Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Rosacea Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing and treating rosacea, a common skin condition. It covers symptoms, causes, risk factors, and a variety of treatment options such as topical medications, laser therapy, and lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis and personalized management are key for controlling symptoms and improving skin health. Learn how modern treatments can help reduce redness, visible blood vessels, and skin thickening, enabling patients to regain confidence and achieve better quality of life. Ideal for those seeking expert advice on rosacea management.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Rosacea Effectively
Rosacea is a prevalent chronic skin condition that often masquerades as acne, but it has distinct features requiring different treatment strategies. Primarily affecting adults over the age of thirty, especially those with fair skin, rosacea can cause persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, and in some cases, skin thickening around the nose. Although more common among women, men tend to experience more severe manifestations due to delays in seeking treatment. Recognizing the early signs and understanding the best management practices can significantly improve patients’ quality of life and skin health.
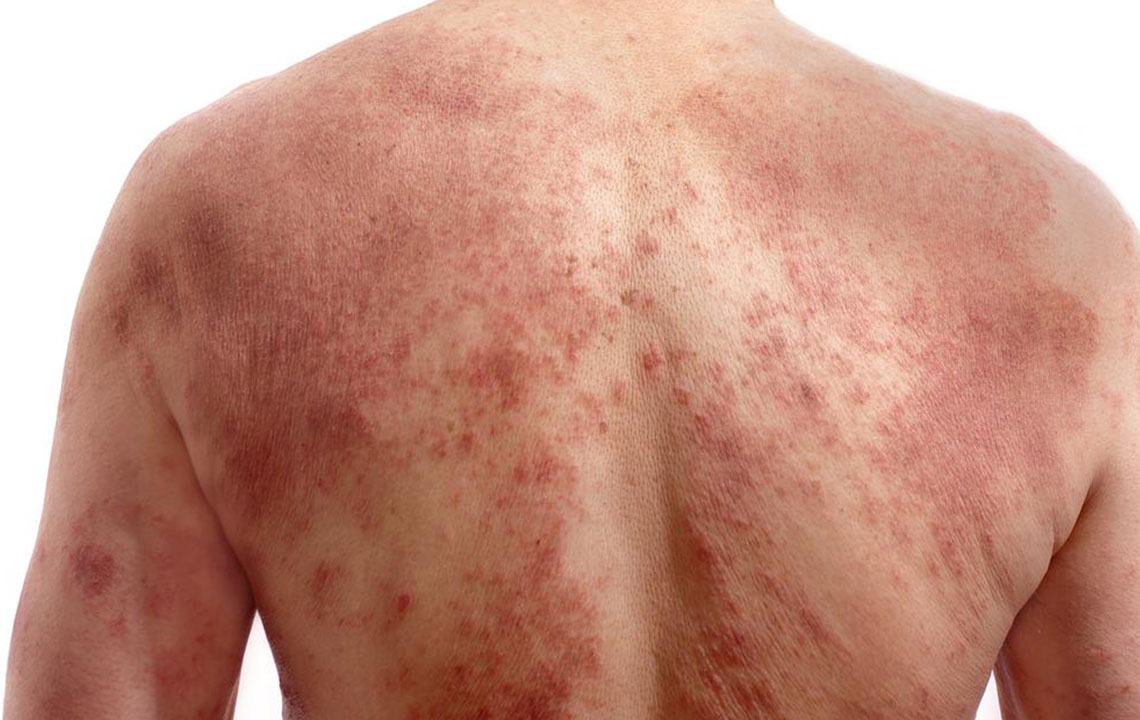
Rosacea’s hallmark symptoms include frequent flushing, persistent redness, and visible dilated blood vessels, predominantly affecting the central face—cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. As the condition progresses, symptoms may involve eye irritation, skin swelling, and thickening, often leading to a bulbous nose known as rhinophyma. If left unaddressed, rosacea can spread beyond the face, affecting the ears, neck, chest, and back. It is essential to understand these varied symptoms to manage the condition effectively and prevent complications.
Understanding the Different Types and Symptoms of Rosacea
Rosacea presents in several forms, each with specific features. Recognizing these can guide appropriate treatment. Typical signs include:
Persistent facial redness that resembles a blush or sunburn
Visible tiny blood vessels, or telangiectasias
Swelling and skin thickening around the nose, leading to rhinophyma
Broken blood vessels on the face, especially on the cheeks and nose
Acne-like bumps, pustules, and papules on reddened skin
Increased skin sensitivity, dryness, and a gritty or burning sensation
Occasional flushing episodes that can last for hours
Eye irritation, redness, dryness, and gritty sensations – a condition known as ocular rosacea
In severe cases, skin thickening can develop on the forehead, chin, and ears, giving a rough or uneven appearance. Ocular rosacea may cause discomfort, light sensitivity, and vision problems if untreated. Fortunately, advancements in dermatological treatments have made it possible to control symptoms effectively, improve skin appearance, and enhance patient comfort.
Causes and Risk Factors of Rosacea
Individuals aged between 30 and 50 are most commonly affected, though it can occur at any age
People with fair skin, particularly those with blonde hair and blue or green eyes
Individuals with sensitive or acne-prone skin
Family history of rosacea or related skin conditions indicating a genetic predisposition
The presence of Demodex mites—a type of skin mite found in higher concentrations on affected skin—may contribute to the condition
Immune system reactions triggered by bacteria such as Bacillus oleronius
Environmental triggers including sun exposure, hot or cold weather, spicy foods, alcohol, and stress
Understanding these risk factors supports early diagnosis and personalized treatment approaches.
Effective Treatments and Management Strategies for Rosacea
Diagnosis primarily hinges on clinical observation, since specific blood tests or skin biopsies are rarely necessary. Many individuals do not realize they have rosacea until symptoms become noticeable. Once diagnosed, dermatologists recommend tailored treatment plans based on the severity, symptoms, and affected areas. The mainstay treatments include:
Topical medications: These are applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation, redness, and bumps. Common topical agents include metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin.
Phototherapy and laser treatments: Laser therapy, including pulsed dye laser and intense pulsed light (IPL), effectively diminishes visible blood vessels and reduces redness, providing noticeable improvement.
Oral antibiotics: Tetracycline, doxycycline, or minocycline are prescribed for moderate to severe cases, especially when bumps or persistent inflammation are involved.
Skin protection: Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreens shields skin from UV exposure, a key trigger for rosacea flare-ups.
Eye care: For ocular rosacea, eyelid hygiene, artificial tears, and prescribed medications help alleviate discomfort and prevent eye complications.
Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding known triggers like spicy foods, alcohol, extreme weather, and managing stress can significantly reduce flare-ups.
Emerging treatments and ongoing research continue to expand the options for managing rosacea effectively. Patients are encouraged to consult dermatologists to develop a comprehensive, personalized plan tailored to their specific needs. Early intervention and consistent skin care routines can prevent progression, minimize visible signs, and boost confidence.
In conclusion, while rosacea is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management, modern therapies offer significant relief and improvement. Educating oneself about the symptoms, triggers, and available treatments is crucial for managing the disease effectively and maintaining a healthy, comfortable skin appearance. With the right approach, individuals affected by rosacea can lead full, confident lives without the burden of visible skin issues.