Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the 8 Major Signs of Lupus
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease with diverse symptoms. Recognizing its early signs—such as fatigue, fever, skin rashes, and joint pain—is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide highlights the 8 key indicators of lupus, emphasizing the importance of prompt medical intervention to prevent serious complications and improve patient outcomes. Understanding these symptoms enables individuals and healthcare providers to act swiftly and optimally manage this chronic condition.
Lupus, medically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a complex and chronic autoimmune disease that impacts millions worldwide. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs, leading to widespread inflammation and tissue damage. As a highly variable disease, lupus presents with a broad spectrum of symptoms, making early identification challenging but critically important for effective management. Although there is currently no cure for lupus, advancements in treatment options enable many patients to lead relatively normal lives by controlling symptoms and preventing severe complications.
Understanding the early and most common signs of lupus is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers. Early diagnosis can significantly improve disease outcomes by enabling timely intervention and personalized treatment plans. Lupus predominantly affects women between the ages of 15 and 45, but it can also affect men, children, and older adults. The manifestations of lupus are highly individualistic; some individuals may experience mild symptoms, while others face severe, life-threatening complications.
One of the crucial steps toward managing lupus effectively is recognizing its hallmark symptoms. These symptoms may appear singly or in combination, often fluctuating over time. Below, we explore the eight key signs that could indicate the presence of lupus, emphasizing the importance of medical consultation upon noticing any of these indicators.
1. Persistent Fatigue
Chronic fatigue is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms experienced by lupus patients. Unlike everyday tiredness, lupus-related fatigue is profound, persistent, and unrelieved by rest. Patients often report feeling exhausted even after adequate sleep or rest, which can interfere with daily activities and diminish quality of life. This symptom occurs due to immune system overactivity and widespread inflammation impacting multiple organ systems. Recognizing persistent fatigue as a potential warning sign warrants prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional, especially if accompanied by other symptoms.
2. Unexplained Fever
Low-grade fever without any apparent cause is another key indicator of lupus. Fever in lupus patients often occurs during disease flares, reflecting underlying immune system activation and inflammation. Unlike infections, lupus-related fever typically persists for days or weeks and does not respond to antibiotics. This symptom can be subtle or significant, but its presence should prompt further medical investigation. Recurrent or persistent unexplained fevers are a signal that an underlying autoimmune process may be at work.
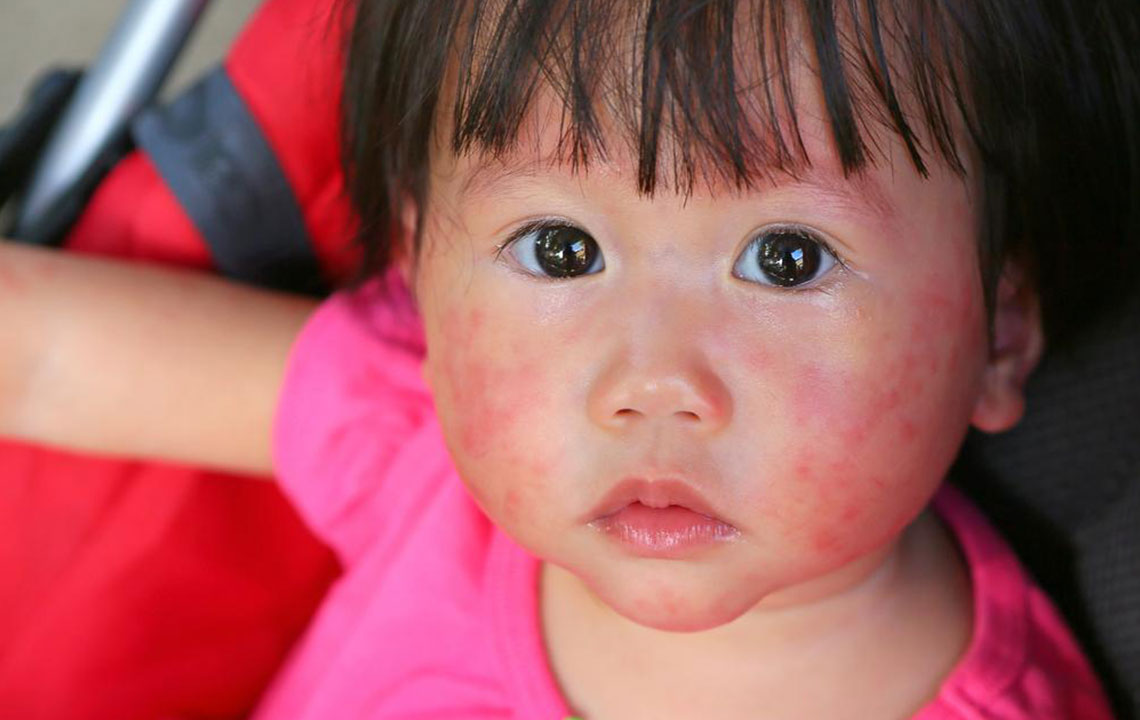
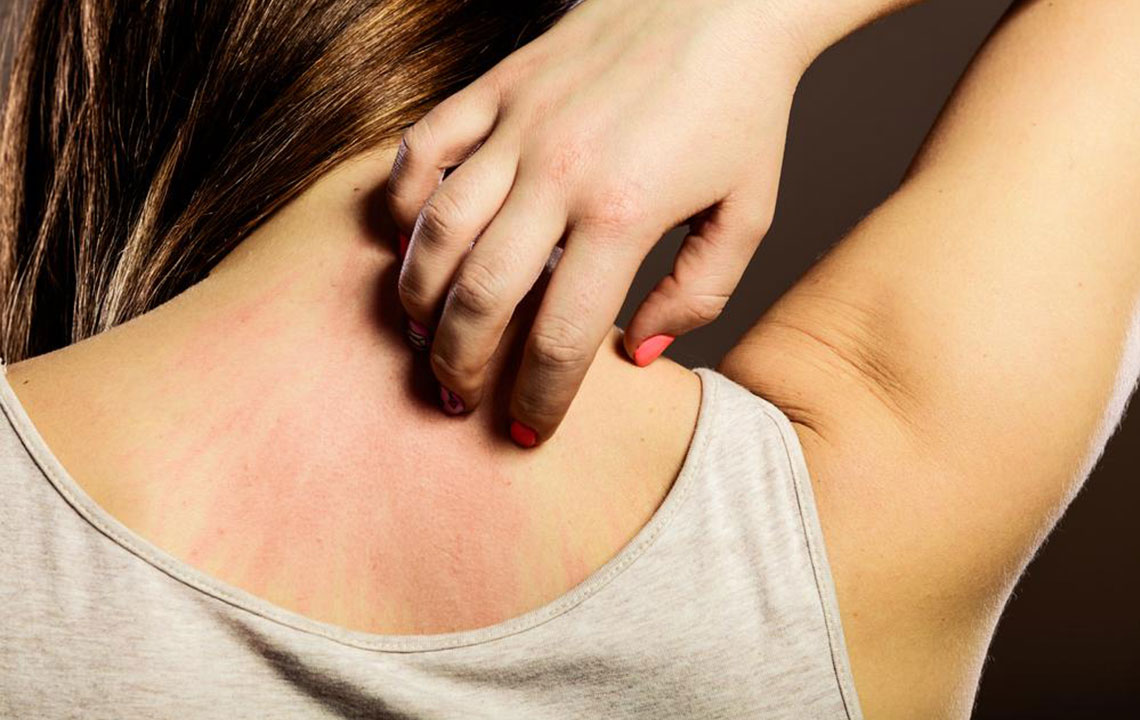
3. Hair Loss and Skin Rash
Many lupus patients notice hair thinning or hair loss, often patchy, which can be distressing. The disease can cause inflammation of the skin and scalp, leading to hair shedding. Additionally, the classic butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and bridge of the nose, known as malar rash, is characteristic of lupus. Skin rashes may also appear as discoid (scaly, disc-shaped) lesions or as other irregular rashes that worsen with sun exposure. Photosensitivity is common, and these skin manifestations are critical clues for diagnosis.
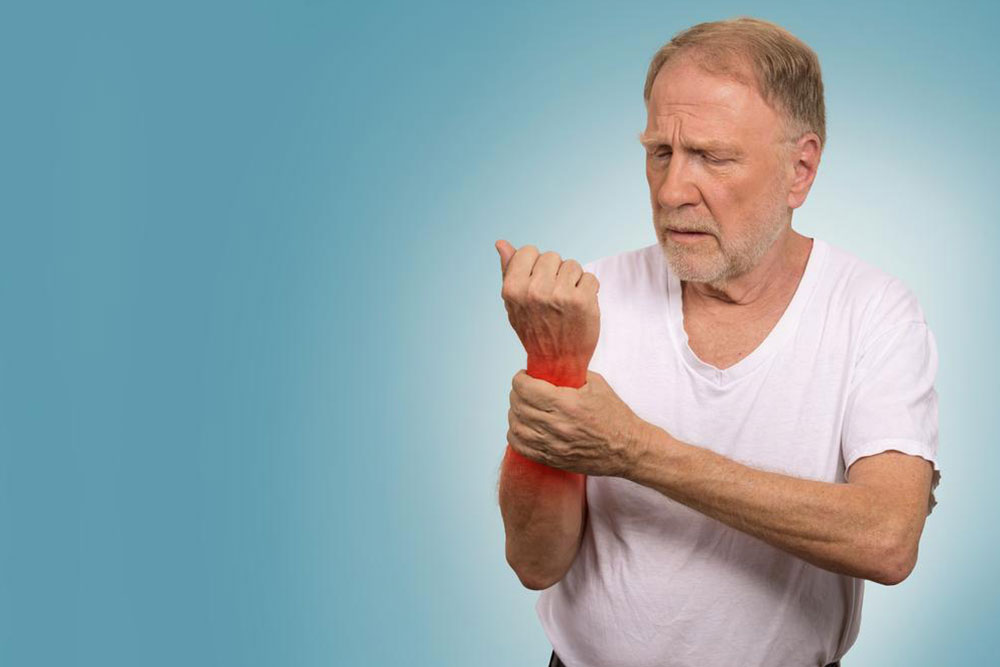
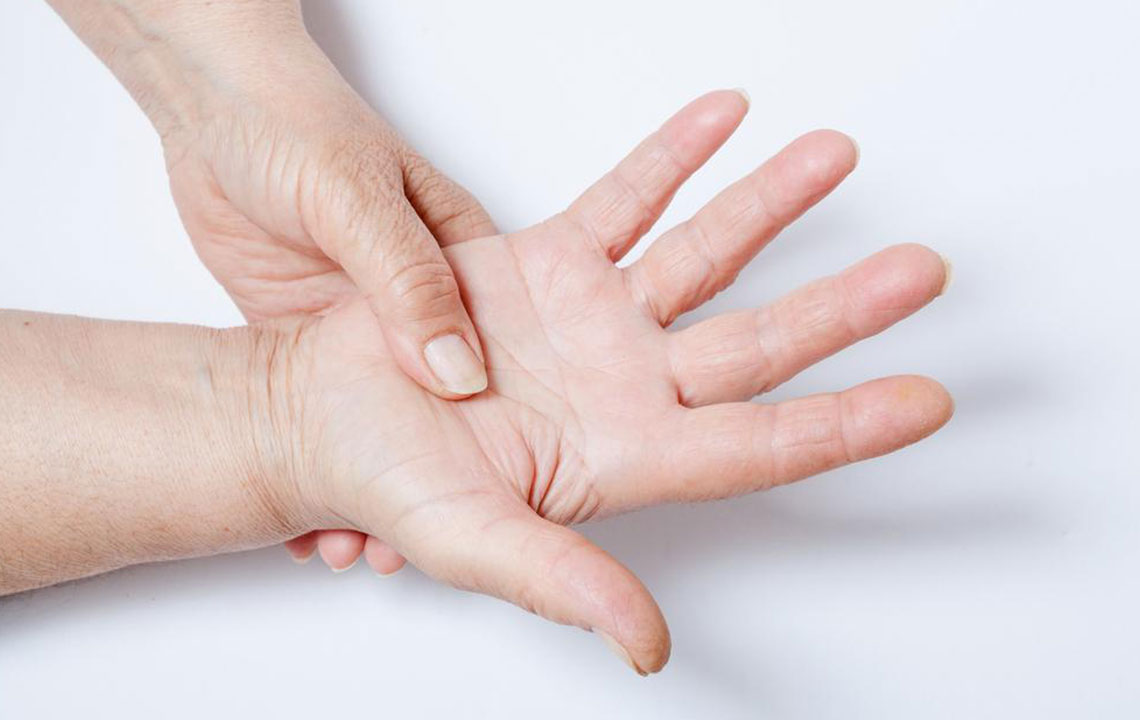
4. Joint Pain and Swelling
Arthritis-like symptoms are frequently observed in lupus patients, with joint pain, tenderness, and swelling affecting small and large joints, including the hands, wrists, knees, and ankles. Unlike osteoarthritis, lupus joint pain tends to be symmetrical and is often accompanied by morning stiffness. This symptom can impair mobility and cause discomfort but does not typically lead to joint destruction if managed properly. Recognizing joint involvement alongside other symptoms can help differentiate lupus from other rheumatologic conditions.
5. Kidney Inflammation (Lupus Nephritis)
One of the more serious manifestations of lupus involves the kidneys. Lupus nephritis occurs when immune complexes deposit in renal tissues, leading to inflammation and impaired kidney function. Symptoms may include swelling in the legs, high blood pressure, urine abnormalities (like protein or blood), and in severe cases, kidney failure. Regular monitoring of kidney function is essential for lupus patients, especially those with other systemic symptoms. Early detection of renal involvement is vital for preventing irreversible damage.
6. Lung Involvement and Shortness of Breath
Lupus can affect the lungs, causing pleuritis (inflammation of the lining surrounding the lungs), pulmonary hypertension, or even lung fibrosis. Symptoms include chest pain, especially with deep breaths, and shortness of breath. These respiratory issues may develop gradually or suddenly, sometimes mistaken for other conditions. Prompt medical attention is crucial to manage lung involvement and prevent complications.
7. Sun Sensitivity and Photosensitivity
Many individuals with lupus exhibit heightened sensitivity to sunlight. Exposure to UV rays can trigger or worsen skin rashes, exacerbate systemic symptoms, and increase disease activity. Patients often develop rash or skin lesions after sun exposure, requiring protective measures like sunscreen and protective clothing. Recognizing photosensitivity is important not only for disease management but also for avoiding potential flare-ups that can hinder overall health.
8. Swelling and Pain in Joints and Muscles
Muscle pain and joint swelling contribute significantly to discomfort among lupus sufferers. These symptoms may fluctuate in intensity over time and can become persistent during flares. While similar to rheumatoid arthritis, lupus often involves multiple organ systems, contributing to the overall disease complexity. Differentiating between various causes of joint pain—degenerative or inflammatory—is critical for correct diagnosis and treatment planning.
Conclusion: The Importance of Early Detection and Medical Consultation
Recognizing these eight key signs of lupus early can be lifesaving. Due to the disease's variability and complex presentation, a high index of suspicion is necessary when multiple symptoms emerge. If you or someone you know experiences persistent fatigue, unexplained fever, skin rashes, joint pain, or other associated symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider—preferably a rheumatologist—is essential for comprehensive evaluation and diagnosis. Laboratory tests such as ANA (antinuclear antibody) and other specific markers will aid in confirming lupus.
Proactive management not only improves quality of life but also helps prevent serious complications such as kidney failure, lung disease, or cardiovascular problems. Awareness, early diagnosis, and tailored treatment strategies are the pillars of effective lupus care. Stay vigilant for the initial signs, and seek medical advice if these symptoms persist or worsen over time.