Comprehensive Guide to Identifying and Managing Enlarged Neck Lymph Nodes
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for enlarged neck lymph nodes. Understanding when to seek medical help and how to manage common conditions can lead to better health outcomes. Learn about identifying signs of infection, inflammation, or serious diseases like cancer and the importance of timely intervention.
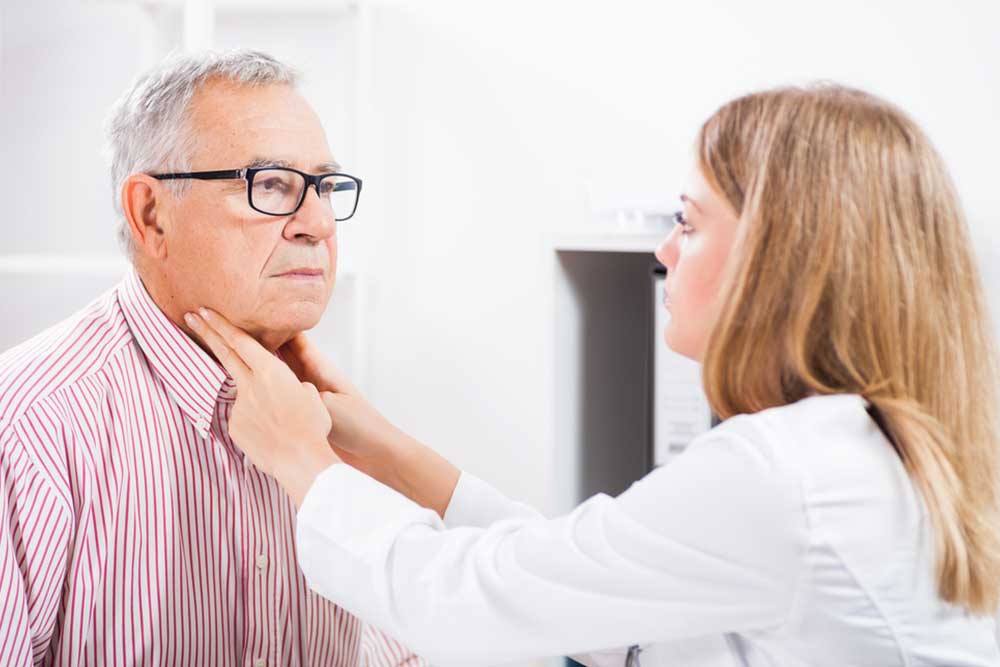
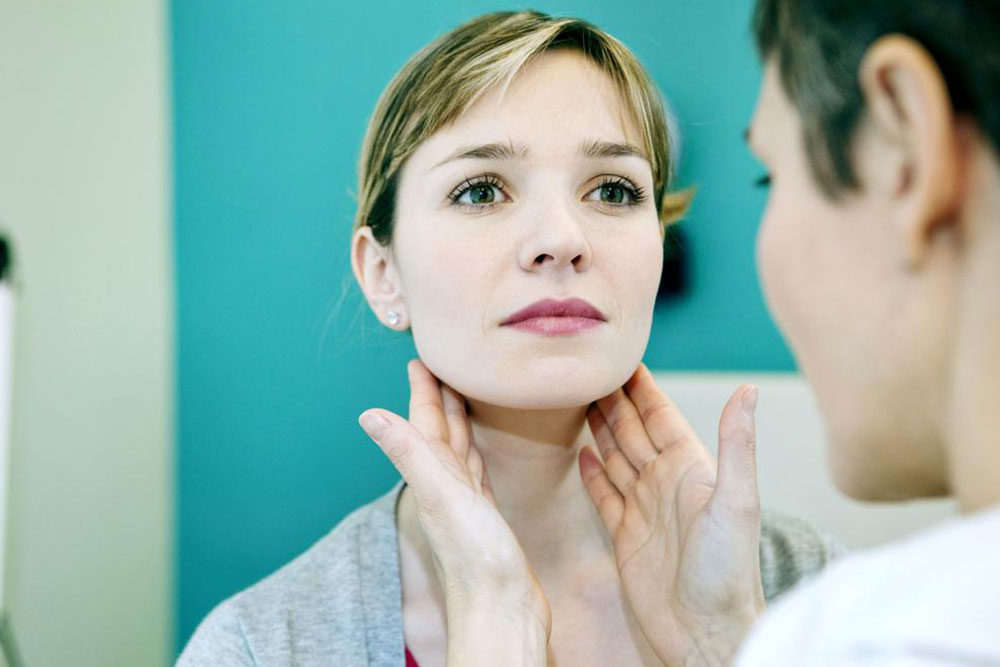
Understanding and Managing Enlarged Neck Lymph Nodes
The swelling of lymph nodes in the neck is a common health concern that can signal a range of underlying conditions. These lymphatic glands are crucial components of the immune system, acting as filters that trap harmful pathogens such as viruses and bacteria. When they become enlarged, it often indicates a response to infection, inflammation, or, in rarer cases, malignancy. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for enlarged neck lymph nodes is essential for timely medical intervention and better health outcomes.
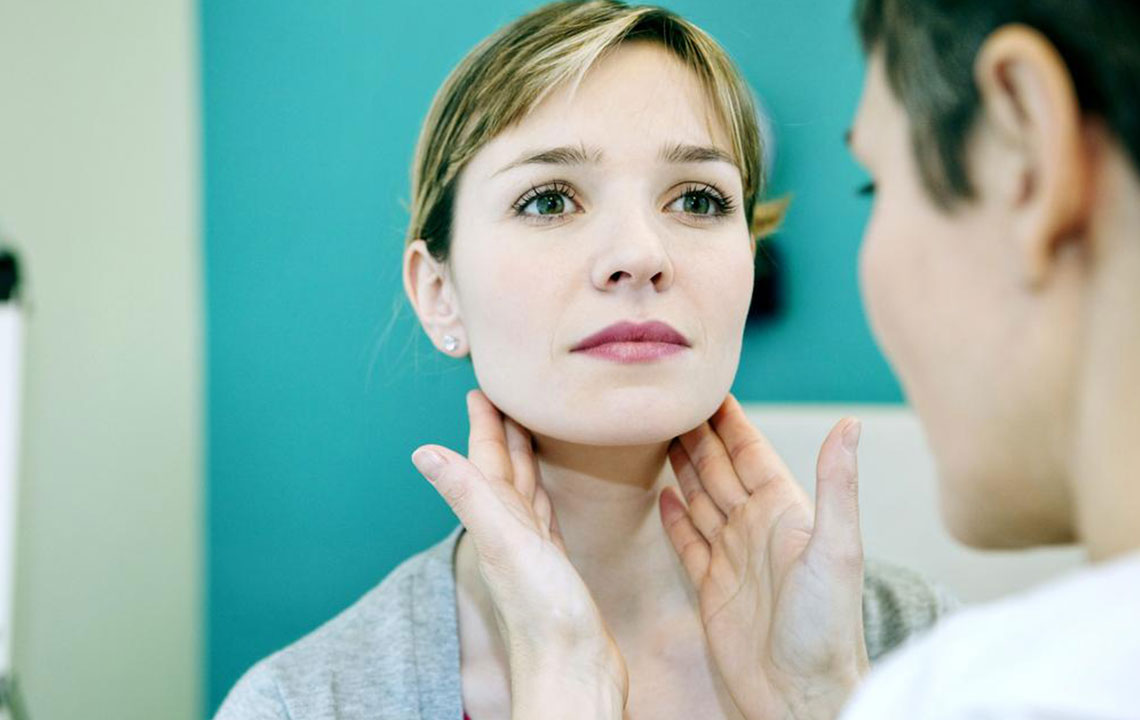
Enlargement of lymph nodes in the neck can occur for various reasons, ranging from commonplace infections to more serious health conditions. It is important to distinguish between benign and potentially dangerous causes to determine the appropriate course of action. Swollen lymph nodes under the chin, in the jawline, or along the sides of the neck are particularly noticeable signs that warrant further investigation.
Recognizing the Symptoms and Causes of Swollen Neck Lymph Nodes
Swollen lymph nodes typically present with symptoms such as tenderness, warmth, and a palpable lump. Often, these symptoms are accompanied by other signs of infection like fever, sore throat, or fatigue. Understanding these indicators can help you decide when to seek medical attention.
The primary causes include:
Viral infections such as the common cold or mononucleosis
Bacterial infections like strep throat or skin abscesses
Chronic inflammatory conditions, including autoimmune diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
Less commonly, persistent or enlarged lymph nodes may signal malignancies such as lymphoma or metastatic cancer
How Healthcare Professionals Diagnose Enlarged Lymph Nodes
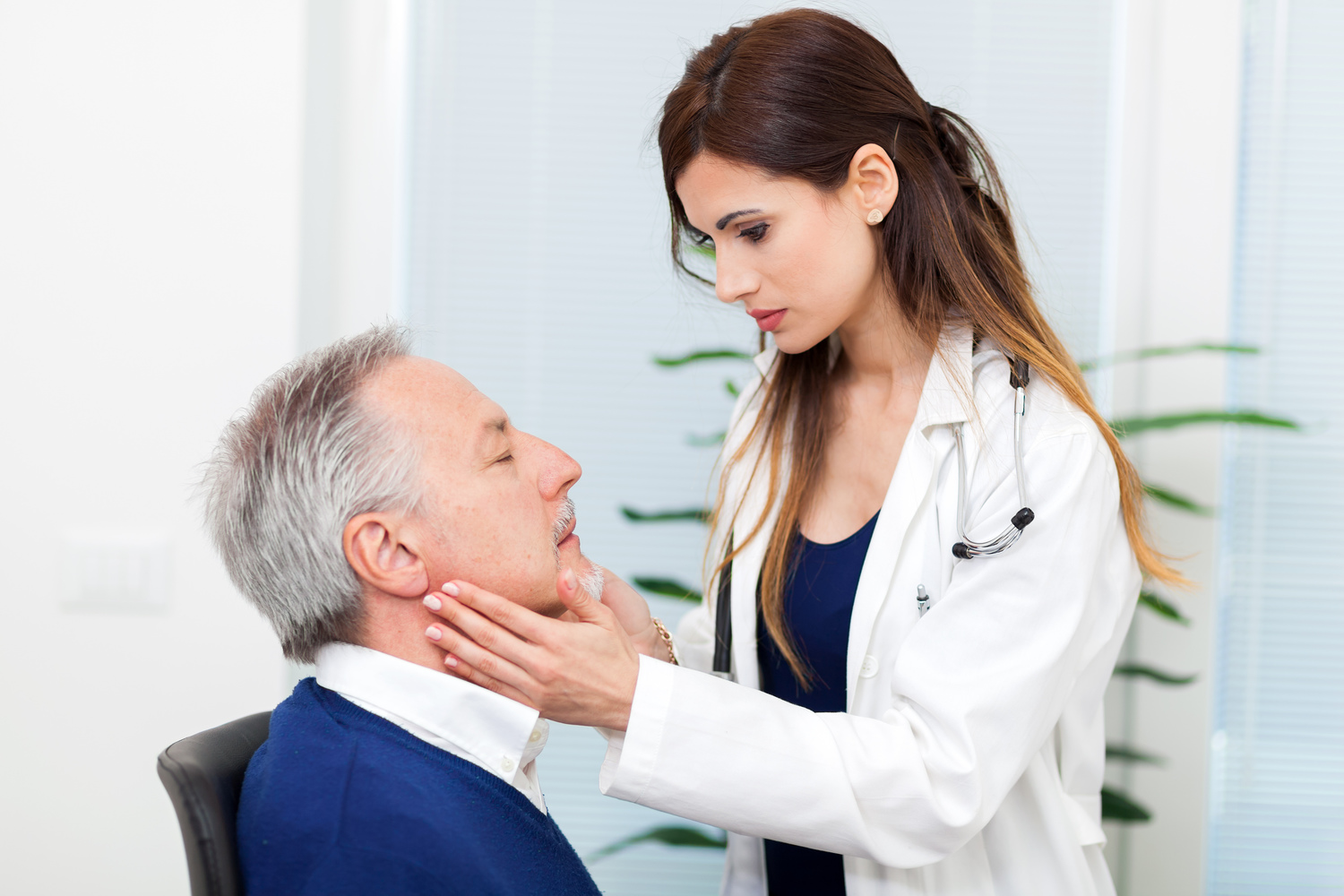
Accurate diagnosis is vital in determining whether the swelling is benign or requires further treatment. Healthcare providers usually begin with a thorough physical examination, focusing on the size, texture, warmth, and tenderness of the lymph nodes.
Following the initial assessment, they may recommend additional diagnostics such as:
Blood tests to analyze infection markers, white blood cell count, and other relevant parameters
Imaging studies—including ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI—to visualize internal structures and locate possible sources of infection or tumor
Lymph node biopsy, where a small tissue sample is extracted for microscopic investigation to detect malignancy or specific infections
Effective Treatment Strategies for Enlarged Neck Lymph Nodes
The treatment approach primarily hinges on the underlying cause of the lymphadenopathy. Here is an overview of typical management options:
Infections: Bacterial infections are usually treated with antibiotics, while viral causes may resolve on their own or require supportive care such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications.
Inflammatory and autoimmune conditions: These may necessitate immunosuppressants or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
Cancer-related cases: Treatment can involve surgical removal of affected lymph nodes, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted biological therapies depending on the specific type and stage of cancer.
In some instances, swollen lymph nodes may diminish naturally without intervention, especially if caused by minor infections. Applying warm compresses can help alleviate discomfort and promote drainage. However, it is paramount to consult a healthcare professional promptly if swelling persists, enlarges, or is associated with systemic symptoms like fever, weight loss, or night sweats.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Swollen Lymph Nodes
While minor swelling during a cold or after minor injury is often harmless, certain signs require urgent medical evaluation:
Swelling that persists beyond two weeks
Rapidly enlarging lymph nodes
Severe pain or tenderness
Associated symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, persistent fever, or night sweats
Hard, fixed, or irregular lymph nodes that do not move easily beneath the skin
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing lymphadenopathy effectively. Keep track of your symptoms, and don't hesitate to seek professional health advice for persistent or concerning swelling.




