Comprehensive Guide to Normal Blood Glucose Levels and Their Vital Role in Health
This comprehensive guide explores normal blood glucose levels and emphasizes their importance in health management. It provides detailed information on blood sugar ranges for different groups, highlights the rising prevalence of diabetes, and offers practical tips for maintaining optimal blood sugar through lifestyle modifications. Understanding these aspects can help individuals prevent severe health complications and enhance overall well-being by staying proactive about blood glucose monitoring and control.

An In-Depth Look at Normal Blood Glucose Levels and Why They Matter
In our daily lives, indulging in sweet treats and sugary snacks might be a common pleasure, but understanding how these habits influence your health is crucial. Excessive intake of sugars, especially from processed foods and snacks, can lead to complications such as elevated blood glucose levels. Monitoring blood sugar is a vital aspect of maintaining overall health, especially as lifestyle changes and dietary habits evolve. Maintaining blood glucose within a healthy range can prevent the onset of chronic illnesses like diabetes, which has become increasingly prevalent worldwide.
The global rise of diabetes is a significant health concern. According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 100 million Americans are dealing with either diabetes or prediabetes. Approximately 30 million individuals, representing about 9.4% of the U.S. population, live with diagnosed diabetes. An additional 84 million are classified as prediabetic, which escalates their risk of developing full-blown diabetes in the next five years if preventive measures aren’t taken. These numbers underscore the importance of regular blood glucose monitoring as a key strategy for early diagnosis and effective management. Understanding what constitutes normal blood glucose levels is essential for both individuals and healthcare providers to identify abnormal patterns that require intervention.
Ignoring blood sugar regulation can result in serious health complications. For example, sustained high blood glucose levels can cause nerve damage, kidney disease, heart problems, and vision loss. Thus, knowing the normal ranges for blood glucose, depending on age, health status, and the presence of diabetes, is vital for maintaining good health. Regular testing helps in catching abnormalities early, allowing timely lifestyle adjustments or medical treatment. Recognizing the standard blood glucose ranges for different groups—non-diabetics, Type 1, and Type 2 diabetics—empowers individuals to take control of their health and avoid potentially life-threatening consequences.
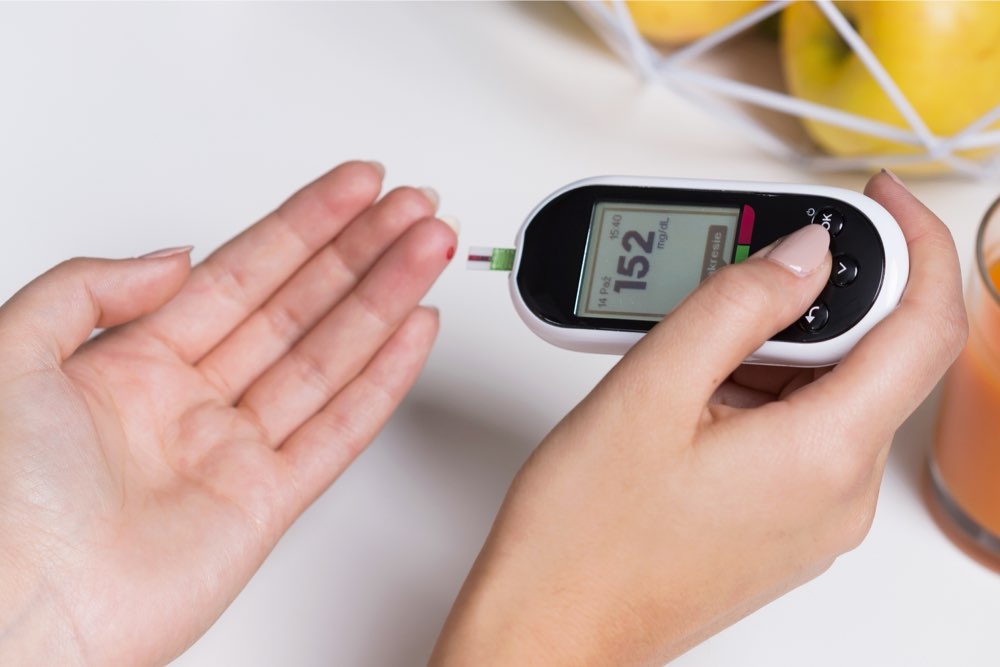
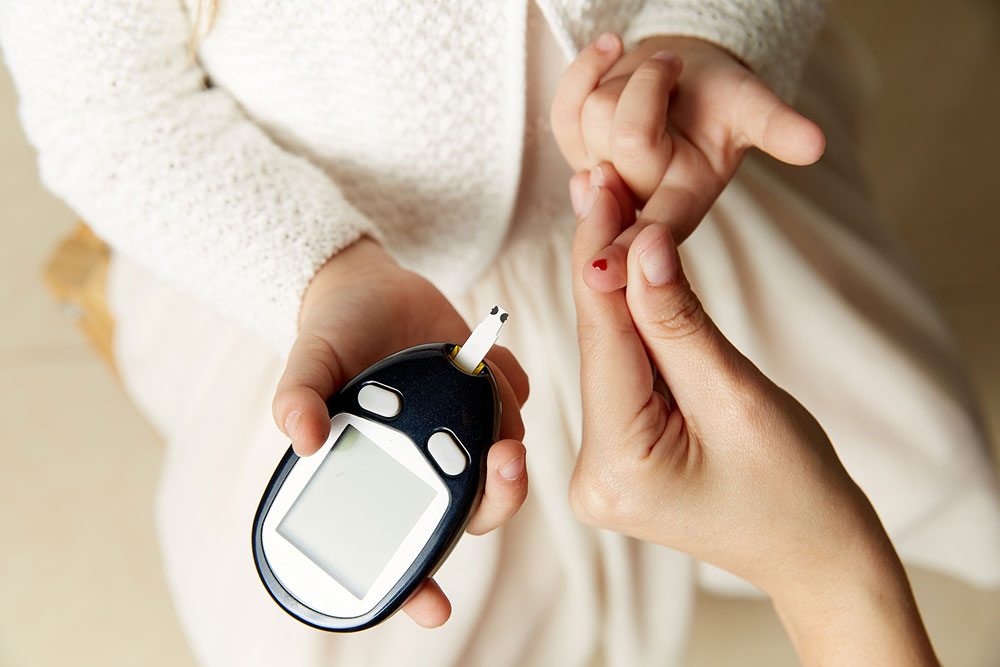
For individuals without diabetes, fasting blood glucose should range from 4.0 to 5.9 mmol/L, and levels may rise slightly to about 7.8 mmol/L after meals. Those with Type 2 diabetes should aim to keep fasting blood sugar between 4 and 7 mmol/L, with post-meal readings staying below 8.5 mmol/L. For people with Type 1 diabetes, maintaining fasting levels between 5 to 7 mmol/L and post-meal levels between 5 to 9 mmol/L is recommended. Consistent self-monitoring allows for better control and helps prevent complications such as hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. If blood sugar readings fall outside these ranges, consulting a healthcare provider is essential to adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Achieving and maintaining balanced blood glucose levels is fundamental to overall health. Poor management can lead to severe complications, including cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision problems. Adopting a balanced diet rich in fiber, low in refined sugars, and engaging in regular physical activity can significantly improve glucose regulation. Small lifestyle modifications—such as eating smaller portion sizes, avoiding sugary drinks, and increasing physical activity—can make a big difference. Regular check-ups and early intervention are critical to preventing the progression from prediabetes to diabetes, ultimately safeguarding long-term health and quality of life.