Comprehensive Guide to Managing Skin Rashes: Causes, Types, and Effective Treatments
This comprehensive guide offers in-depth information on skin rashes, covering their causes, symptoms, classifications, and effective treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of proper diagnosis, home remedies, and when to visit a healthcare professional for persistent or severe cases. Perfect for those seeking reliable skin health advice, especially parents caring for infants, and anyone interested in understanding skin rash management thoroughly.

All You Need to Know About Skin Rashes
Understanding Skin Rashes and Their Impact
Skin is the body's largest organ, serving as a vital protective barrier against environmental threats such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and harmful chemicals. Its health and integrity are crucial for overall well-being. When skin becomes inflamed or irritated, it manifests as rashes—a common condition affecting people of all ages, especially vulnerable populations like infants and the elderly. Recognizing the signs, understanding the causes, and knowing how to manage skin rashes are essential steps toward maintaining healthy skin.
In infants, the skin is still developing, making it particularly fragile and more susceptible to irritations and infections. Factors such as diapering, environmental exposures, allergic reactions, or underlying health conditions can trigger skin rashes in babies. Proper skincare routines and timely medical consultation can prevent complications and promote faster healing.
Signs and Symptoms of Skin Rashes
Skin rashes can present in numerous ways, depending on their cause and severity. Common symptoms include:
Redness or erythema—an indicator of inflammation
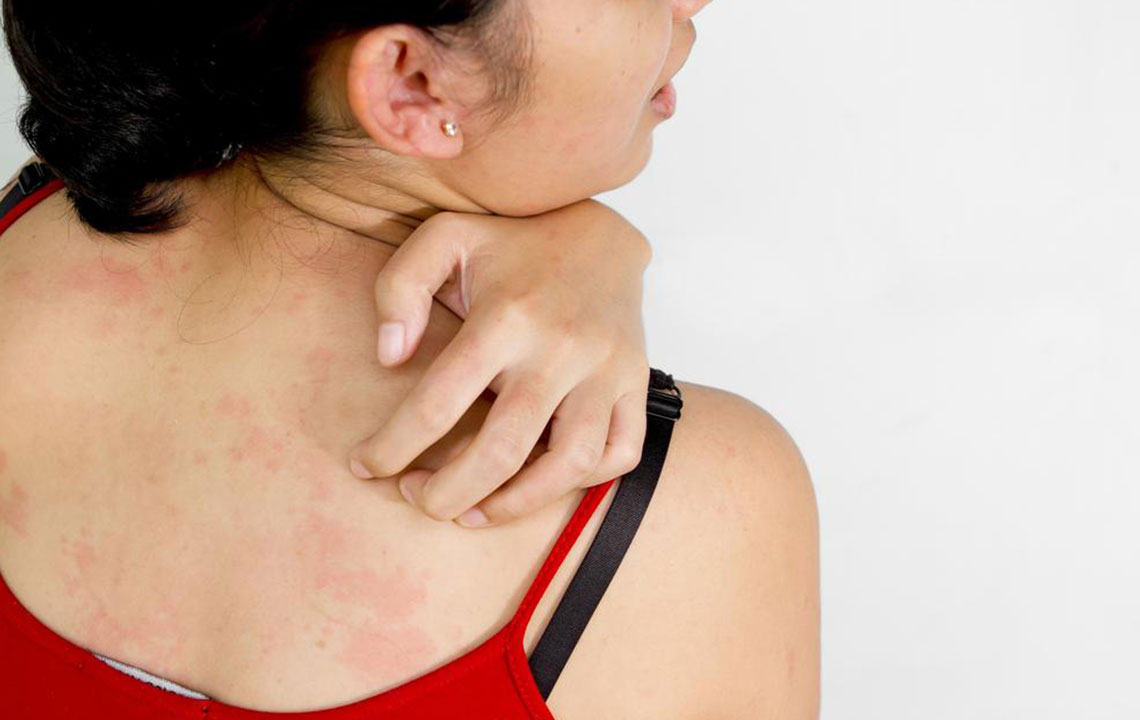
Itching—often leading to scratching and potential secondary infections
Raised bumps filled with pus—signaling bacterial infections
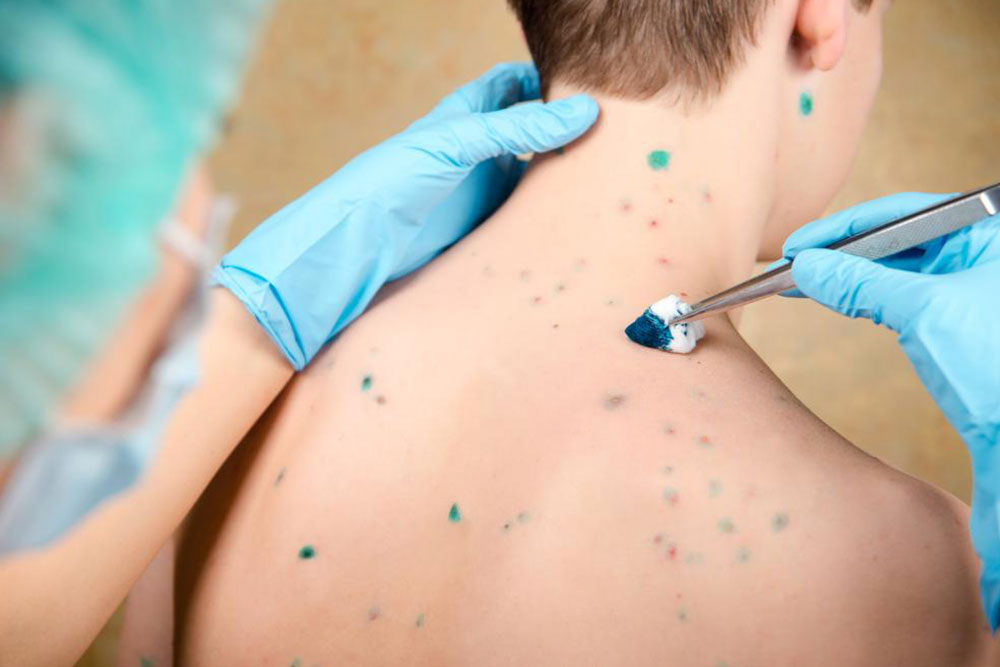
Blisters and fluid-filled sacs—common with viral infections like chickenpox
Dry, scaly patches or flaky skin—associated with eczema or psoriasis
Some rashes may appear in specific patterns, such as ring-shaped lesions or linear streaks, which can aid healthcare providers in diagnosis. Persistent or worsening symptoms should prompt consultation with a dermatologist to avoid complications and ensure appropriate treatment.
Classification of Skin Rashes: Types and Causes
Understanding the different types of skin rashes is vital for effective management. Rashes are generally categorized into infectious and non-infectious types, each with distinct causes and characteristics.
Noninfectious Rashes
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): A chronic, inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy patches. Often triggered by allergens, irritants, or genetic predisposition.
Psoriasis: An autoimmune disorder leading to the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in thick, scaly plaques.
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affects oily areas like the scalp and face, causing flaky, yellowish scales.
Drug Reactions: Allergic responses to medications can cause widespread rashes, including rosacea and contact dermatitis.
Dry Skin (Xerosis): Characterized by rough, flaky skin, often worsened by cold weather or harsh soaps.
Allergic Dermatitis: Skin reacts to allergens such as certain foods, insect bites, or contact with plants like poison ivy.
Infectious Rashes
Ringworm: A fungal infection presenting as ring-shaped, scaly patches.
Impetigo: A bacterial skin infection causing honey-colored crusting lesions.
Herpes Viruses (Chickenpox, Shingles): Viral infections characterized by grouped vesicles and pain.
Other Pathogens: Parasites and fungi can also cause rashes, transmitting through direct contact or contaminated surfaces.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation of Skin Rashes
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare professionals, especially dermatologists, utilize a combination of visual examination and patient history analysis to identify the rash type and underlying causes.
Visual Inspection: Recognizing the pattern, location, and morphology of rashes—such as linear, circular, or diffuse lesions—helps narrow down possibilities.
Symptom Assessment: Noting associated symptoms like blistering, ulceration, peeling, or swelling guides diagnostic considerations.
Laboratory Tests: When necessary, skin scrapings, blood tests, or cultures are performed to detect infectious agents or allergies.
Imaging and Biopsy: In complex cases, skin biopsy helps confirm diagnoses like psoriasis or more severe infections.
Always seek professional medical advice for persistent rashes or those accompanied by fever, pain, or other systemic symptoms.Effective Home Remedies and Treatments for Skin Rashes
Many skin rashes can be managed with simple home remedies and over-the-counter medications. However, consulting a healthcare provider is always recommended before starting any treatment, especially in infants or persistent cases.
Vinegar Compress: Diluted white vinegar (one teaspoon in eight teaspoons of water) can help soothe irritation by balancing skin pH levels. Apply gently with a soft cloth to reduce redness and itching, especially in diaper rash or fungal infections.
Corticosteroid Creams: Over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams are effective in reducing inflammation and alleviating itching. Use as directed, and consult a doctor if symptoms persist or worsen.
Antifungal Medications: Clotrimazole or miconazole creams are commonly prescribed for fungal rashes like athlete's foot, ringworm, or yeast infections.
Skin Barrier Protectants: Petroleum jelly creates a protective layer that prevents irritants from aggravating the rash and helps maintain moisture during healing.
Antihistamines: Medications like loratadine or cetirizine can relieve allergic reactions, but should only be used under medical supervision to avoid adverse effects.
In addition to topical treatments, maintaining good hygiene, avoiding known allergens, and keeping affected areas dry and clean can significantly promote healing and prevent recurrence.
While many minor rashes resolve with home care, it’s crucial to monitor the condition and seek medical advice for persistent, recurring, or worsening symptoms to prevent complications and long-term skin damage.