foot health is often overlooked but critically important, as diabetes significantly increases the risk of foot complications, which can sometimes lead to devastating consequences like ulcers, infections, and even limb amputations if not properly managed. Understanding how diabetes influences foot health, along with implementing effective preventative measures, is essential for diabetic individuals to maintain mobility and quality of life.
Diabetes impacts foot health primarily through two mechanisms: nerve damage (neuropathy) and impaired circulation. Elevated blood glucose levels over time damage peripheral nerves, leading to a condition known as diabetic peripheral neuropathy. This nerve damage diminishes sensation in the feet, making it difficult for patients to feel injuries, blisters, or other minor wounds. As a result, unnoticed injuries can worsen, potentially developing into ulcers or infections.
Simultaneously, high blood sugar adversely affects blood flow, leading to peripheral vascular disease. The reduced circulation hampers the body's ability to deliver essential nutrients and oxygen to foot tissues, impairing healing processes. This combination of nerve damage and poor circulation creates a perfect storm for foot ulcers, infections, and tissue necrosis, which can quickly escalate into life-threatening situations if untreated.
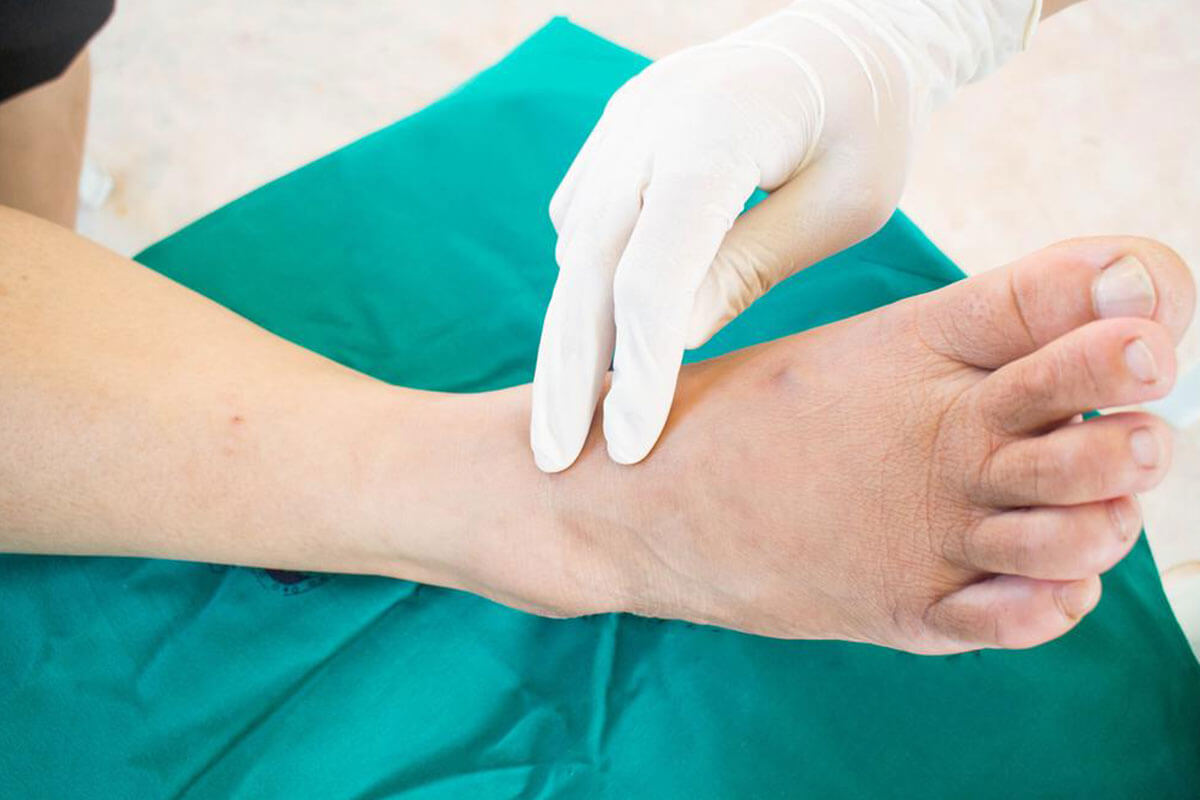
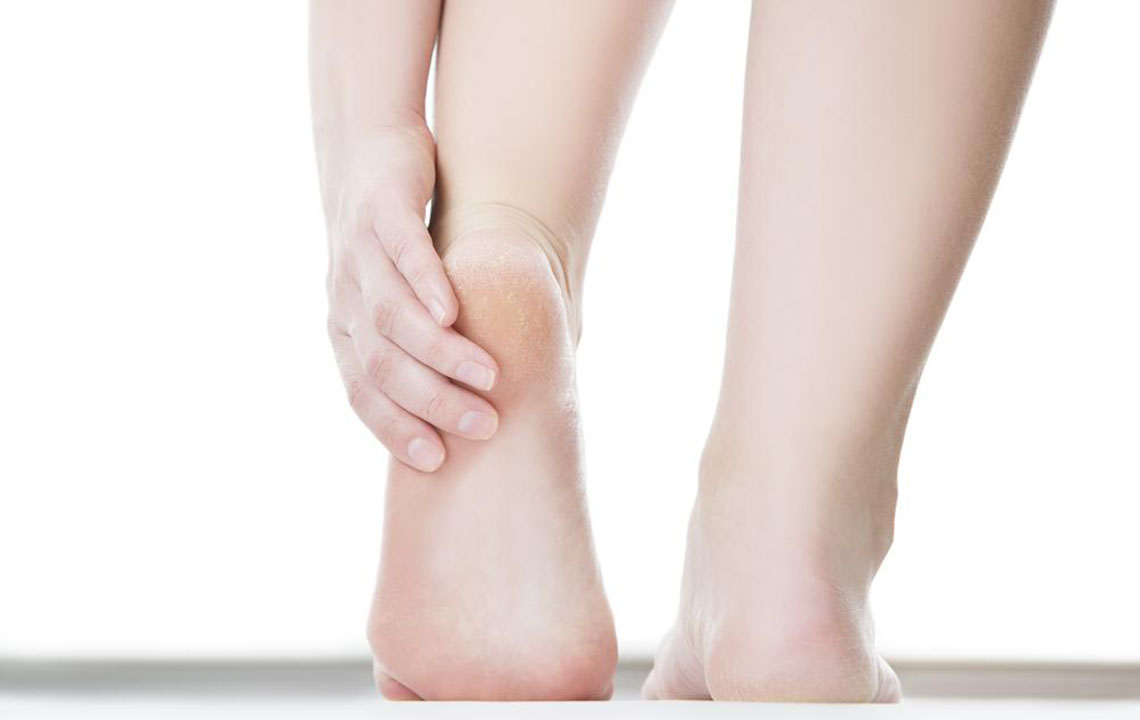
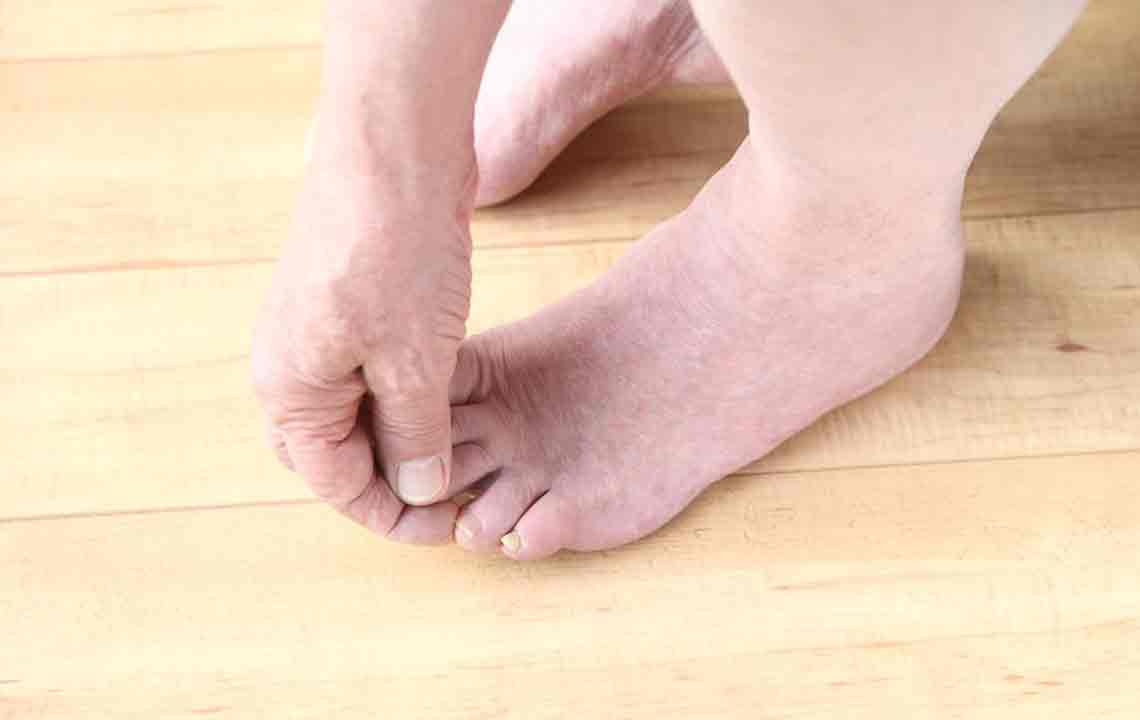
Preventative foot care is crucial for diabetics. Regular foot inspections allow early detection of any cuts, blisters, or abnormalities. Daily hygiene routines, including washing feet with lukewarm water and mild soap, followed by gentle drying—especially between the toes—help prevent bacterial or fungal infections. Applying moisturizer keeps skin supple but should be avoided between toes to prevent excess moisture buildup, which encourages fungal growth.
Choosing the appropriate footwear is equally important. Well-fitted, comfortable shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning reduce pressure points and prevent injuries. Interacting with podiatrists to select custom orthotics or insoles can further enhance foot stability and comfort. Patients should avoid walking barefoot even indoors, as this increases the risk of injuries unnoticed in neuropathic feet.
Monitoring blood sugar levels diligently is a fundamental aspect of preventing foot complications. Strict glycemic control can slow or halt the progression of neuropathy and vascular issues. Lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and medication adherence form the backbone of effective management.
When foot issues do arise, prompt medical attention is essential. Early intervention by healthcare professionals can prevent minor problems from escalating into severe infections or amputations. If ulcers, blisters, redness, swelling, or persistent pain are present, consulting a podiatrist or diabetic foot specialist should be a priority.
Additional tips for diabetics include quitting smoking, as tobacco use constricts blood vessels, worsening circulation problems. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding pressure or friction points on the feet can further reduce risks. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers, including routine foot examinations, are vital parts of comprehensive diabetic care.
In conclusion, managing foot health in diabetic patients involves a proactive approach emphasizing daily care, proper footwear, glycemic control, and prompt treatment of any foot abnormalities. Educating oneself about the risks and preventive strategies can significantly reduce the likelihood of complications, preserving mobility and overall health. Remember, taking preventive measures today can make a profound difference in the future well-being of diabetic individuals.