A Comprehensive Guide to Normal Blood Pressure Across Different Age Groups
This comprehensive article explains the importance of maintaining normal blood pressure across various age groups, highlighting measurement methods, classification thresholds, and lifestyle factors influencing cardiovascular health. It emphasizes the role of regular monitoring and healthy habits in preventing hypertension and ensuring optimal organ function, providing valuable insights for individuals seeking to manage their blood pressure effectively throughout life.
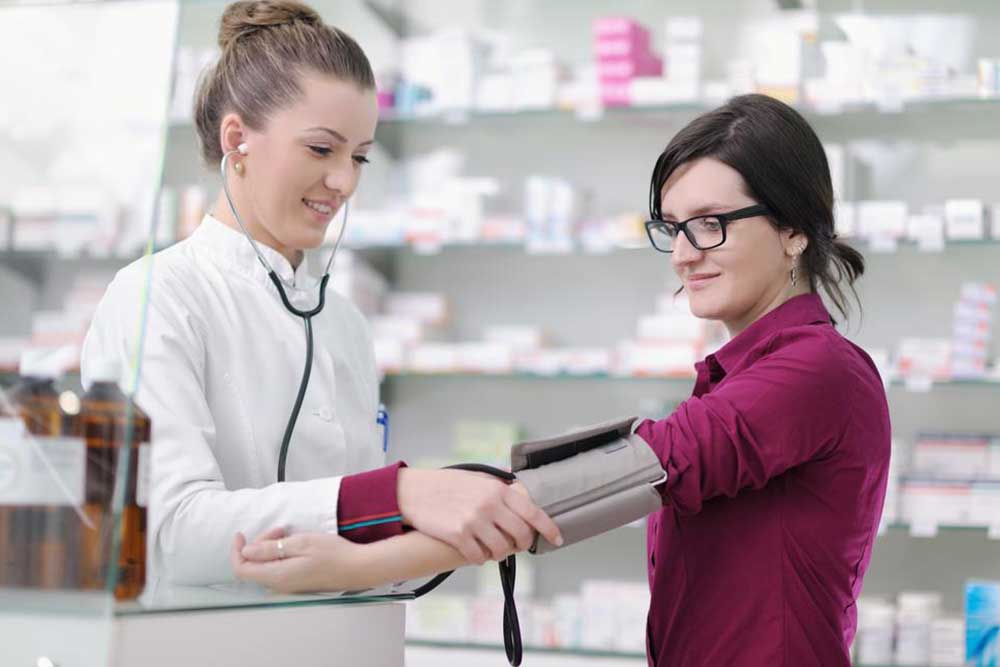

Understanding Normal Blood Pressure Across Different Age Groups
The human circulatory system plays a vital role in maintaining overall health by transporting blood, oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body. An essential aspect of cardiovascular health is blood pressure, which measures the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Maintaining blood pressure within optimal ranges is critical for ensuring proper organ function and preventing long-term health complications.
Blood acts as the body's delivery system, providing oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing metabolic waste. It contains vital components such as oxygen, hormones, and antibodies, which are crucial for maintaining immunity and metabolic processes. The heart functions as an efficient pump, creating the necessary pressure to propel blood through a complex network of arteries and veins. This pressure varies at different points in the circulatory system—being highest near the heart in the aorta and gradually decreasing as blood moves into smaller arteries and capillaries. Elastic arteries, characterized by their flexible walls, help accommodate blood flow fluctuations, ensuring steady circulation.
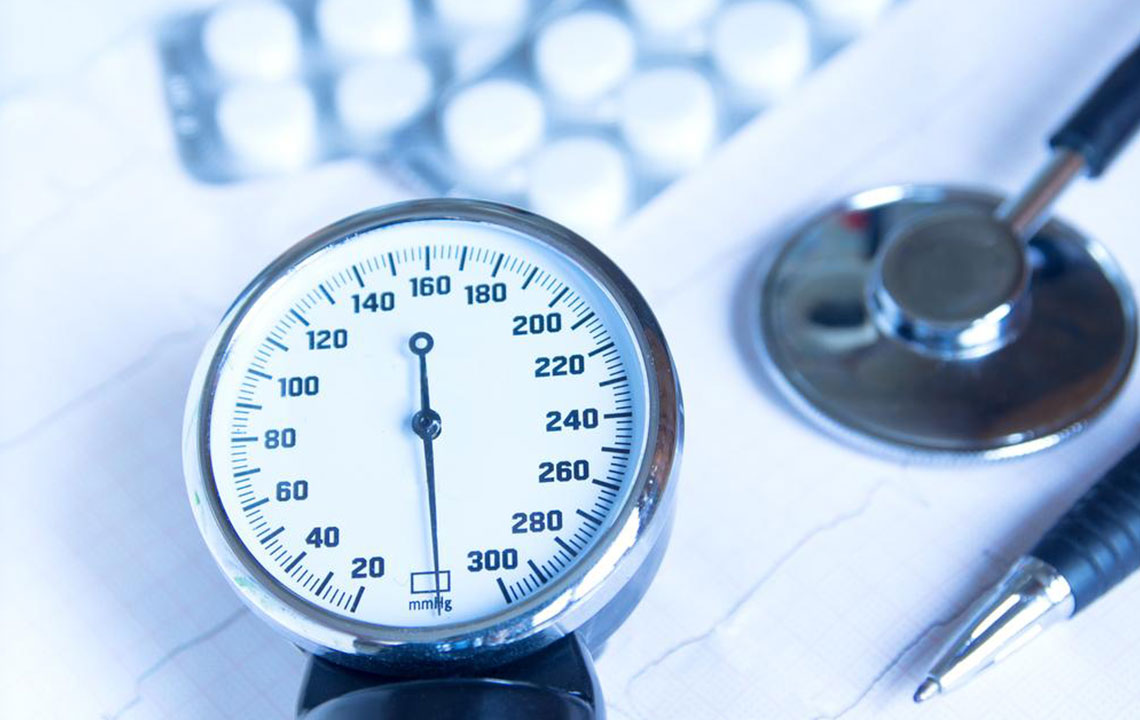
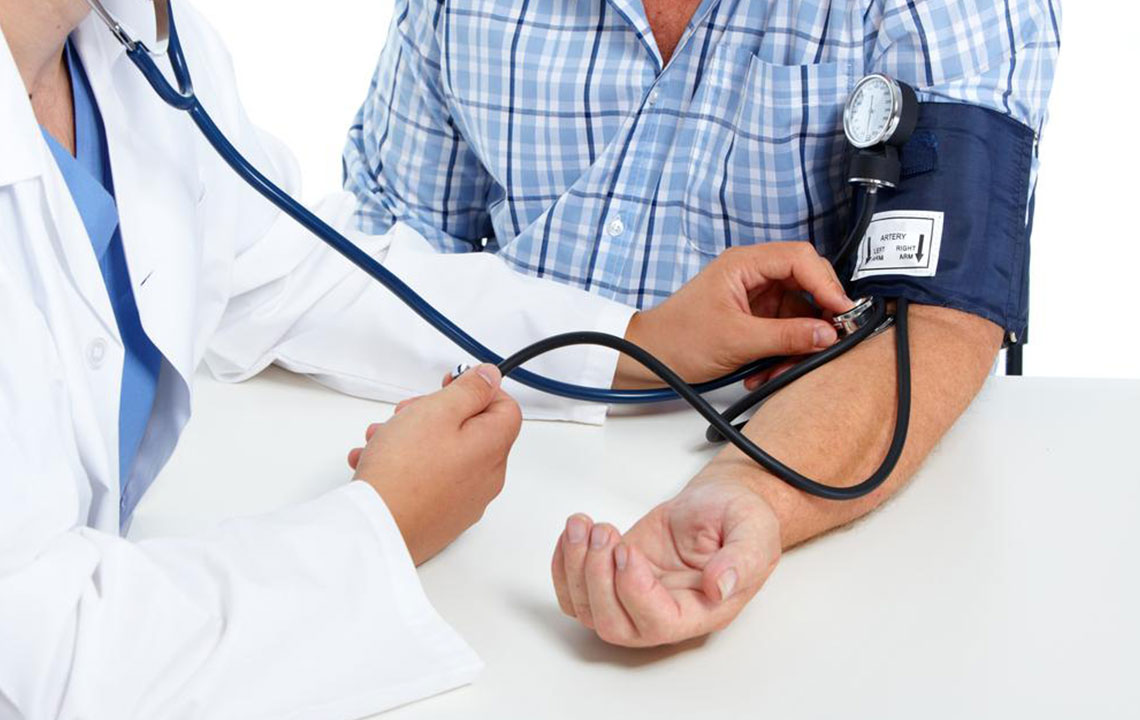
Healthcare professionals utilize instruments like sphygmomanometers to measure blood pressure, expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Accurate readings are essential for diagnosing and managing blood pressure-related conditions. Medical experts often refer to established blood pressure charts and guidelines to assess whether an individual's blood pressure falls within the healthy range, considering factors such as age, gender, and overall health.
According to established health guidelines, a systolic blood pressure reading—representing the pressure during heartbeats—of around 120 mmHg, combined with a diastolic reading—representing the pressure between beats—of approximately 80 mmHg, is considered ideal or normal for most adults. Readings significantly higher than this, particularly values exceeding 130/80 mmHg, may suggest the presence of hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure. Conversely, low blood pressure readings—below 90/60 mmHg—might indicate hypotension, which can cause dizziness or fainting.
Blood pressure categories are classified as follows: low blood pressure (hypotension) ranges from about 70/40 to 90/60, normal blood pressure falls roughly between 90/60 and 120/80, prehypertension spans from 120/80 to 140/90, and high blood pressure (hypertension) is generally defined as readings above 140/90. It’s important to note that these thresholds can shift depending on age and individual health conditions. As people age, blood vessels tend to stiffen, leading to changes in blood pressure patterns. Therefore, what is considered healthy varies across age groups, and lifestyle interventions become increasingly important for maintaining optimal levels.
Maintaining healthy arteries—free from narrowing and blockages—is fundamental in regulating blood pressure effectively. Narrowed arteries, often caused by atherosclerosis (plaque buildup), can elevate blood pressure, increasing the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. Factors like diet, physical activity, weight management, smoking cessation, and stress reduction play a vital role in promoting vascular health. Regular blood pressure monitoring helps individuals track their health status, allowing timely interventions if readings drift outside normal ranges.
In summary, understanding the normal blood pressure parameters relative to age and lifestyle is crucial for preventive health care. Consistent monitoring, coupled with healthy habits, empowers individuals to maintain optimal cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of related diseases. Awareness of blood pressure trends across different life stages allows for tailored management strategies, ultimately fostering long-term well-being and vitality.