Ultimate Guide to Managing and Treating Rosacea Effectively
This comprehensive guide offers detailed insights into rosacea, covering symptoms, causes, triggers, risk factors, and effective treatments. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and personalized management strategies to control flare-ups and improve skin health, providing valuable information for those affected by this common skin condition.

Ultimate Guide to Managing and Treating Rosacea Effectively
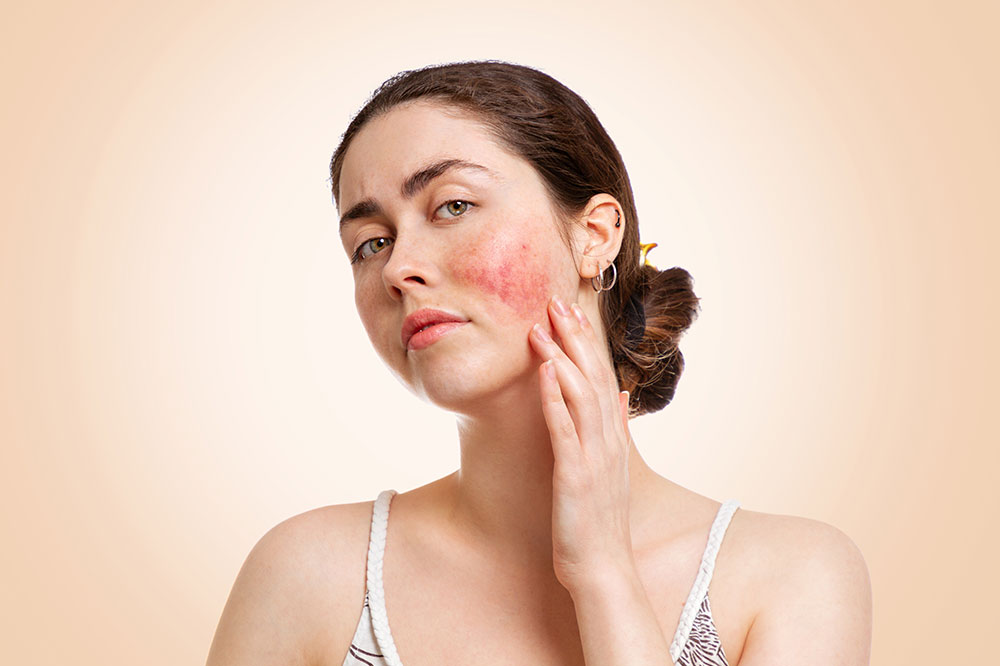
Rosacea is a common chronic skin disorder that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes swelling, this condition can significantly impact one’s self-esteem and quality of life. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the available treatment options are crucial for effective management. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, risk factors, triggers, and detailed treatment strategies to help you control rosacea and improve your skin health.
Symptoms and Signs of Rosacea:
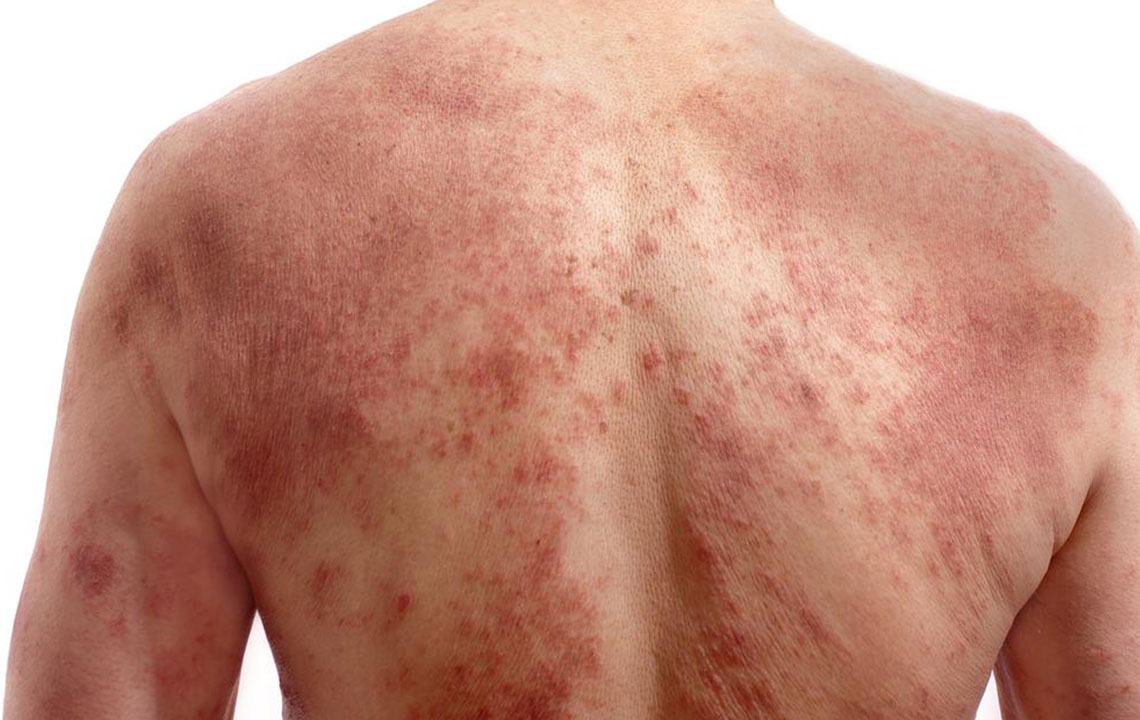
Persistent Facial Redness
The hallmark of rosacea is enduring redness primarily on the central face, including cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. This redness often resembles blushing but persists deeper in the skin, giving the face a flushed appearance over time. Blood vessels beneath the skin may become enlarged and visible, creating a pattern often referred to as telangiectasia.
Red Bumps and Pimples
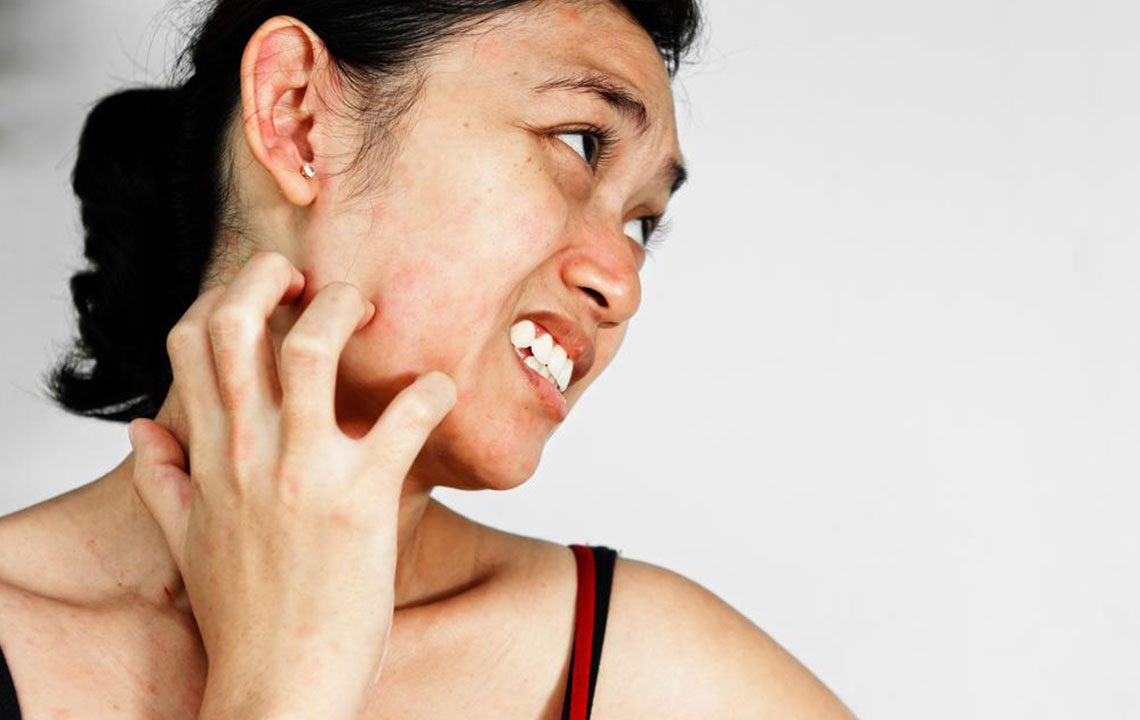
Similar to acne, rosacea can cause small red papules and pustules that may contain pus. These bumps may be accompanied by skin irritation, burning, and stinging sensations, further contributing to discomfort and embarrassment.
Ocular Symptoms (Ocular Rosacea)
About half of those with facial rosacea may develop eye-related issues. Symptoms include dry, itchy, and reddened eyelids and eyes, light sensitivity, blurred vision, and a feeling of grittiness or foreign body sensation. Ocular rosacea requires prompt ophthalmologic assessment to prevent complications.
Swelling and Skin Thickening
In severe cases, particularly rhinophyma, the nose becomes enlarged, thickened, and irregularly shaped due to excess tissue buildup. This disfigurement is more common in men and can be socially distressing.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you experience persistent facial redness, new or worsening skin bumps, eye symptoms, or noticeable swelling, consulting a dermatologist is essential. Early diagnosis allows for more effective control and prevents potential severity escalation.
The cause of rosacea remains elusive, yet researchers suggest a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors play a role. The condition appears more frequently in individuals with fair skin, and it tends to develop after the age of 30. It is also linked to increased family history, indicating a hereditary component.
Common triggers that can aggravate rosacea include:
Spicy foods and hot beverages such as coffee and tea
Extreme temperatures—hot or cold weather
Windy conditions
Prolonged sun exposure
Emotional stress and anxiety
Vigorous physical activity
Use of harsh skincare products or cosmetics
Certain medications that dilate blood vessels
Identification and avoidance of these triggers can significantly reduce flare-ups and improve the skin’s appearance.
Risk factors for developing rosacea include:
Having fair skin that burns easily
Being over 30 years old
Family history of rosacea or related skin conditions
Gender differences, with women more commonly affected, but men prone to more severe forms like rhinophyma
Understanding these risks can aid early detection and intervention, especially for susceptible populations.
Effective management of rosacea revolves around tailored treatment plans that address the individual’s specific symptoms and severity. A multidisciplinary approach involving skincare routines, lifestyle modifications, and medications is standard practice.
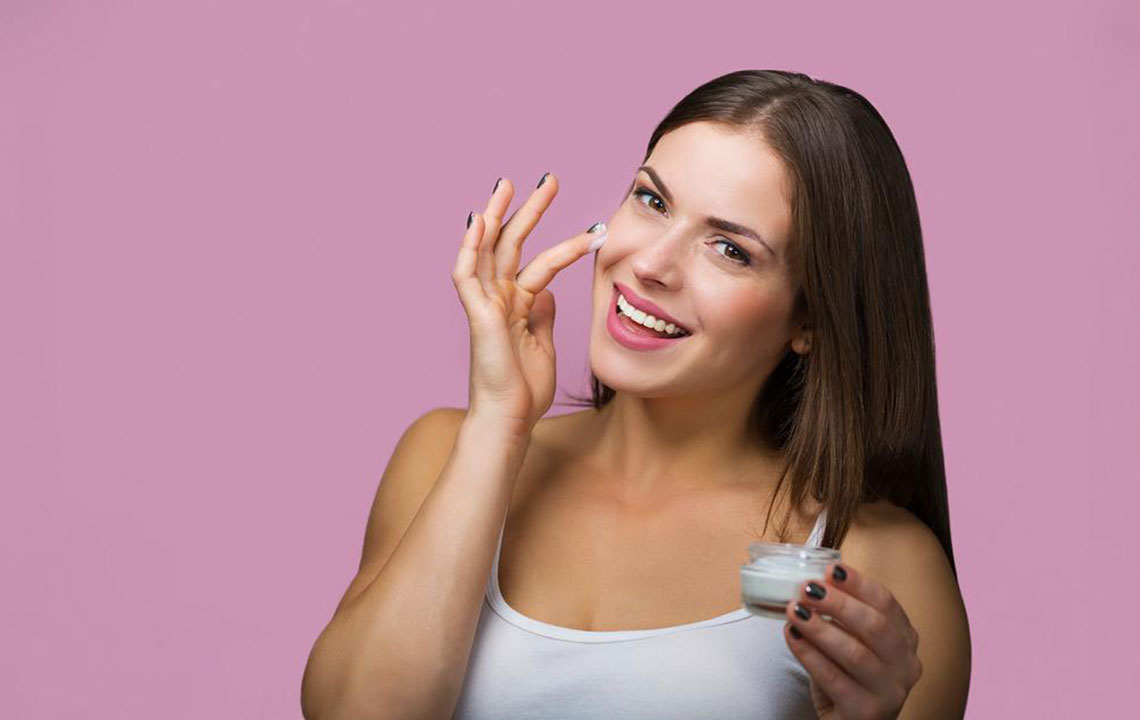
Skincare routines should focus on gentle cleansing and hydrating products. Avoiding irritants such as alcohol-based toners or abrasive scrubs minimizes skin sensitivity.
Topical medications are often prescribed to reduce redness, inflammation, and bumps. Common agents include metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin. These help diminish inflammatory lesions, reduce blood vessel visibility, and soothe the skin.
Oral medications may be recommended in more severe cases, especially when there is significant inflammation or ocular involvement. Antibiotics like doxycycline and tetracycline are effective in reducing bacterial proliferation and inflammation without necessarily having antibacterial effects.
Other treatment options include laser therapy and intense pulsed light (IPL) to target and diminish visible blood vessels and redness. These procedures can provide significant cosmetic improvement but require specialist assessment and follow-up.
Consistency and regular consultation with a dermatologist are key to managing rosacea effectively. Personalized treatment plans, based on skin type and severity, contribute to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Emerging therapies and ongoing research continue to provide hope for more effective treatments in the future, including newer topical agents and medical devices that target the underlying vascular and inflammatory components of rosacea.
In summary, rosacea is a manageable condition through early detection, trigger avoidance, proper skin care, and appropriate medical treatment. With ongoing vigilance and professional guidance, individuals can control symptoms and maintain healthy, comfortable skin.