Complete Guide to Recognizing and Treating Varicose Veins for Better Venous Health
Explore this comprehensive guide on varicose veins, including causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options. Learn how lifestyle adjustments and medical procedures can help manage vein health effectively, reducing discomfort and preventing complications for a better quality of life.

The Essential Guide to Understanding and Managing Varicose Veins
In recent decades, the prevalence of vein-related health issues has seen a significant rise worldwide. Among these, varicose veins stand out as one of the most common and bothersome conditions affecting millions of individuals across various age groups. This condition not only impacts aesthetic appearance but also poses potential health risks if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, preventative measures, and available treatment options for varicose veins is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life.
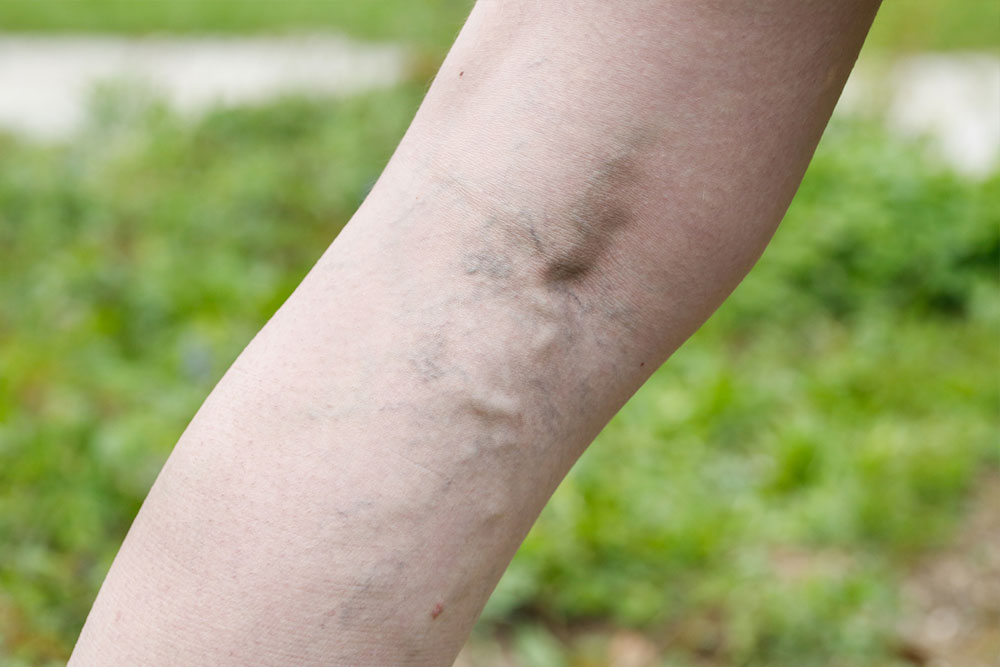
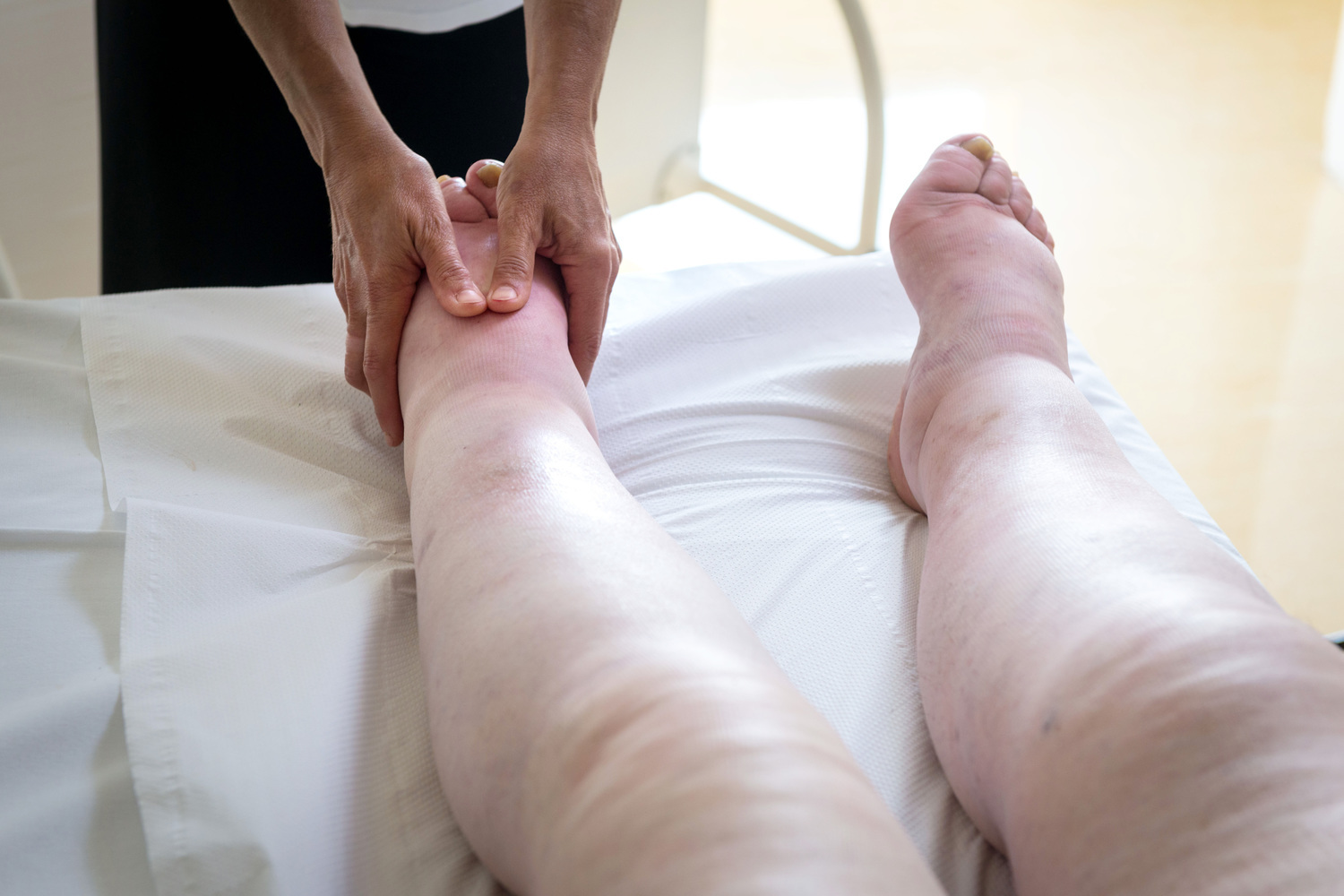
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that often develop in the legs and feet. The reason behind this is related to the complex function of the circulatory system, where arteries and veins perform distinct roles. Arteries are responsible for transporting oxygen-rich blood from the heart to various tissues, while veins gather deoxygenated blood and return it to the heart. This process works against gravity, which creates a constant challenge for venous return, especially in the lower extremities.
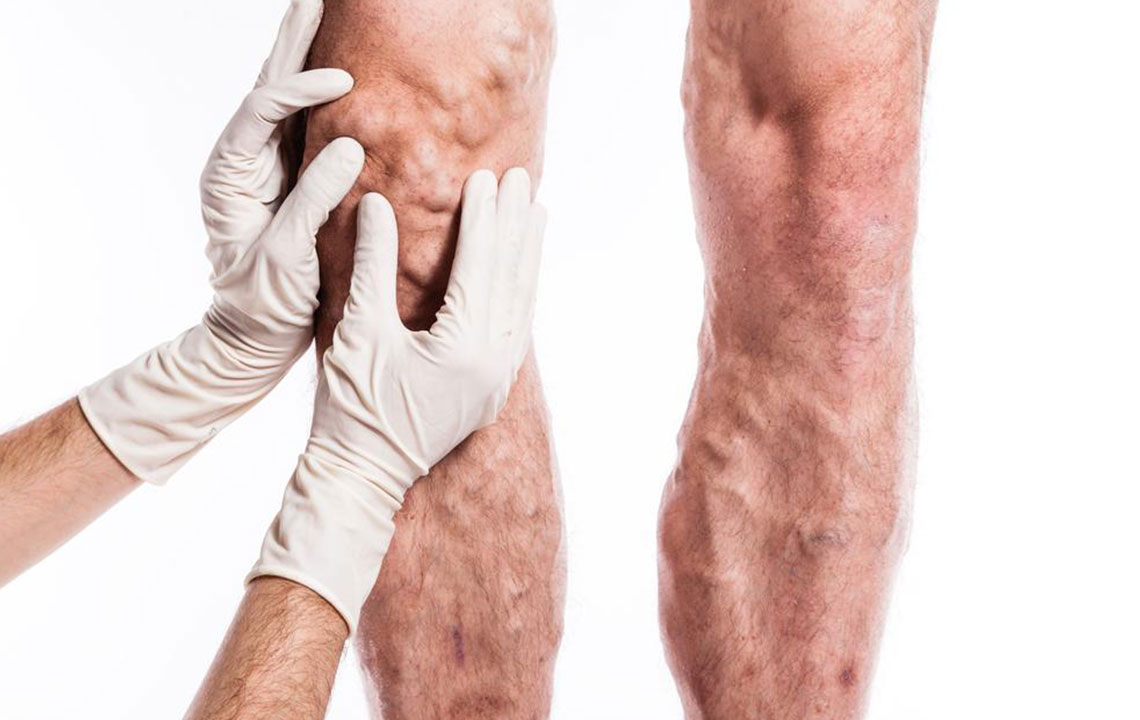
Veins contain specialized valves that ensure blood flows upward toward the heart, preventing backflow. These valves work in tandem with muscle movements, particularly during walking or exercise, which helps propel blood against gravity. However, when these valves weaken or become damaged, blood can start to pool within the veins. This pooling causes the veins to become distended, twisting, and bulging, resulting in the characteristic appearance of varicose veins. This condition often manifests as raised, lumpy veins that are visible under the skin, especially on the legs.
Key Causes of Varicose Veins
Genetic Predisposition: Family history plays a significant role; if relatives have varicose veins, the likelihood of developing them increases.
Pregnancy: As the uterus enlarges during pregnancy, it exerts additional pressure on the pelvic and leg veins, which can lead to varicosity. Hormonal changes during pregnancy also weaken vein walls.
Lifestyle Choices: Sedentary behavior, prolonged standing or sitting, wearing tight clothing, and poor ergonomic habits contribute to vein strain and damage.
Obesity: Excess weight increases pressure inside the veins, making it harder for blood to return to the heart efficiently.
Smoking: Tobacco use impairs vascular health, damages vein walls, and promotes inflammation, all of which worsen vein condition.
Advancing Age: As we age, veins lose elasticity and become more susceptible to weakening, making the development of varicose veins more likely.
Gender Specific Factors: Women are at higher risk due to hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy-related changes, and use of hormonal contraceptives which can influence vein integrity.
Recognizing the Symptoms
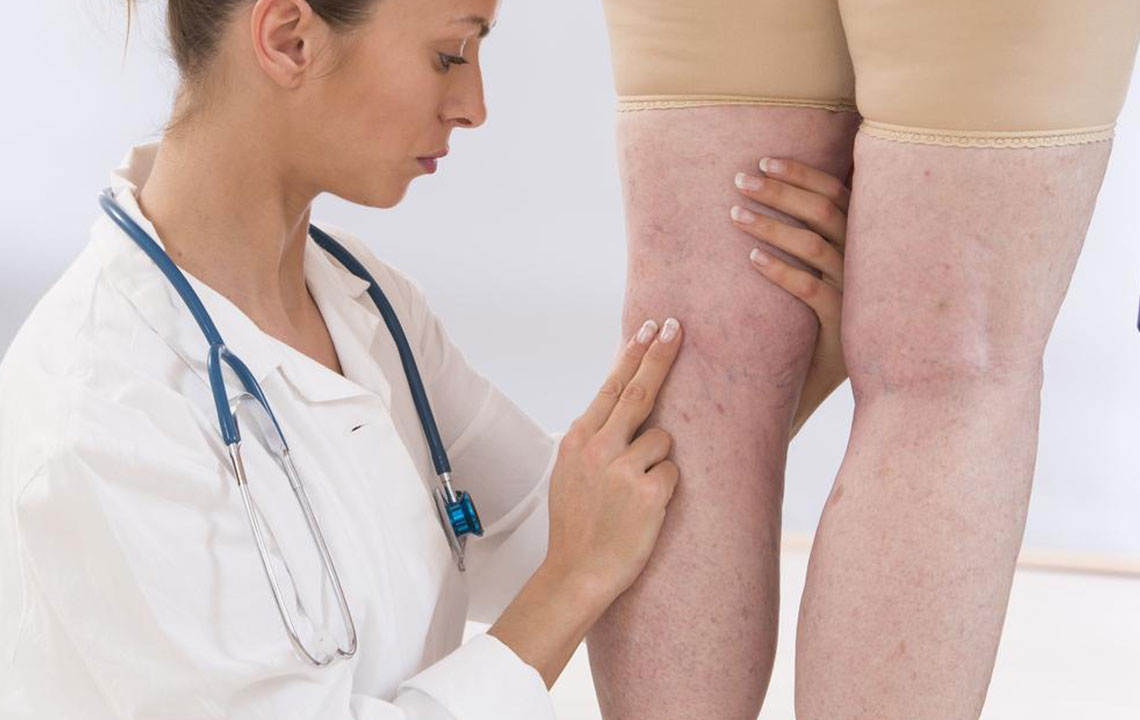
Early detection of varicose veins involves observing specific signs and symptoms. Common indicators include visibly swollen or twisted veins on the legs, ankles, or feet. Patients often report a feeling of heaviness, fatigue, or throbbing pain in the lower limbs, especially after prolonged standing or sitting. Restless legs syndrome, a persistent urge to move the legs during periods of inactivity, is also associated with vein issues.
Additional signs include skin discoloration such as darkening or bluish-purple veins, swelling around the ankles, cramping episodes during the night, and skin inflammation or dermatitis which can cause itchiness, ulcers, or open sores in severe cases.
Strategies for Prevention and Management
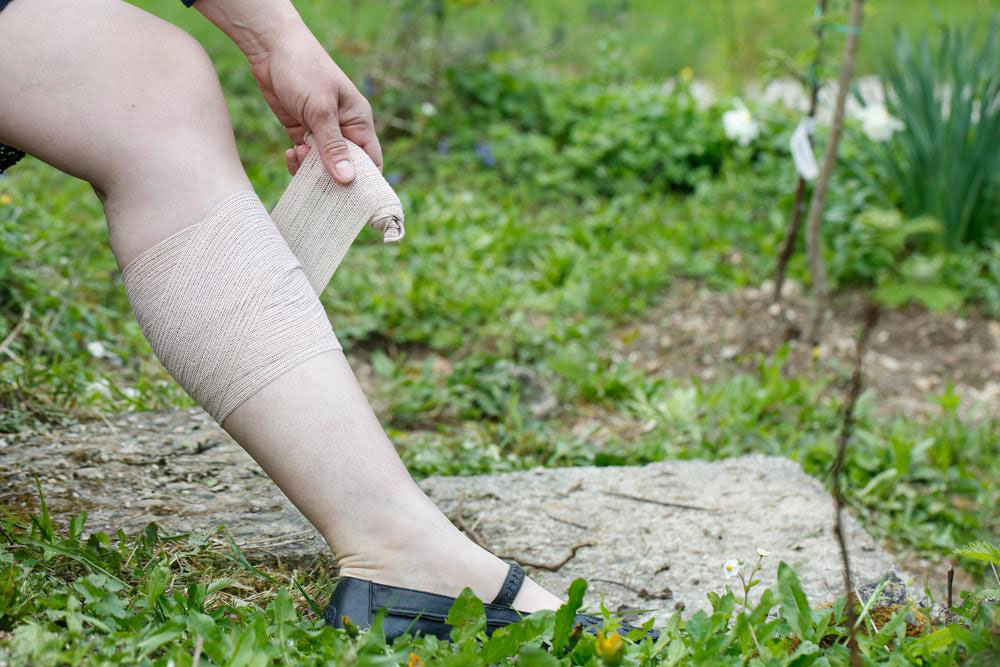
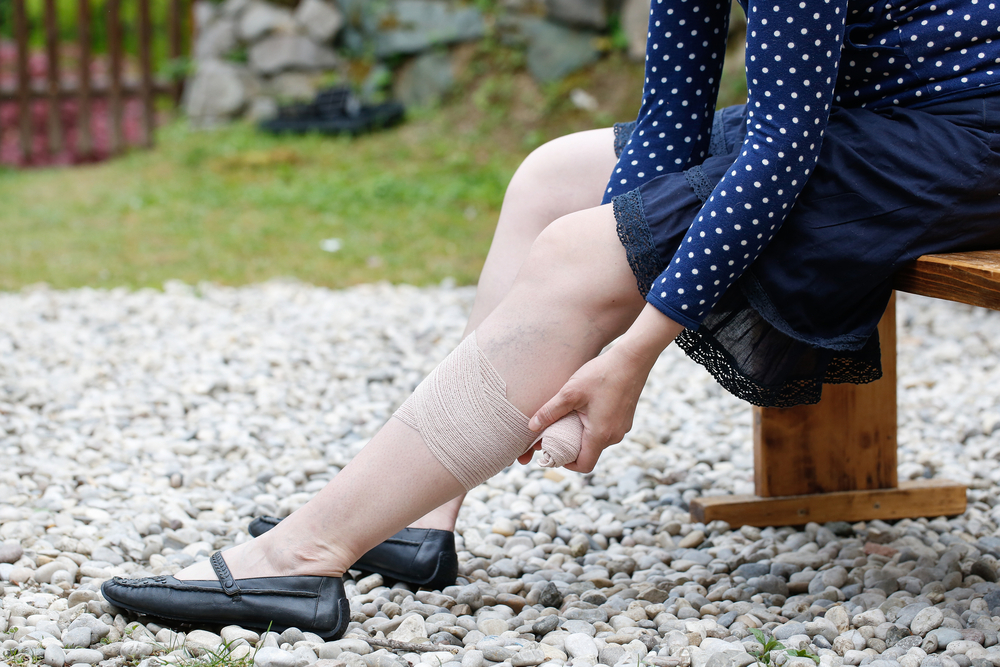
While some risk factors like genetics cannot be modified, lifestyle adjustments can significantly lower the chances of developing or worsening varicose veins. Wearing compression stockings is a widely recommended conservative treatment; these specialized stockings apply graduated pressure to legs, facilitating venous blood flow, reducing swelling, and alleviating symptoms.
Engaging in regular physical activity such as walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging helps improve overall circulation and strengthens calf muscles, which support vein health. Elevating the legs whenever possible, especially after long periods of standing, encourages blood flow back towards the heart and reduces venous pressure.
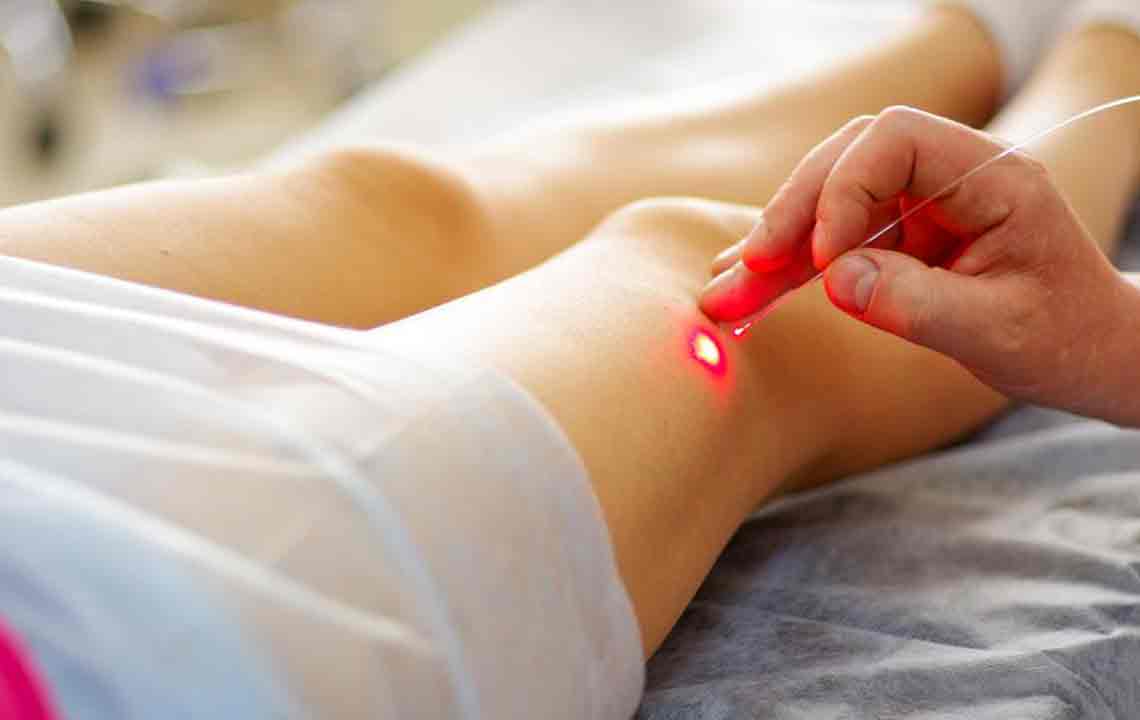
In terms of medical treatment options, laser therapy, sclerotherapy, and ambulatory phlebectomy are minimally invasive procedures that can effectively eliminate or shrink problematic veins. For advanced cases involving ulcers, blood clots, or significant vein damage, surgical interventions like endoscopic vein surgery or vein stripping may be necessary.
Early diagnosis and appropriate management are essential for preventing complications such as skin ulcers, bleeding, or deep vein thrombosis. Patients are advised to seek consultative care if they notice any persistent symptoms or visual changes in their leg veins.