Comprehensive Guide to Preventing and Managing Diabetic Foot Problems
This comprehensive guide provides practical strategies for diabetics to prevent and manage foot health issues. Through daily inspections, proper hygiene, appropriate footwear, physical activity, and blood sugar control, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of infections, ulcers, and potential amputations. Regular medical consultations and early detection are emphasized as vital components of effective diabetic foot care. Implementing these routines can greatly improve quality of life and prevent serious complications related to diabetic foot health.
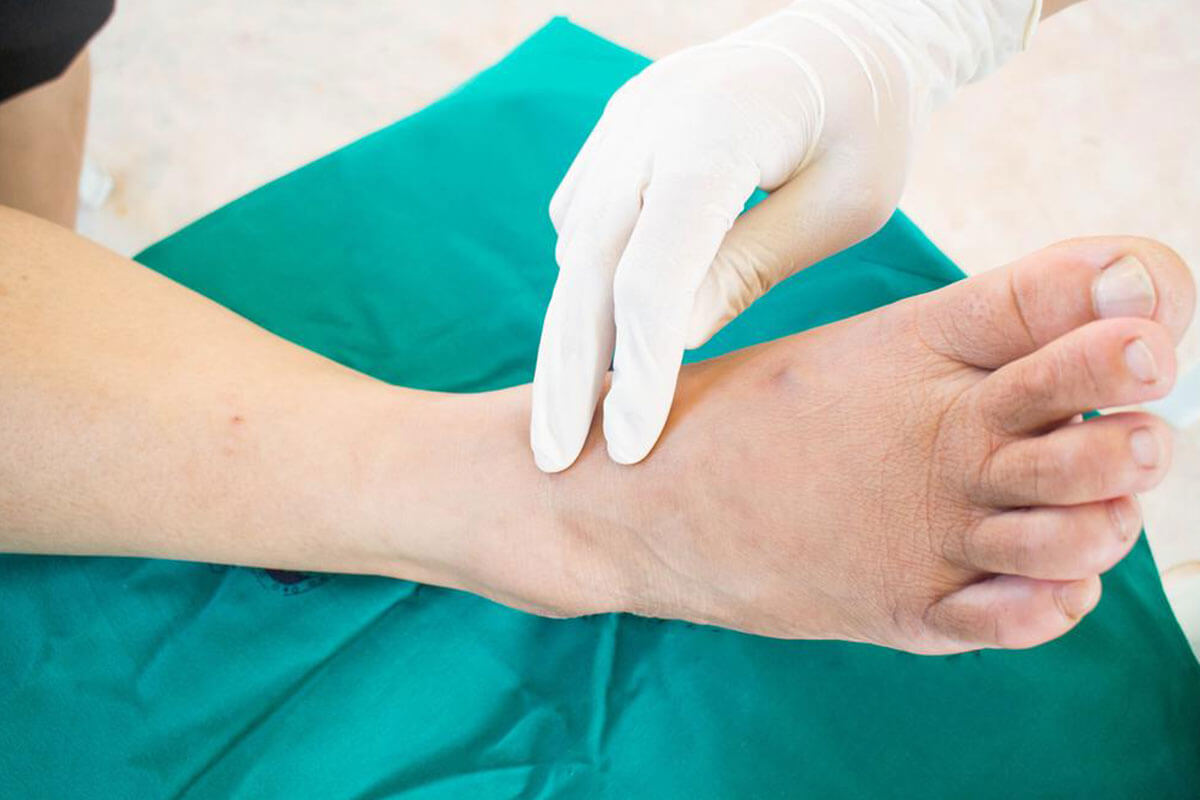
Comprehensive Strategies for Diabetic Foot Prevention and Care
If you are living with diabetes, preserving foot health is essential to prevent complications that can significantly impact quality of life. Foot-related issues such as numbness, pain, ulcers, and infections are common among diabetics due to elevated blood sugar levels affecting circulation and nerve health. Implementing effective foot care routines and making lifestyle adjustments can help minimize these risks and promote overall foot health.
Diabetic foot problems arise mainly because high blood sugar impairs nerve function and diminishes blood flow, making the feet more vulnerable to injuries, infections, and delayed healing. Conditions such as blisters, corns, calluses, bunions, hammertoes, fungal toenails, and ingrown nails are frequent concerns. Although these might appear minor initially, ignoring symptoms can lead to painful ulcers, severe infections, and even amputations in advanced cases. Therefore, proactive foot care and regular medical check-ups are critical for individuals with diabetes.
Maintaining optimal foot health involves simple but disciplined daily routines and ongoing medical attention. Below are detailed strategies to help diabetics care for their feet effectively and prevent common issues:
Daily Foot Inspections
Every day, dedicate a few moments to thoroughly examine your feet. Look for signs of redness, blisters, cuts, swelling, or any skin abnormalities. It’s particularly important to check between the toes and the soles, as these areas are prone to unnoticed injuries. If mobility is limited or sight is compromised, seek assistance from a family member or caregiver. Regular inspections allow for early detection of potential problems, which is crucial in preventing infections and complications.
Proper Foot Hygiene
Wash your feet daily using warm (not hot) water to remove dirt and bacteria. Avoid soaking your feet for long periods, as excessive moisture can weaken the skin. After washing, be sure to dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections. Using a soft towel, gently pat your feet dry and apply a moisturizer suitable for sensitive skin to keep the skin soft and prevent cracking.
Skin Care and Moisturization
Diabetes can cause dry, cracked skin, which increases susceptibility to infections. Regularly apply a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated, but avoid applying moisturizer between the toes to prevent excess moisture buildup. Monitor your skin for signs of dryness or irritation, and address any issues promptly to maintain healthy skin integrity.
Managing Corns, Calluses, and Nail Care
Trim toenails straight across to prevent ingrowth and avoid cutting them too short. Use a pumice stone or foot file after bathing to gently smooth corns and calluses. If persistent or painful areas develop, consult a podiatrist or foot specialist. Proper foot hygiene and timely treatment reduce the risk of ulcers and infections originating from neglected skin issues.
Appropriate Footwear Selection
Wear well-fitting, comfortable shoes that provide adequate support and avoid tight or narrow footwear that can cause blisters or pressure points. Always try on new shoes in the late afternoon when feet tend to be more swollen to ensure a proper fit. Use thick socks to minimize friction, and check insides of shoes before wearing to eliminate rough seams or debris. Breaking in new shoes gradually helps to prevent sore spots and blisters.
Physical Activity and Circulation Boosters
Engage in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, cycling, or yoga to promote healthy blood circulation to the feet. Avoid prolonged periods of sitting and incorporate foot and leg movements to improve blood flow. Regular activity helps reduce the risk of nerve damage and poor circulation, which are major risk factors for foot ulcers. Always consult your healthcare provider before beginning any new exercise regimen.
Blood Sugar Control
Keeping blood glucose levels within target ranges is crucial in preventing nerve and blood flow damage that contribute to foot problems. Adopting a balanced diet focused on low glycemic index foods, quitting smoking, managing stress, and following your medication plan help stabilize blood sugar. Regular medical check-ups and foot examinations ensure that issues are caught early and managed effectively, reducing the likelihood of serious complications.
By diligently following these comprehensive foot care practices, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of developing serious foot problems. Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are key to avoiding severe consequences. Incorporate these habits into your daily routine and keep up with regular visits to your healthcare team to maintain healthy, pain-free feet.