Comprehensive Guide to Mold Allergies: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores mold allergies, detailing their causes, common symptoms, and effective prevention strategies. Understanding mold's impact on health helps individuals take proactive steps to reduce exposure, manage symptoms, and maintain a healthier indoor environment. Learn how to identify mold sources, recognize allergy symptoms, and implement practical prevention methods to live comfortably and safely in mold-prone settings.
Comprehensive Guide to Mold Allergies: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
Mold allergies are a common yet often underrecognized health issue that can significantly impact an individual’s respiratory health and overall well-being. Mold is a type of fungi that thrives in damp and humid environments, both indoors and outdoors. These molds can grow on numerous surfaces, including wood, fabric, drywall, and even in less obvious places like behind wallpaper or under carpets. The microscopic spores they release into the air are a primary concern because, when inhaled, they can provoke allergic reactions, especially in sensitive individuals. Understanding the nuances of mold allergies, including their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, is essential for maintaining a healthy living environment and improving quality of life.
What Are Mold Allergies and How Do They Develop?
Mold allergies are hypersensitive immune responses to mold spores in the environment. Unlike some mold species that are useful or harmless in nature, certain molds produce spores that can trigger allergic reactions. The human immune system perceives these spores as threats and responds by releasing chemicals such as histamines, which lead to allergy symptoms.
Molds are ubiquitous, with over a thousand species identified across the United States alone. Among these, some species are visible to the naked eye, while many are microscopic. Molds reproduce rapidly in the presence of moisture, so damp areas in homes, workplaces, and outdoor environments serve as breeding grounds. People living in humid regions or with poor ventilation are at a higher risk of mold exposure and subsequent allergies.
Pathways of Exposure and Vulnerable Populations
The primary route of exposure to mold allergens is through inhalation of airborne spores. However, contact with mold-contaminated surfaces can also cause skin or eye reactions. Individuals with pre-existing allergies, asthma, respiratory conditions, or weakened immune systems are particularly vulnerable. Children, elderly individuals, and those living in damp or poorly maintained buildings are at an increased risk of developing symptoms and experiencing adverse health effects.
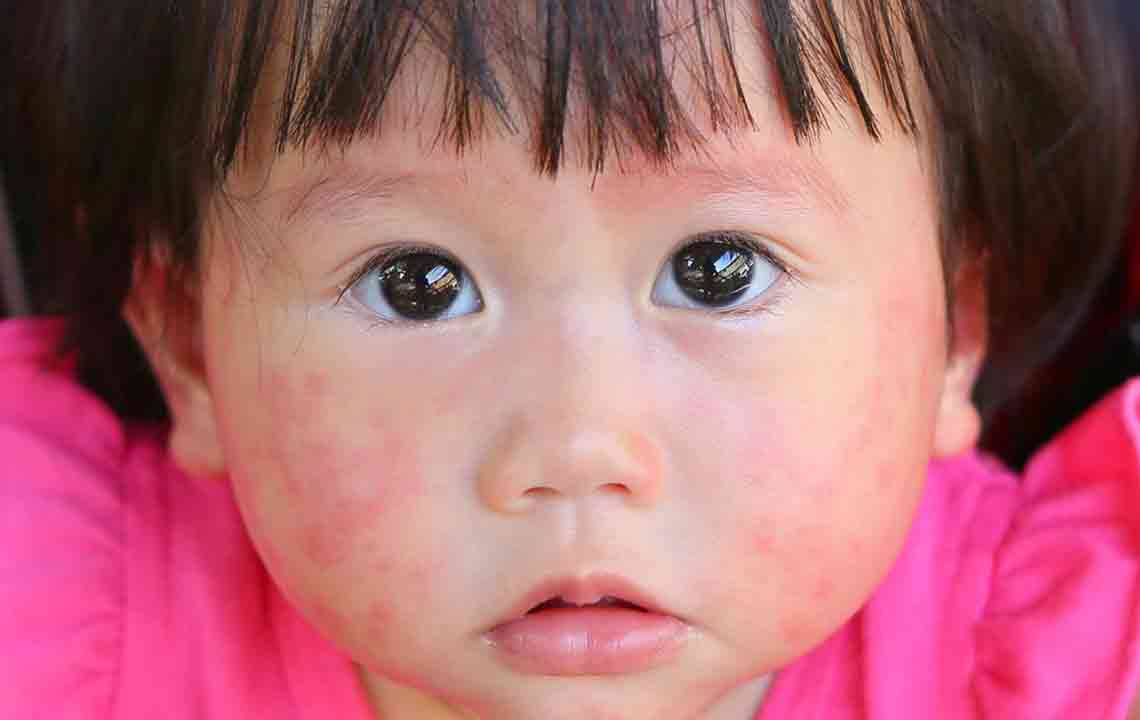
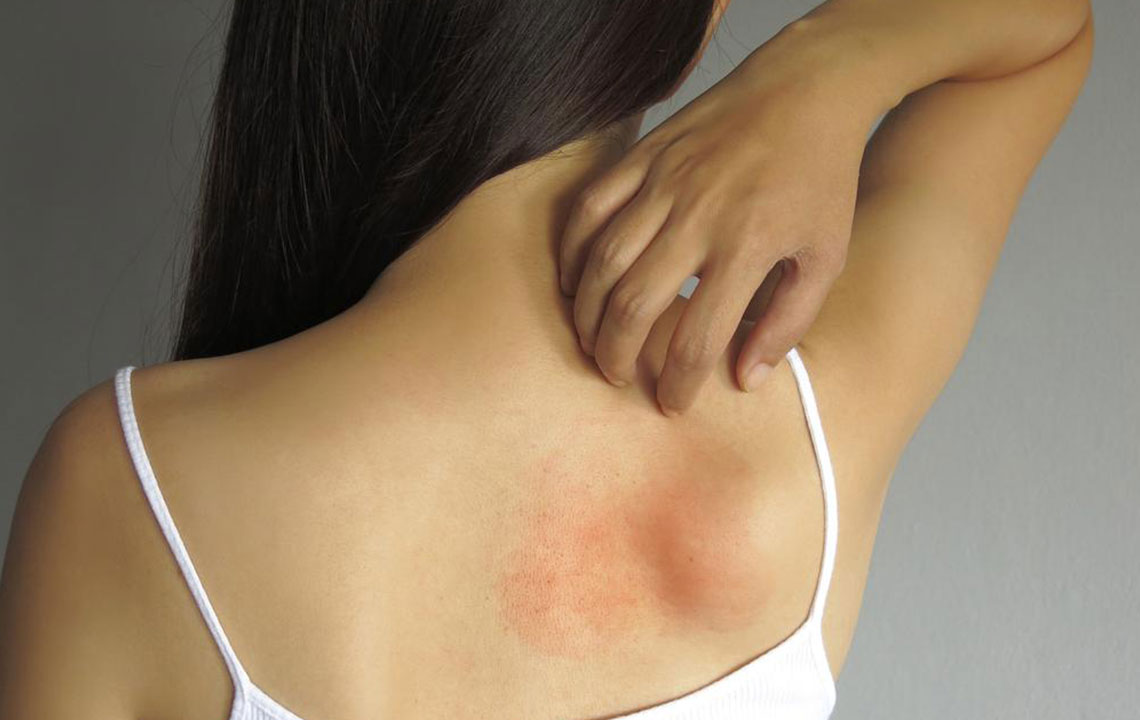
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Mold Allergies
Identifying mold allergy symptoms can be challenging because they often resemble those of other respiratory illnesses. Common signs include:
Nasal congestion, runny nose, or sinus pressure
Persistent sneezing and coughing
Itchy or watery eyes
Itchy throat or postnasal drip
Wheezing, chest tightness, or difficulty breathing
Eye irritation and redness
Skin rash or contact dermatitis in some cases
Some individuals may experience more severe reactions, such as shortness of breath or exacerbation of asthma symptoms, which require immediate medical attention. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely management and improve health outcomes.
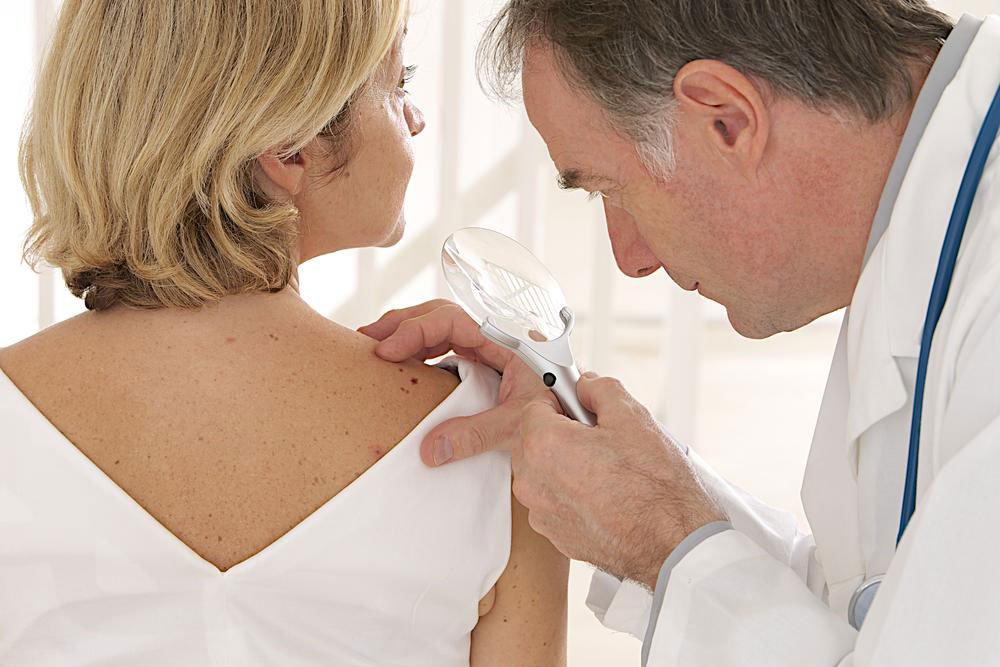
Diagnosing Mold Allergies
If you suspect a mold allergy, consulting an allergist is crucial for accurate diagnosis. The specialist may perform skin prick tests, blood tests, or both to detect specific IgE antibodies to mold spores. These tests help differentiate mold allergies from other respiratory conditions like allergies to pollen or dust mites. Proper diagnosis ensures targeted treatment and effective management strategies.
Managing and Treating Mold Allergies
Once diagnosed, the primary goal is to minimize exposure to mold spores and alleviate symptoms. Medications such as antihistamines, decongestants, or nasal corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce allergic responses. In some cases, allergy immunotherapy (allergy shots) might offer long-term relief by gradually desensitizing the immune system.
In addition to medication, practical steps include wearing masks during mold-prone activities, maintaining good ventilation, and keeping indoor humidity levels below 50%. Regular cleaning with HEPA filters, removing mold-contaminated materials, and avoiding known mold-prone areas can significantly improve comfort and health.
Prevention Strategies to Reduce Mold Exposure
Preventing mold growth is the cornerstone of managing mold allergies. Effective preventative measures include:
Promptly repairing leaks, roof damages, or plumbing issues to prevent moisture accumulation.
Using exhaust fans in moisture-prone areas such as kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms.
Employing dehumidifiers to maintain indoor humidity below 50%, making the environment less hospitable for mold.
Ensuring proper ventilation by opening windows and doors when weather permits to promote air circulation.
Regularly cleaning and disinfecting areas prone to mold, such as bathroom tiles, shower curtains, and air conditioning units.
Cleaning or replacing items that collect moisture, including carpets, curtains, and upholstery.
Controlling outdoor sources of mold, like fallen leaves or compost piles, near residential areas.
Maintaining these practices consistently can substantially reduce mold exposure, thereby decreasing allergy symptoms and promoting a healthier indoor environment.Conclusion: Living Well with Mold Allergies
Understanding mold allergies, their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures is pivotal for anyone living in environments prone to mold growth. Proactive management through cleanliness, moisture control, and medical consultation can lead to a significant reduction in health risks and improve quality of life. For sensitive individuals, awareness and prompt action are vital in minimizing the impact of mold exposure. With proper strategies and cooperation, individuals can enjoy a healthier, mold-free living space and reduce the frequency and severity of allergy symptoms.