Comprehensive Guide to Lupus: Causes, Symptoms, and Early Detection
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation affecting various organs, often manifesting with symptoms like fatigue, skin rashes, joint pain, and kidney issues. Recognizing early warning signs and triggers is crucial for effective management and improving quality of life. This comprehensive guide covers causes, symptoms, and strategies for early detection, providing valuable insights for patients and caregivers.
An In-Depth Overview of Lupus: Causes, Warning Signs, and Management
Lupus, scientifically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a multifaceted autoimmune disease that poses significant challenges for diagnosis and treatment. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation that can affect various organs and systems in the body. The symptoms of lupus are highly variable, making it a particularly elusive condition for medical professionals and patients alike. Typically manifesting in young adults, especially before the age of 30, lupus requires heightened awareness of its warning signs and potential triggers to ensure timely intervention.
Understanding the Underlying Causes of Lupus and Its Skin Manifestations
The precise origins of lupus remain complex and not fully understood. While there is no definitive cause, research indicates that a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors plays a critical role. Individuals with a family history of autoimmune diseases are at increased risk, suggesting a genetic component. However, environmental triggers are equally influential in activating the disease process.
It is essential to clarify that lupus is an autoimmune disorder that is not contagious. It cannot be transmitted from person to person through contact or other means, contrary to some misconceptions. Its development appears to involve a complex interplay between genetic vulnerabilities and external influences, which can provoke symptoms or exacerbate existing conditions.
Known Triggers for Lupus Flare-Ups and Skin Problems
The triggers for lupus are diverse and sometimes unpredictable. Recognizing these triggers can significantly aid in managing the disease and reducing the frequency of flare-ups. Key environmental and lifestyle factors contributing to lupus symptoms include:
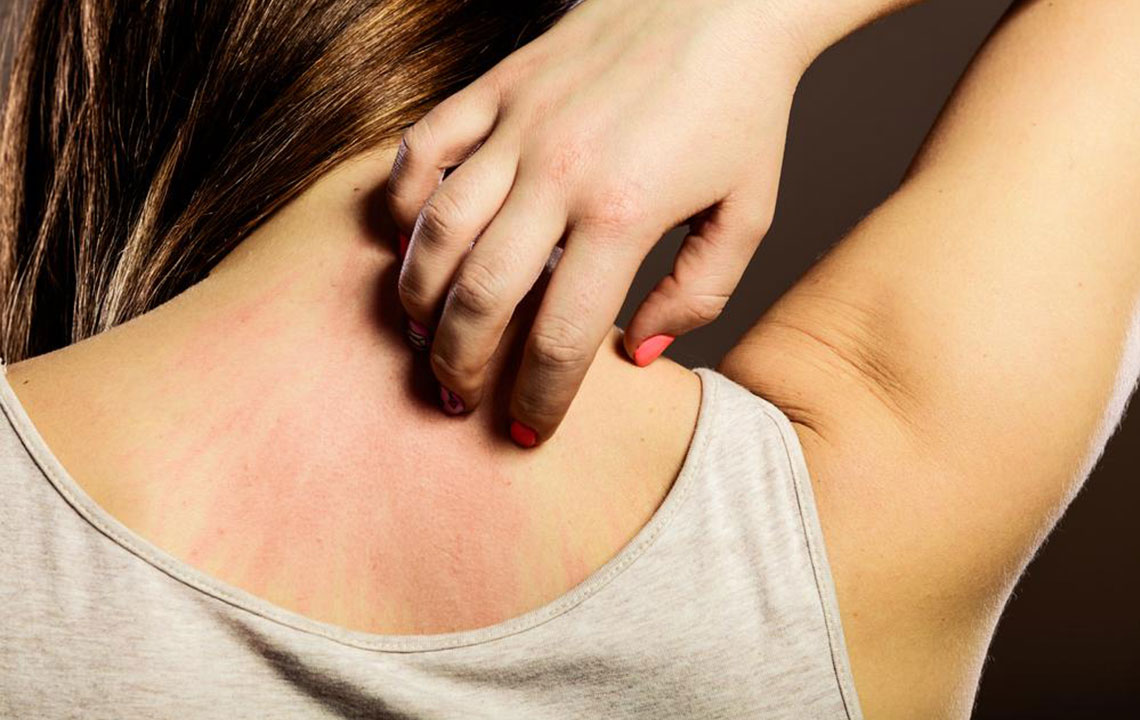
Sun exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight can sharply increase inflammation and skin rashes in genetically susceptible individuals. Protecting skin from sun exposure is a crucial aspect of disease management.
Infections: Certain bacterial, viral, and fungal infections may activate or worsen lupus symptoms by stimulating the immune system abnormally.
Medications: Drugs such as antihypertensives, antibiotics, and anti-seizure medications have been linked to drug-induced lupus. Symptoms often subside upon discontinuation of the offending medication.
Major Symptoms and Warning Signs of Lupus-Related Skin and Systemic Issues
Understanding the broad spectrum of symptoms associated with lupus is vital for early diagnosis and effective management. Here are some of the most common and critical signs to watch for:
Persistent Fatigue: Nearly 90% of individuals with lupus report enduring tiredness that isn’t relieved by sleep. Managing fatigue involves balanced activity levels, adequate rest, and sometimes medical intervention.
Unexplained Fever: Recurrent low-grade fevers, typically ranging from 98.5°F to 101°F, can be early indicators. Persistent fever warrants thorough medical evaluation to rule out infections or lupus activity.
Hair Loss: Inflammation affecting the scalp and skin can lead to hair thinning, patchy hair loss, or shedding. This symptom often improves with proper lupus treatment and skin care.
Lung Inflammation: Pulmonary involvement can cause symptoms such as chest pain during breathing, shortness of breath, and in severe cases, shrinking of lung tissue, which is referred to as vanishing lung syndrome. Early detection is crucial to prevent irreversible damage.
Kidney Involvement (Nephritis): Kidney inflammation might develop after years of disease. Signs include swelling of the legs and feet, dark or bloody urine, frequent urination at night, and localized flank pain. Kidney health monitoring is vital for lupus patients.
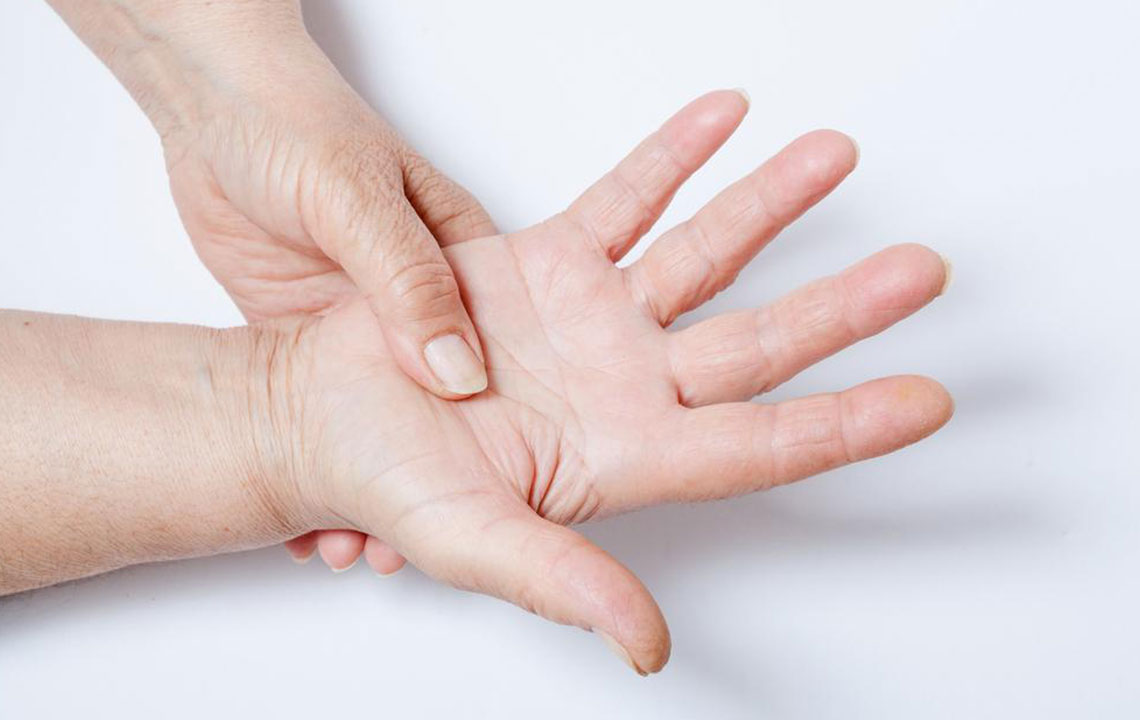
Joint Pain and Stiffness: Inflammation in joints causes discomfort, swelling, and reduced mobility. These symptoms can fluctuate and often require tailored medical management beyond over-the-counter medications.
Thyroid Disorders: Many lupus patients also experience thyroid abnormalities such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, which influence metabolism and can lead to weight changes, fatigue, and other systemic issues.
If you notice any of these symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is essential. Early diagnosis allows for more effective treatment strategies, helping to manage symptoms, prevent severe complications, and improve overall quality of life. Maintaining a vigilant approach and working closely with healthcare providers can make a significant difference in managing lupus over the long term.