Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Pollen Allergies and Reducing Symptoms
Discover comprehensive and effective strategies to prevent pollen allergies. This detailed guide covers symptom identification, medical treatment, outdoor activity adjustments, protective gear usage, indoor air quality management, and dietary considerations. Implement these proven tips to reduce allergy symptoms, improve respiratory health, and enjoy seasonal changes comfortably.

Comprehensive Strategies to Prevent Pollen Allergies and Manage Symptoms Effectively
Pollen allergies, also known as hay fever or allergic rhinitis, are a common respiratory condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. These allergies are primarily triggered by exposure to airborne pollen released by trees, grasses, and weeds during peak seasons. While pollen allergies are usually harmless, they can significantly diminish quality of life due to persistent symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, nasal congestion, and fatigue. Fortunately, adopting effective prevention strategies can greatly minimize exposure and alleviate symptoms. This extensive guide offers scientifically backed methods to help you combat pollen allergies, safeguard your health, and enjoy the changing seasons without discomfort.
Understanding Pollen Allergies: Causes and Symptoms
Before diving into prevention techniques, it’s crucial to understand what causes pollen allergies and how to identify symptoms accurately. Pollen allergies occur when your immune system overreacts to pollen particles inhaled into the respiratory system. Factors contributing to heightened pollen exposure include environmental conditions like humidity, wind speed, and temperature fluctuations, which influence pollen dispersal in the air. Personal hygiene habits, such as infrequent cleaning or inadequate indoor air management, also play a role in aggravating allergy symptoms.
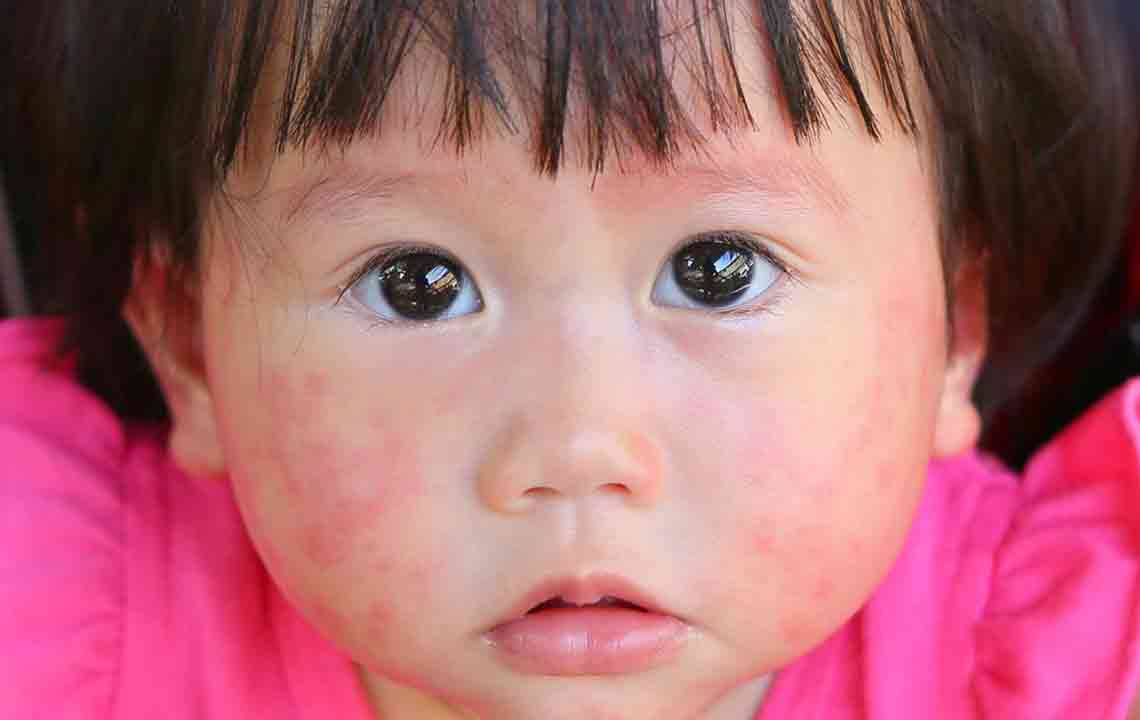
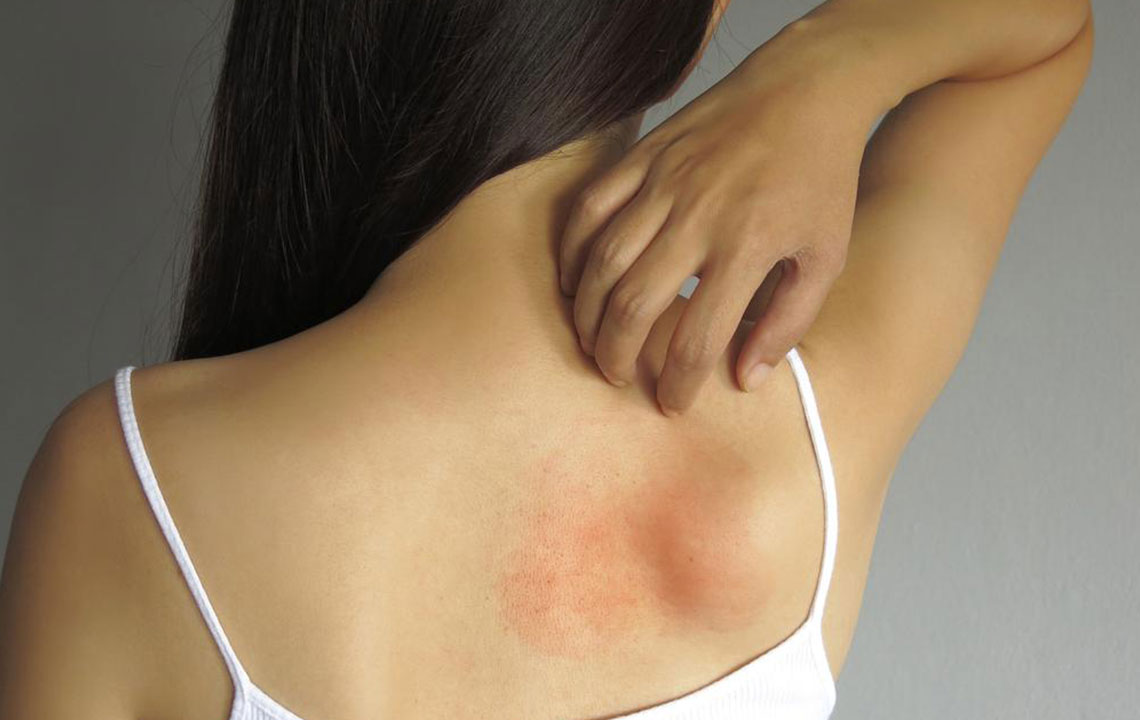
Common symptoms of pollen allergy include:
Sneezing episodes, often in rapid succession
Runny or congested nose
Itchy and watery eyes
Sore throat and cough
Fatigue and irritability due to disrupted sleep
It’s vital to distinguish pollen allergies from other respiratory illnesses like the flu or common cold. Allergies typically do not involve fever and are directly correlated with outdoor pollen levels or seasonal changes.
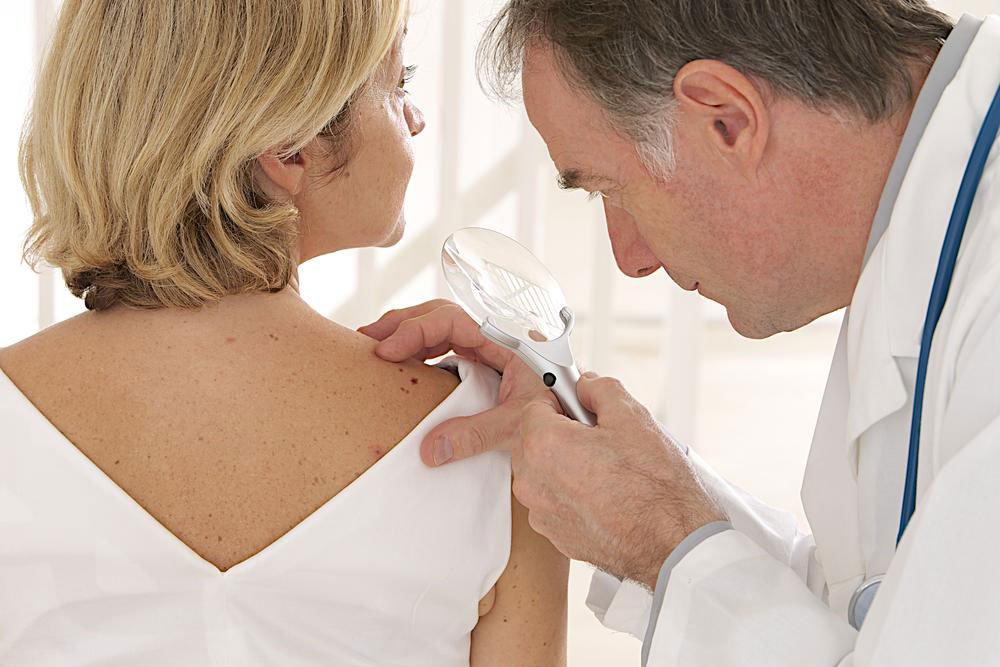
Seek Professional Medical Advice for Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment
If you experience persistent allergy symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Proper diagnosis often involves allergy testing to identify specific pollen types causing your symptoms. Without accurate identification, it’s challenging to implement targeted prevention and treatment plans.
There are various over-the-counter medications such as antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal corticosteroids that can provide relief. When symptoms are severe or do not respond to initial treatments, allergists may recommend immunotherapy, which involves controlled exposure to allergens to build tolerance over time. Early consultation ensures you receive personalized advice suited to your allergy profile, improving quality of life and reducing reliance on medication.
Adjust Your Outdoor Activities According to Pollen Levels
One of the most effective ways to prevent pollen allergy symptoms is to modify your outdoor routines based on pollen forecasts. Pollen counts are usually highest during early mornings and midday hours when the sun is at its peak, and pollen dispersal is at its strongest. If you are sensitive to pollen, scheduling outdoor activities during late evenings or after rainfalls can significantly reduce exposure. Rainfall helps to wash pollen particles out of the air, temporarily lowering pollen levels.
Furthermore, staying indoors during peak pollen times can make a substantial difference. Many weather apps and local news stations provide daily pollen forecasts—use these to plan your outdoor activities optimally. When unavoidable outdoor exposure is necessary, take proactive steps such as wearing protective gear and limiting the duration of outdoor workouts.
Using Protective Gear to Reduce Contact with Pollen
Protective gear acts as a physical barrier against airborne pollen, especially during outdoor activities like gardening, hiking, or walking in dusty or grassy areas. Essential protective items include:
Face masks, preferably N95 or higher-grade masks, which filter out pollen particles effectively
Sunglasses to shield your eyes from airborne allergens
Wide-brimmed hats to prevent pollen from settling on your hair and face
Gloves when handling flowers or working with soil to avoid pollen contact through skin
When you return indoors, remove your protective gear carefully to prevent pollen transfer inside. Regularly washing these items minimizes allergen buildup, maintaining a healthier environment both indoors and outdoors.
Maintain Indoor Air Quality for Long-Term Relief
Indoor environments should be optimized to reduce pollen exposure, especially during high pollen seasons. Strategies include:
Keeping windows and doors closed on days with high pollen counts to prevent pollen ingress
Using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters in air purifiers to trap airborne allergens
Regularly cleaning and replacing air conditioning and ventilation system filters
Vacuuming carpets and upholstery frequently with HEPA filters to remove settled pollen particles
Washing bedding and curtains regularly to eliminate accumulated pollen and other allergens
Creating a pollen-free indoor zone significantly reduces allergy flare-ups and supports overall respiratory health.
Monitor Your Diet to Prevent Food-Pollen Interactions
Some foods can trigger or worsen allergy symptoms due to cross-reactivity with pollen proteins, a condition known as oral allergy syndrome (OAS). Common foods associated with pollen allergies include certain fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
For example, individuals sensitive to birch pollen might experience reactions to apples or carrots. Consulting with an allergist or dietitian can help identify potential food triggers. Avoiding these foods during peak pollen seasons can prevent additional discomfort. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods—like omega-3 fatty acids, berries, and leafy greens—may also bolster immune function and reduce allergy severity.
Additional Tips for Comprehensive Pollen Allergy Prevention
Beyond the core strategies, several lifestyle adjustments and environmental modifications can enhance your allergy protection:
Stay hydrated to keep mucous membranes moist, aiding in the clearing of allergens from your respiratory tract
Avoid outdoor activities during windy days, as winds facilitate pollen dispersal over large areas
Maintain a clean indoor environment and reduce dust accumulation to minimize overall allergic triggers
Consider natural remedies like saline nasal sprays or herbal supplements after consulting with healthcare providers
Implement seasonal cleaning routines to remove pollen buildup from blinds, carpets, and surfaces
Conclusion: Take Proactive Steps for a Pollen-Free Life
While pollen allergies are a common seasonal nuisance, proactive measures can substantially reduce their impact on your daily life. By understanding your allergy triggers, seeking appropriate medical advice, adjusting outdoor activities, utilizing protective gear, maintaining indoor air quality, and managing diet, you can enjoy the changing seasons with minimal discomfort. Consistent application of these strategies not only alleviates symptoms but also enhances overall respiratory health. Remember, staying informed about pollen forecasts and implementing tailored prevention techniques empower you to live a healthier, allergy-free life regardless of the season.