Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Atopic Dermatitis Effectively
This comprehensive guide provides detailed strategies to manage atopic dermatitis effectively. Covering skincare routines, medical treatments, and natural remedies, it helps sufferers understand how to reduce symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and improve skin health through personalized approaches and professional guidance. Perfect for anyone seeking to better control this chronic condition and enhance their quality of life.

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing and Treating Atopic Dermatitis
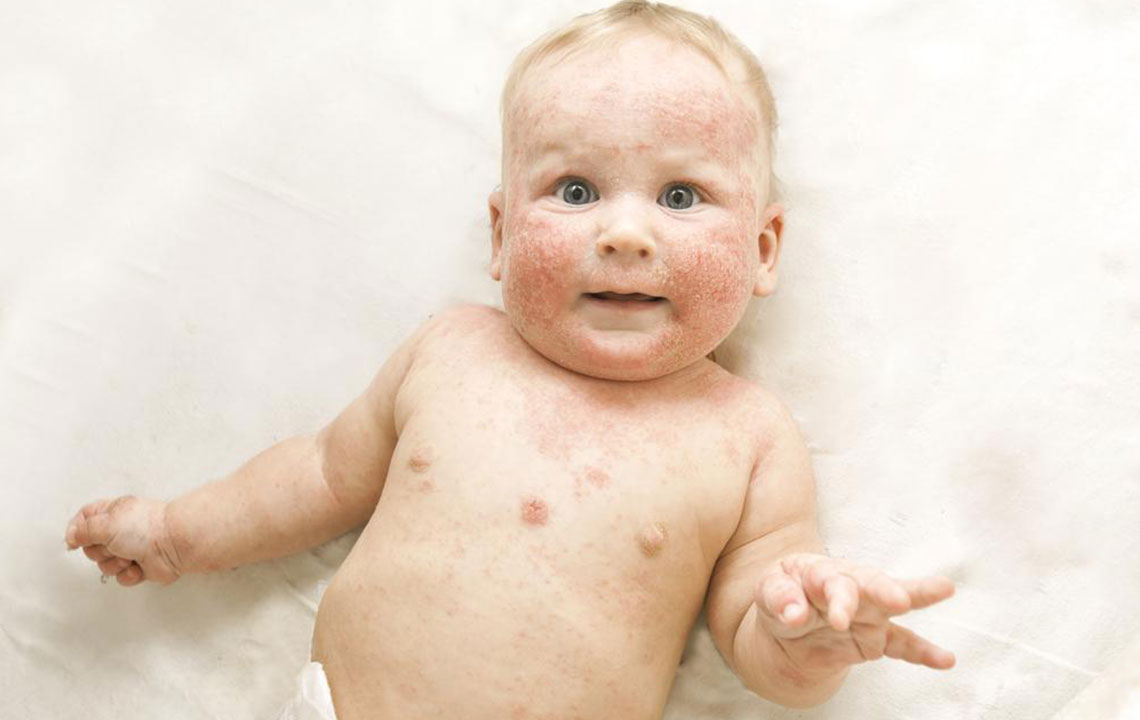
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a persistent and often distressing skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Characterized by dry, itchy, inflamed skin, it can significantly impact daily life and overall well-being if not managed effectively. While a definitive cure remains elusive due to its complex nature involving genetic, environmental, and immune factors, understanding the available treatment options and adopting proper skin care routines are essential steps toward reducing symptoms and enhancing quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various strategies, including both medical interventions and home remedies, designed to help individuals control atopic dermatitis, prevent flare-ups, and maintain healthier skin. Proper management involves a combination of targeted treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and informed skincare practices tailored to each individual's needs.
Core Treatment Approaches for Atopic Dermatitis
The primary goal in managing atopic dermatitis is to minimize skin dryness, reduce inflammation, and prevent infections. Achieving these objectives requires a multifaceted approach, outlined as follows:
Effective Skin Moisturization
Hydrating the skin is the bedrock of atopic dermatitis management. Moisturizers help restore the skin barrier function, prevent water loss, and alleviate dryness. Applying moisturizers immediately after bathing, while the skin is still damp, enhances their efficacy. Selecting the right type of moisturizer based on the severity of the condition is crucial:
Lotion: Lotion formulations are water-in-oil emulsions that are lightweight and easy to spread. They are suitable for mild cases of eczema or for daytime use. However, in severe cases, lotions may evaporate quickly, leading to continued dryness and irritation.
Creams: Creams contain a higher proportion of oil compared to lotions, offering better hydration and barrier reinforcement. They are ideal for daily use on dry or mildly irritated skin, providing a good balance of hydration and skin comfort.
Ointments: Ointments are semisolid, high-oil formulations that provide intense moisture and form a protective barrier over the skin. They are often free from fragrances and irritants, making them suitable for sensitive, severely dry skin, or areas prone to cracking. Because of their occlusive nature, ointments are often recommended for acute flare-ups.
Medical Treatments and Pharmacotherapy
While skincare routines form the foundation of eczema management, medical treatments play a vital role during flare-ups or persistent symptoms. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for personalized treatment guidance:
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are the most commonly prescribed medications for reducing inflammation and controlling flare-ups. They come in various potencies; generally, low-potency options like hydrocortisone are used for mild cases or sensitive areas such as the face. Proper application, following medical advice, can minimize side effects such as skin thinning while effectively managing inflammation. Use corticosteroids for short periods to avoid potential adverse effects, and always adhere to prescribed regimens.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
For sensitive areas or long-term management, medications like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can help regulate immune responses without the side effects associated with steroids. They are helpful in reducing flare-ups and maintaining remission.
Oral Antihistamines
While antihistamines do not directly treat eczema, they can help relieve associated itching and improve sleep quality when itching is severe. They are supportive medications and should be used under medical supervision.
Phototherapy and Light Therapy
In cases where topical treatments are ineffective, controlled exposure to narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) light can help decrease inflammation and improve skin condition. Typically administered 2-3 times per week under medical supervision, phototherapy is an effective adjunct therapy for chronic eczema.
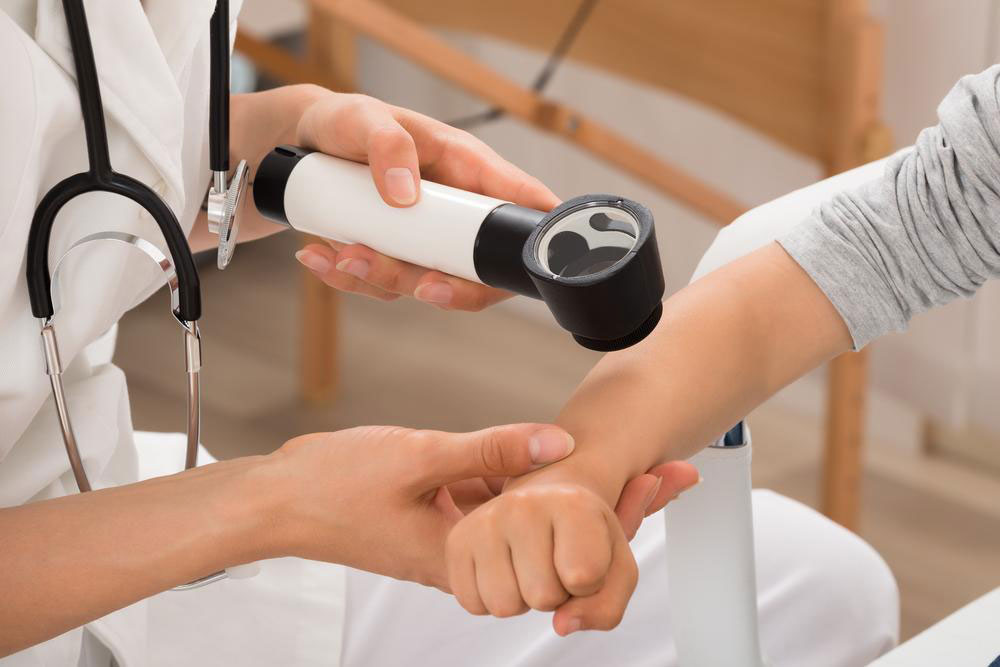
Before initiating any treatment plan, a thorough consultation with a dermatologist or healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable options based on individual circumstances and severity of the condition.
Natural and Home Remedies for Symptom Relief
In addition to medical treatments, many individuals find relief through natural remedies that soothe itching, reduce inflammation, and promote skin healing. These approaches can be used as complementary strategies to enhance skin comfort and prevent flare-ups:
To effectively manage atopic dermatitis, combining medical treatment with proper skincare routines and natural remedies can significantly improve the condition. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding known triggers such as allergens or irritants, and staying vigilant about skin care can make a substantial difference in controlling this chronic skin disorder. Remember, individual responses vary, so working closely with healthcare providers is essential for developing an optimal management plan tailored to your needs.
By understanding the triggers, adopting effective treatment strategies, and maintaining consistent skincare, those affected by atopic dermatitis can lead more comfortable, healthier lives. Staying informed about new developments and ongoing research in eczema management also ensures access to the latest therapies and recommendations.