Comprehensive Guide to Mold Allergies: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Prevention Methods
Mold allergies pose health risks, especially in damp environments. This comprehensive guide explains the causes, symptoms, and effective prevention strategies to help you create a healthier indoor environment. Learn how to identify mold-prone areas, implement control measures, and manage allergic reactions with proper medical advice. Understanding these essential aspects can significantly improve your respiratory health and overall well-being.

Understanding Mold Allergies: Causes, Common Symptoms, and How to Prevent Them
Molds are a widespread group of fungi that exist in diverse environments, especially thriving in areas that are damp, dark, and warm. These microscopic organisms play vital roles in nature, aiding in the decomposition of organic matter. However, when molds grow indoors, they pose significant health risks, particularly in the form of allergies. Mold spores are released into the air when mold colonies are disturbed, which often occurs during cleaning, renovation, or changes in environmental conditions. Understanding where mold grows, how it affects health, and effective prevention strategies are crucial for maintaining a healthy living environment.
Mold growth is most prevalent in areas with high humidity, poor ventilation, or water damage. Common indoor locations include basements, bathrooms, behind wallpaper, around windows, kitchen areas, and even in HVAC systems. Outdoors, mold spores can be found near water bodies, decaying vegetation, or compost heaps. Events like flooding, leaks, or high humidity levels significantly promote mold proliferation. When inhaled, mold spores can trigger allergic reactions, especially in individuals with heightened sensitivity or underlying respiratory conditions such as asthma, sinusitis, or allergic rhinitis.
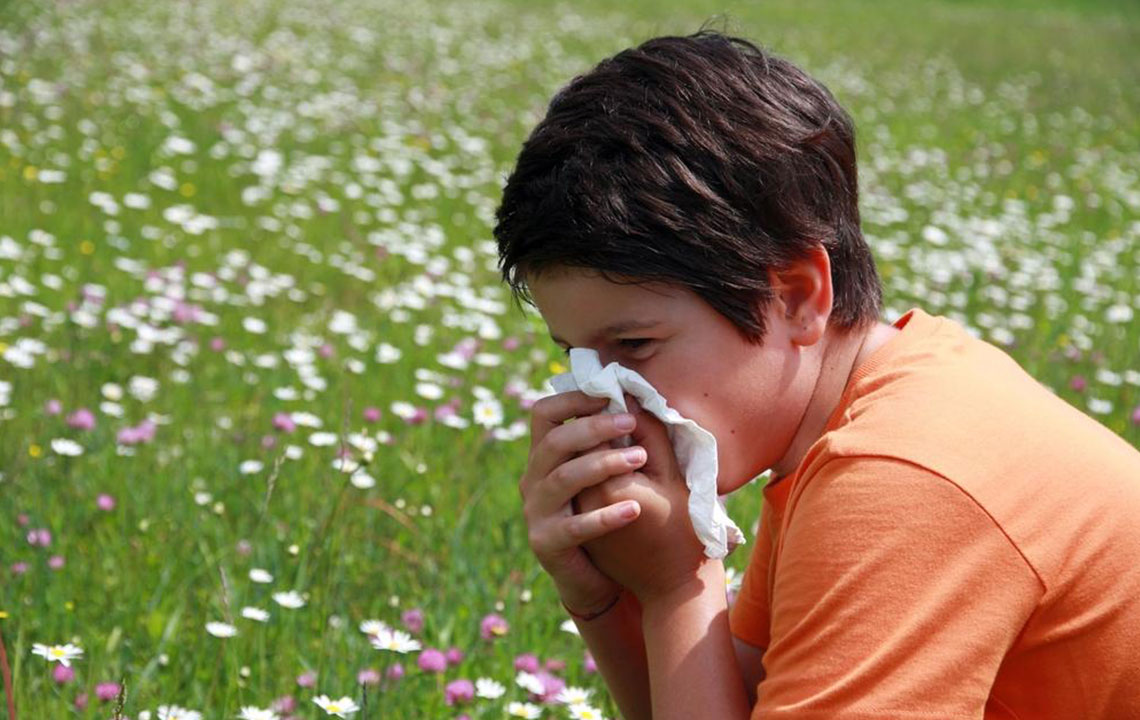
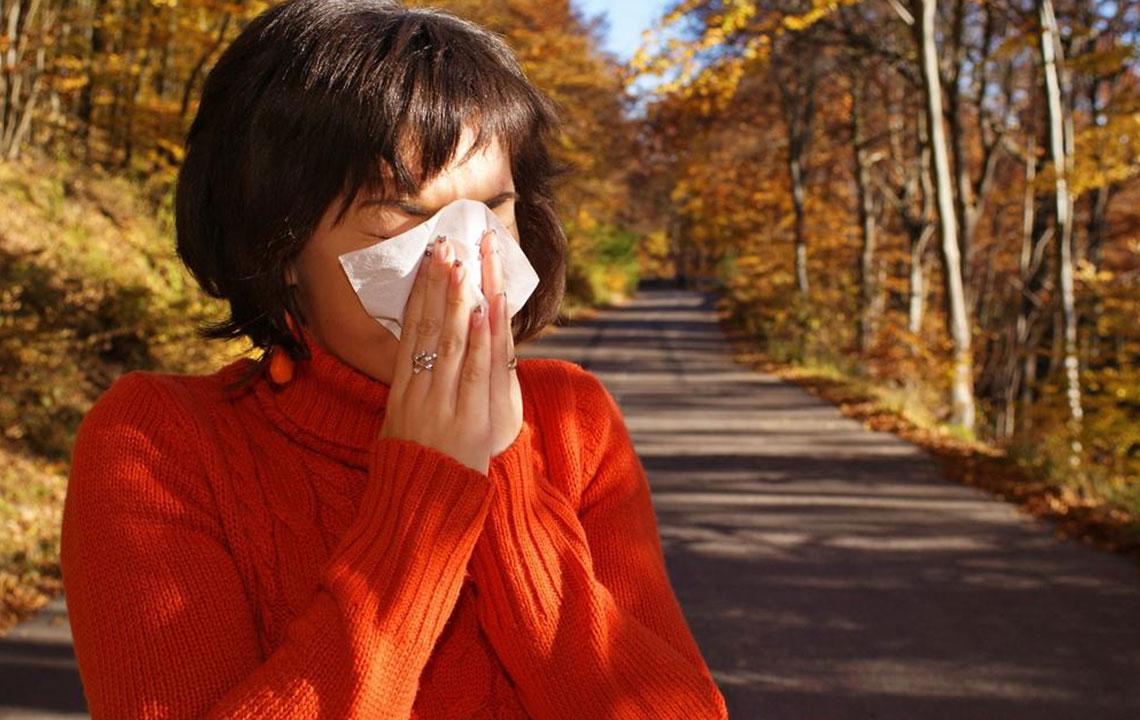
For many, mold presence is more than just an unsightly nuisance; it can lead to severe allergic responses. The immune system perceives mold spores as harmful invaders and reacts accordingly. This overreaction results in various symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, impacting daily life and overall health. It’s important to be able to recognize the signs of mold allergies and implement effective control measures. Addressing mold issues promptly and efficiently can significantly reduce health risks and improve indoor air quality.
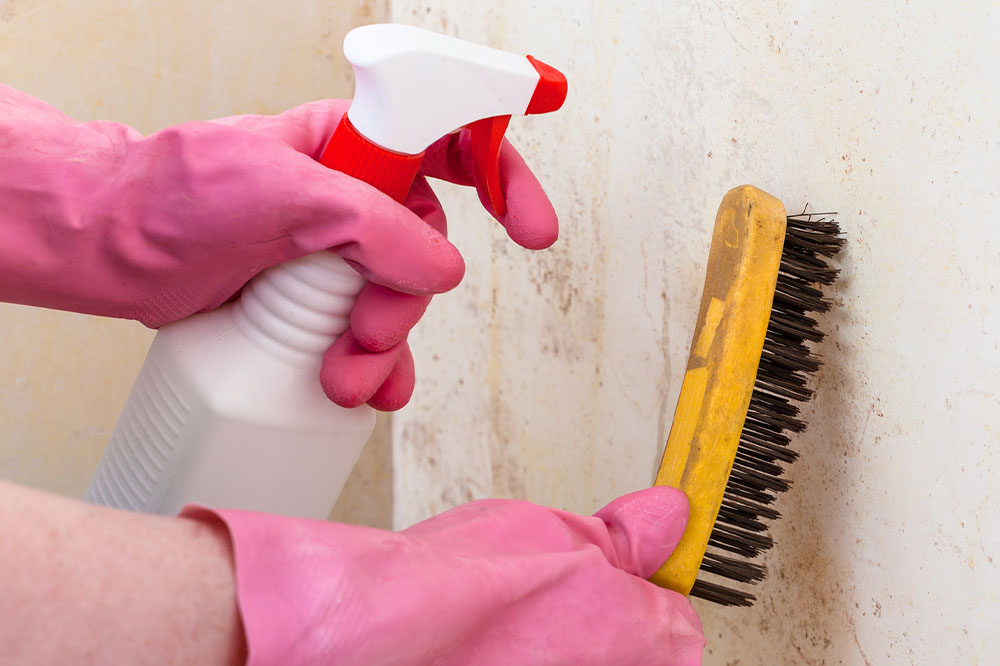
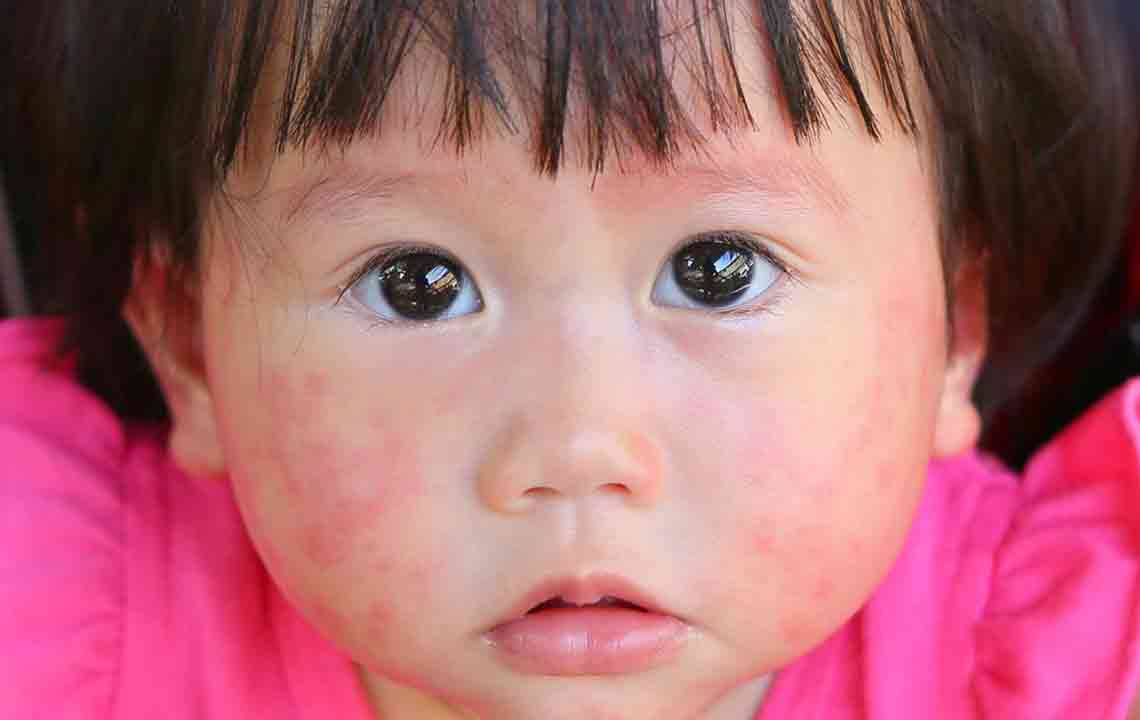
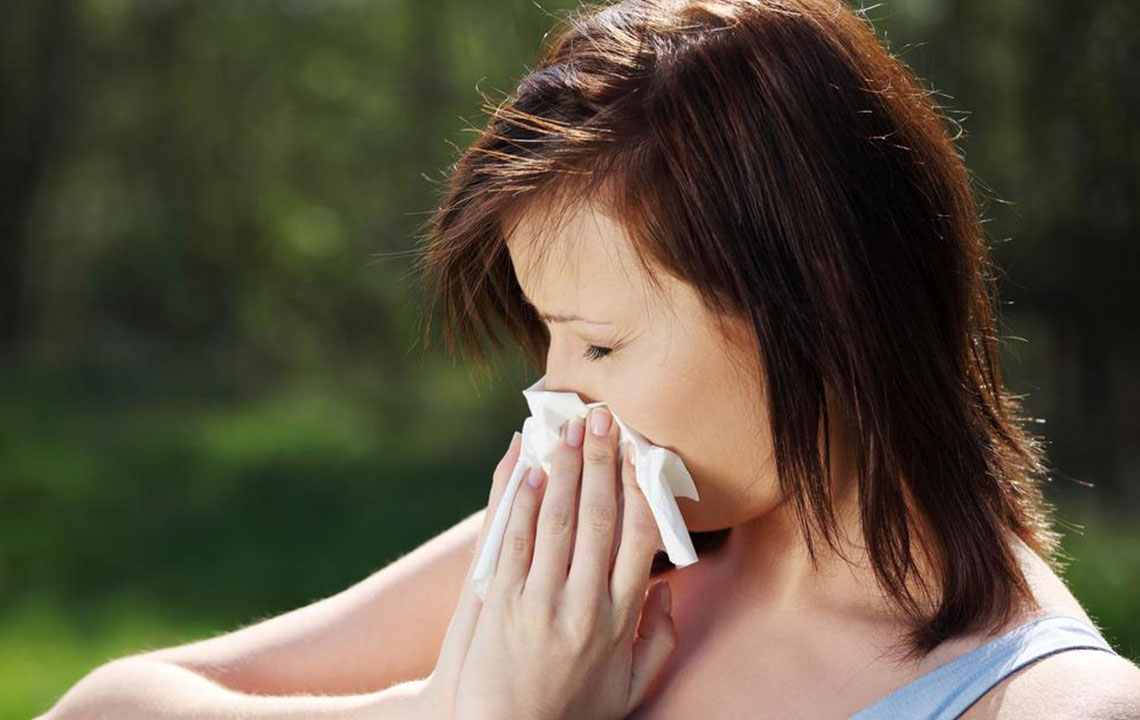
Common symptoms of mold allergies include persistent nasal congestion, sneezing, coughing, itchy or watery eyes, skin rashes, and in some cases, difficulty breathing. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma, are at greater risk of experiencing more intense symptoms or exacerbations. Prevention involves identifying potential mold hotspots within your living space, maintaining optimal humidity levels, and ensuring proper ventilation. Using dehumidifiers, fixing leaks, and routine cleaning with protective gear are practical steps to limit mold growth. Eliminating mold from indoor environments may require professional remediation in severe cases.
When it comes to managing symptoms, medications such as antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal corticosteroids are prescribed by healthcare providers. For persistent or severe cases, allergy immunotherapy (allergy shots) can help desensitize individuals to mold allergens over time. It is essential to consult healthcare professionals before starting any treatment to ensure safety and appropriateness. Maintaining indoor humidity levels between 30-50%, ensuring good airflow, and regular cleaning are fundamental practices to prevent mold proliferation. By understanding mold’s sources and recognizing allergy symptoms early, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce exposure and enhance their quality of life.