Comprehensive Guide to Neck Lymph Node Swelling: Causes, Symptoms, and Medical Insights
This comprehensive article explores the causes and symptoms of neck lymph node swelling, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. It covers viral, bacterial, parasitic, fungal infections, and other medical conditions, providing detailed insights to help readers understand when to seek medical advice. Recognizing symptoms like pain, tenderness, and systemic signs can aid in early intervention, ensuring better health outcomes. A thorough understanding of lymphadenopathy empowers individuals to act promptly and consult healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and care.
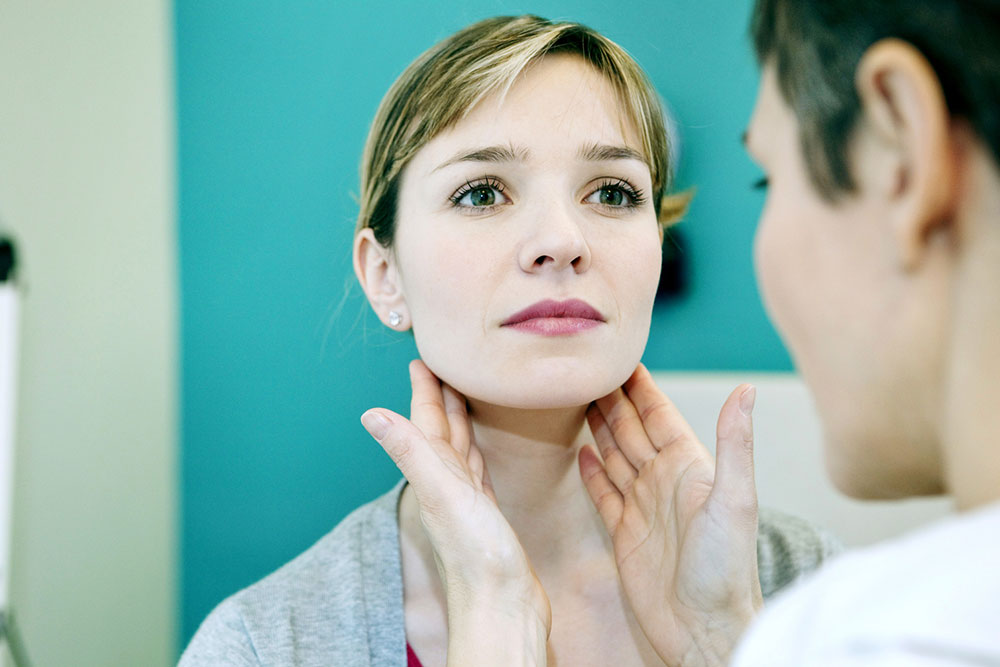

Understanding Neck Lymph Node Swelling: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Approaches
Lymph nodes play an essential role in the human body's immune defense system, acting as filters that trap viruses, bacteria, and other harmful substances. Located along the lymphatic vessels, these small, bean-shaped structures are scattered throughout the body, with a concentration in regions such as the neck, armpits, groin, and under the jaw. One of the most noticeable signs of immune activity or underlying health issues is swelling of the lymph nodes, particularly in the neck area. Such swelling can be a benign response to infection or a sign of more serious conditions like malignancies.
Typically, swollen lymph nodes in the neck are palpable and visible, often presenting as small, soft lumps behind the ears, along the sides of the neck, or under the jaw. They may be tender or painful to touch, especially during active infections. Recognizing when lymph node swelling warrants medical attention is vital because it can help in prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Misinterpreting this symptom could delay the identification of more severe health problems, including cancers or systemic infections.
This comprehensive guide explores the primary causes of neck lymph node swelling, the symptoms associated with it, and the importance of seeking medical care. Understanding these aspects can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Primary Causes of Neck Lymph Node Swelling
The enlargement of lymph nodes in the neck is usually caused by infections, immune system responses, or other medical conditions. These causes can range from common viral infections to more complex diseases, including cancer. Differentiating the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and prognosis.
Viral Infections: Viral infections are among the most common reasons for swollen lymph nodes. When the body detects a viral invasion, lymph nodes work overtime to filter out pathogens, leading to visible swelling. Common viral causes include:
Varicella (chickenpox), which causes widespread skin rashes and immune activation.
Infectious mononucleosis, often caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, manifests with severe fatigue, sore throat, and swollen nodes.
HIV/AIDS, leading to persistent lymphadenopathy and weakened immune function.
Measles, presenting with characteristic skin rashes and immune system activation.
Adenovirus infections, responsible for respiratory illnesses.
Common cold viruses, which frequently cause temporary lymph node swelling in the neck.
Herpes viruses, which can cause recurrent sores and immune response.
The body's response to such viral infections involves lymph nodes enlarging to trap and eliminate infected cells, thus making swelling a natural, though temporary, part of the immune response.
Parasitic Causes: Parasites can also lead to lymph node enlargement, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. Notable parasitic causes include:
Leishmaniasis, transmitted through sandfly bites causing systemic symptoms and lymphadenopathy.
Toxoplasmosis, often contracted from contaminated food or cat feces, leading to enlarged nodes and flu-like symptoms.
Fungal Infections: Infections caused by fungi, though less common, can result in lymph node swelling, especially in immunocompromised individuals. Examples include:
Histoplasmosis, associated with bird droppings and soil disturbance, causing systemic infection.
Coccidioidomycosis (Valley fever), endemic to certain regions, affecting lungs and lymph nodes.
Bacterial Infections: Bacterial agents are prominent causes of lymphadenopathy. These include:
Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species, common in skin infections and sore throats.
Tuberculosis, which can cause persistent lymph node enlargement, especially in the neck.
Cat scratch disease, transmitted from cat bites or scratches, leading to localized swelling.
Chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections, which can involve cervical lymph nodes.
Syphilis, a sexually transmitted disease that can cause lymphadenopathy during different stages.
Medical Conditions and Other Factors: Beyond infections, several non-infectious medical conditions can cause neck lymph node swelling:
Cancer: Lymphomas (Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin), leukemias, and metastases from cancers such as breast and lung can involve lymph nodes. Enlarged nodes may be hard, fixed, or painless in malignancies.
Inflammatory Diseases: Autoimmune disorders such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions result in lymphadenopathy as the immune system becomes hyperactive.
Less common causes involve organ rejection after transplant, rare genetic disorders like lipid storage diseases, and sarcoidosis, which causes granulomatous inflammation.
Importantly, not all swollen lymph nodes are signs of severe illness. Many are benign and resolve once the infection or condition subsides. Nevertheless, persistent, hard, or enlarging nodes warrant medical assessment to exclude serious underlying health issues.
Recognizing Symptoms Associated with Neck Lymph Node Swelling
Besides visible swelling, several accompanying symptoms can provide clues about the underlying cause. The nature, location, and duration of the swelling, combined with other signs, help healthcare professionals determine the diagnosis.
Temporary tenderness or pain in enlarged nodes that worsens during infections indicates active immune response.
Persistent, non-tender hard nodes may suggest neoplastic processes such as lymphoma or metastasis.
Additional signs include sore throat, nasal congestion, cough, fever, chills, and fatigue.
Visual indicators such as redness, skin warmth, or streaking over the swollen area can point toward infection or skin inflammation.
Swelling in the groin area may cause discomfort during walking or movement, especially if associated with systemic illness.
Other systemic symptoms like night sweats, unexplained weight loss, and persistent fever often accompany serious conditions like cancers.
It's crucial to seek prompt medical attention if you experience persistent or painful swelling of lymph nodes, especially if accompanied by other concerning symptoms. Early diagnosis can significantly influence treatment outcomes, particularly in cases of infections or malignancies. Proper medical evaluation often involves physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scans, and sometimes biopsy.
In summary, understanding the causes, symptoms, and appropriate response to neck lymph node swelling can lead to timely medical intervention, improving health outcomes and preventing complications. Maintaining awareness and seeking professional advice are key steps in managing this common but potentially serious health concern.