Comprehensive Guide to Varicose Veins: Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Treatment Options
This comprehensive guide explores varicose veins, detailing their symptoms, causes, diagnostic methods, and a wide array of treatment options. Emphasizing early detection and lifestyle modifications, it offers valuable insights into managing and preventing complications related to this common vascular condition. Whether mild or severe, understanding varicose veins can help individuals take proactive steps toward healthier legs and better circulatory health.
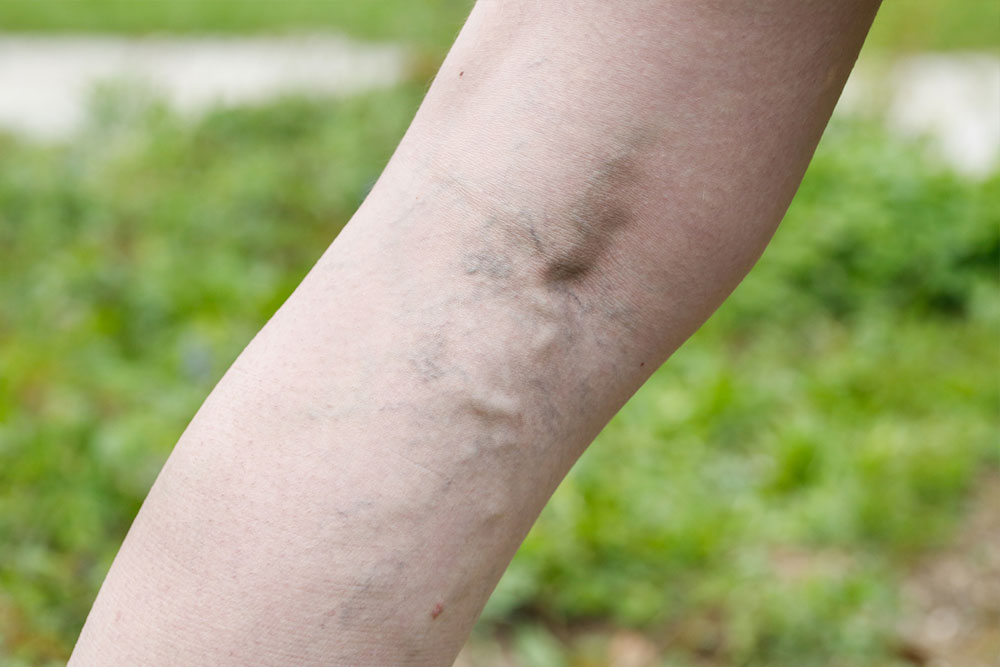
Comprehensive Guide to Varicose Veins: Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Treatment Options
Varicose veins present as enlarged, twisted, and often bulging veins that are typically visible on the surface of the skin, commonly appearing on the legs and sometimes on other parts of the body. While many individuals might not initially consider them a significant health concern, their presence can sometimes indicate underlying circulatory issues that require medical attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for effective management and preventing potential complications.
Varicose veins develop due to malfunctioning valves within the veins, which impair the normal flow of blood back to the heart. When these valves become weak or damaged, blood can pool in the veins, causing them to enlarge and become visible. This condition primarily affects adults, especially those with certain risk factors such as pregnancy, obesity, prolonged standing, or a family history of venous disease. Pregnant women are particularly susceptible because increased blood volume and hormonal changes can weaken vein walls and valves.
Understanding the Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Many individuals with varicose veins experience a range of symptoms, which can vary from mild to severe. Recognizing these symptoms is vital for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include:
Swollen, twisted, and lumpy veins that are often visible just under the skin’s surface
Persistent or intermittent aching, throbbing, or heaviness in the legs, especially after prolonged standing or physical activity
Swelling in the ankles and lower legs, often worsening towards the end of the day
Discoloration of the skin, usually a brownish hue near the affected veins
Venous eczema, which involves itchy, inflamed skin in the area surrounding the veins
Development of skin ulcers in severe cases, particularly near the ankles
Excessive bleeding from minor cuts or injuries over the affected veins
Additional Symptoms and Complications
In some cases, patients report symptoms such as leg cramps, restless legs syndrome, or skin thinning around affected areas. If untreated, varicose veins can lead to more serious health issues like venous ulcers, skin infections, and blood clots (deep vein thrombosis). Recognizing these symptoms early can significantly improve the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the risk of complications.
Diagnosing Varicose Veins
The diagnostic process begins with a thorough physical examination, where a healthcare professional will assess the appearance of the veins and ask about symptoms. The next step often involves ultrasound imaging, particularly Doppler ultrasound, which evaluates blood flow within the veins and detects any abnormalities such as blood clots or valve failures. This non-invasive test provides critical information needed to formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Varicose Veins
Treatment options for varicose veins depend on the severity of the condition, symptoms, and individual patient factors. The goal is to relieve symptoms, prevent progression, and minimize complications. A combination of lifestyle modifications and medical procedures provides the most comprehensive approach.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
For mild cases, simple lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference. These include maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the veins, engaging in regular leg exercises to promote circulation, elevating the legs when resting, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting. Wearing compression stockings can improve blood flow, decrease swelling, and provide relief from discomfort.
Medical Procedures and Interventions
When lifestyle modifications are insufficient, medical treatments are recommended. Several minimally invasive procedures are now commonplace, each offering effective relief with minimal recovery time:
Sclerotherapy: A solution is injected into the affected veins, causing them to collapse and fade over time.
Laser Therapy (Endovenous Laser Ablation): A laser fiber is inserted into the vein to heat and close it, rerouting blood flow through healthier veins.
Radiofrequency Ablation: Similar to laser therapy, this technique uses radiofrequency energy to close off problematic veins.
Vein Stripping and Phlebectomy: Surgical removal of large, twisted veins when other treatments are inadequate or unsuitable.
Additional Supportive Treatments
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to improve vein strength or address secondary symptoms. Post-treatment, patients are often advised to continue wearing compression stockings and to follow a healthy lifestyle to maintain long-term results.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you notice persistent pain, swelling, skin discoloration, or any signs of skin ulcers, consulting a healthcare professional promptly is crucial. Early intervention can prevent the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of complications such as ulcers, infections, or blood clots. A vascular specialist can recommend the most appropriate treatment tailored to your specific condition.
Preventive Measures and Long-term Care
Preventing varicose veins involves maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, avoiding prolonged periods of immobility, and wearing compression stockings if you are at risk. Regular check-ups and early treatment of symptoms can go a long way in managing this common vascular condition effectively.
In conclusion, varicose veins are a prevalent condition that can cause discomfort and potentially lead to more severe health issues if left untreated. With advances in medical technology and a focus on preventative care, managing this condition has become more straightforward and effective. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment can significantly improve quality of life and prevent complications.





