Comprehensive Guide to Elevated Blood Pressure and Its Impact on Health
This comprehensive article explores the importance of understanding high blood pressure, its measurement, interpretation, and management strategies. As a common yet serious health concern, hypertension requires awareness and proactive measures to prevent severe cardiovascular risks. From monitoring techniques to lifestyle changes, learn how to keep your blood pressure under control and safeguard your overall health effectively.
Comprehensive Guide to Elevated Blood Pressure and Its Impact on Health
High blood pressure, medically known as hypertension, is one of the most common and serious health issues affecting people worldwide today. With rising lifestyle changes and an aging global population, understanding the intricacies of blood pressure, its causes, effects, and management is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing severe cardiovascular complications. This detailed guide delves into what high blood pressure means, how to monitor it accurately, interpret the readings, and adopt effective strategies to keep it under control, thus safeguarding your heart and body.
Understanding Blood Pressure and Its Measurement
Blood pressure (BP) is a critical vital sign that measures the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of your arteries throughout each heartbeat. It is typically expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and represented as two numbers: systolic over diastolic. The systolic pressure is the higher number and reflects the pressure when the heart contracts and pumps blood out, whereas the diastolic is the lower number indicating the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
The importance of monitoring blood pressure stems from its direct correlation with cardiovascular health. Elevated readings can be a warning sign of underlying health issues, while low blood pressure (hypotension) can lead to dizziness and fainting. However, most medical discussions focus on managing high blood pressure to prevent future health risks.
Normal and Elevated Blood Pressure Ranges
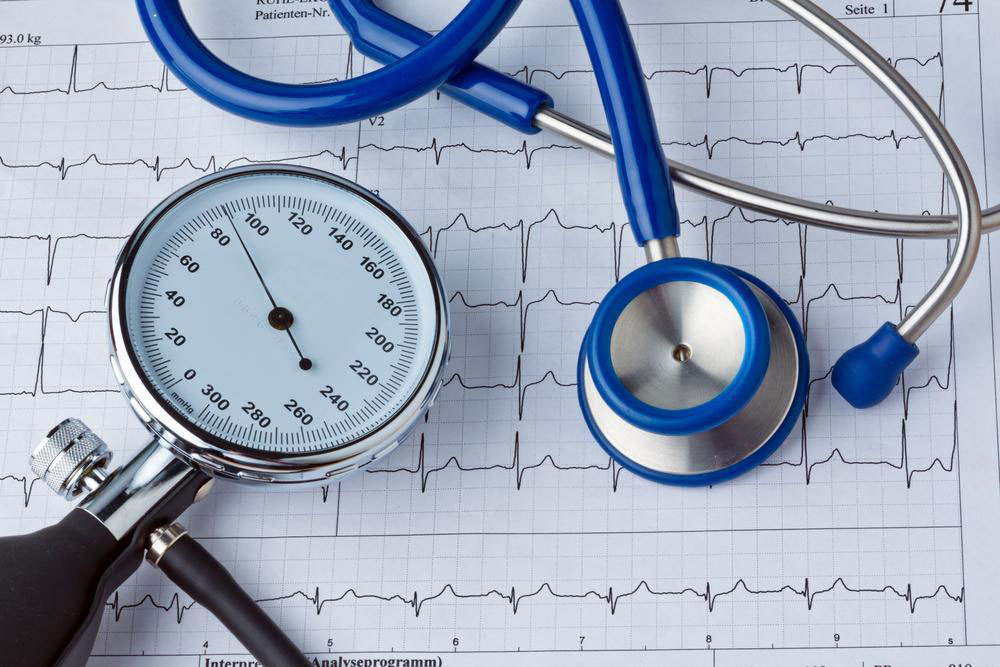
Generally, a blood pressure reading below 120/80 mmHg is classified as normal and ideal. Readings between 120/80 mmHg and 139/89 mmHg are considered in the normal to elevated range—this is an area where lifestyle adjustments can prevent progression to hypertension.
Persistent high blood pressure, especially readings consistently above 140/90 mmHg, warrants medical attention. Chronic hypertension increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney damage, and other severe health complications. With age, the likelihood of developing hypertension naturally increases, making routine monitoring vital for middle-aged and older adults.
Deciphering Blood Pressure Readings
A typical blood pressure reading consists of two numbers: systolic and diastolic. The systolic number indicates the pressure in the arteries during the contraction of the heart, whereas the diastolic number indicates the pressure when the heart is resting between beats. For example, a reading of 130/85 mmHg means a systolic pressure of 130 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of 85 mmHg.
Understanding how to interpret these numbers is crucial for assessing your cardiovascular health. Healthcare providers often use BP charts or apps to help you compare your readings against standard ranges and identify any abnormalities that may require medical intervention.
Recognizing Symptoms of Hypertension
Hypertension is often called the "silent killer" because it typically shows no overt symptoms until it has caused significant damage. Still, some individuals may experience headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath, or blurred vision if their blood pressure reaches dangerously high levels.
Blood pressure readings of 140/90 mmHg or higher are indicative of hypertension, especially if persistent over multiple checks. Regular monitoring and early diagnosis enable timely intervention, which can significantly reduce the risk of severe cardiovascular events.
Strategies for Managing High Blood Pressure
Effectively managing hypertension involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatment, and regular health check-ups. Lifestyle modifications such as adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low in saturated fats and sodium are fundamental.
In addition, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, limiting alcohol intake, and quitting smoking can significantly lower blood pressure levels. Adequate sleep and stress management through relaxation techniques also contribute to better blood pressure control.
For some individuals, medication prescribed by healthcare professionals becomes necessary to keep BP in check. Consistent monitoring, adherence to prescribed medications, and follow-up visits are key to preventing complications associated with chronic high blood pressure.