Comprehensive Guide to Rosacea: Types, Causes, and Effective Treatment Options
Discover an in-depth guide to rosacea, including its four primary types, causes, and effective treatment options. Learn how lifestyle modifications, medical therapies, and trigger avoidance can significantly improve skin health and quality of life. This comprehensive article offers insights into managing this chronic skin condition for lasting results.
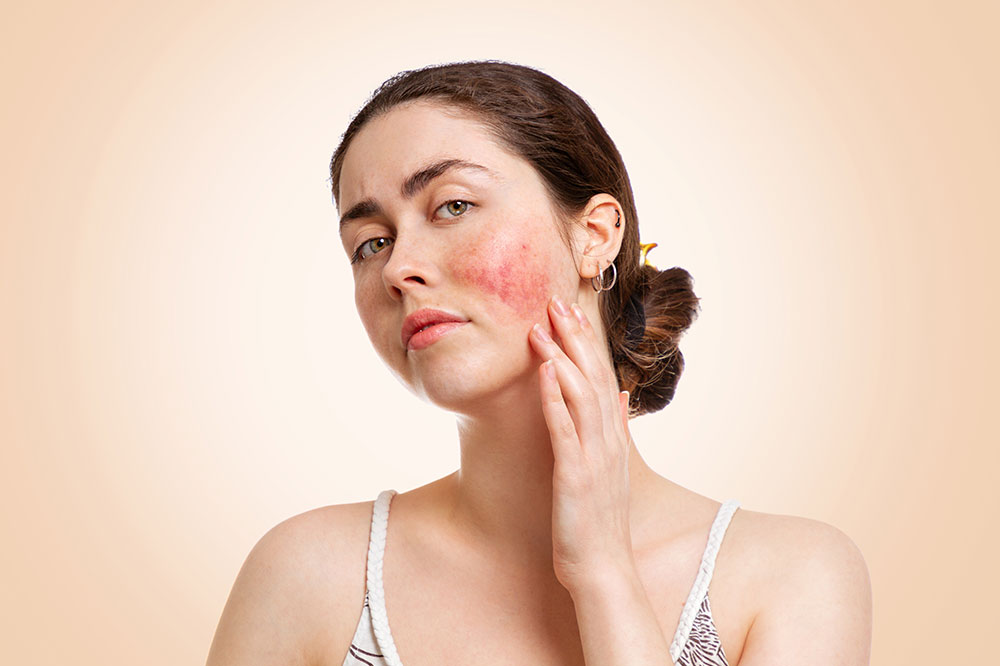

Comprehensive Guide to Rosacea: Types, Causes, and Effective Treatment Options
Rosacea is a chronic dermatological condition that affects millions worldwide, with estimates suggesting over 16 million people living with this skin disorder. Predominantly observed in middle-aged women, rosacea often presents as a frustrating and sometimes embarrassing skin issue that, while not life-threatening, can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. The condition typically influences areas such as the nose, cheeks, and forehead, manifesting as small, red bumps that may contain pus. These symptoms tend to flare periodically, entering active phases followed by remission, which makes managing rosacea particularly challenging.
Understanding the Types and Causes of Rosacea
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, rosacea is classified into four primary types based on clinical presentation, each requiring different management strategies. Recognizing these types is essential for effective treatment and lifestyle adjustments that can mitigate symptoms and improve overall skin health.
Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): This most common form involves persistent facial redness, flushing episodes, and visibly dilated blood vessels (telangiectasias). Individuals may experience heightened skin sensitivity, swelling, dryness, and rough patches, which can be triggered or exacerbated by environmental factors and lifestyle choices.
Papulopustular Rosacea: Often mistaken for acne, this type is characterized by redness, swelling, and the presence of acne-like lesions. Oily and sensitive skin, broken blood vessels, and inflammation frequently accompany this form, leading to discomfort and cosmetic concerns.
Phyma Rosacea: A relatively rare but serious form that primarily affects men, causing skin thickening, bumpy texture, and large pores, especially on the nose, cheeks, chin, and forehead. Over time, this can result in a bulbous appearance, with skin hypertrophy affecting facial contours. It can also cause thickening in other facial areas and prominent pore formation.
Ocular Rosacea: Focusing on the eyes, this subtype manifests as redness, dryness, itching, watery eyes, and burning sensations. It may also lead to vision problems, cyst formation, and visible broken blood vessels around the eyelids, significantly impacting eye health and daily comfort.
While the exact etiology of rosacea remains unclear, research indicates that a combination of genetic predisposition, abnormalities in facial blood vessels, and fair skin type are common contributing factors. Additionally, various triggers can worsen symptoms, making disease management complex. Common environmental and lifestyle triggers include extreme weather conditions, strenuous physical activities, emotional stress, alcohol consumption, spicy foods, and hot beverages. Recognizing and avoiding these triggers is a fundamental step in controlling flare-ups.
Effective management of rosacea involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical treatments. Topical medications, such as metronidazole and azelaic acid, are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and redness. Oral antibiotics, including doxycycline and tetracycline, may be used in more severe cases to control inflammation and bacterial involvement. Laser therapy, particularly vascular laser treatments, effectively targets visible blood vessels (telangiectasias), thereby decreasing redness and improving skin appearance. Additionally, gentle skin care routines that avoid irritants like alcohol, menthol, and fragrances are crucial. Using broad-spectrum sunscreens and avoiding excessive sun exposure can also decrease flare episodes.
Monitoring diet plays a vital role; individuals are encouraged to track their food and beverage intake to identify personal triggers. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and plenty of water can support skin health. Stress management techniques, including mindfulness, yoga, or relaxation exercises, can further reduce flare-ups. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans developed with a dermatologist can significantly enhance quality of life for those suffering from rosacea. With consistent care and awareness, many patients experience improved skin condition and reduced symptom severity, leading to better self-esteem and confidence.
In conclusion, rosacea is a multifaceted condition requiring a comprehensive approach for effective management. By understanding the different types, recognizing individual triggers, adopting proper skincare routines, and seeking medical advice, individuals can effectively control symptoms and prevent disease progression. Staying informed and proactive can help maintain healthier, clearer skin and enhance overall well-being.