Comprehensive Guide to Swollen Neck Lymph Nodes: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for swollen neck lymph nodes. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and medical intervention for infections, autoimmune diseases, or cancers affecting lymph nodes. The article offers detailed insights into when to seek professional help, diagnostic procedures, and effective management strategies to ensure proper recovery and health maintenance.

In-Depth Insights into the Causes, Symptoms, and Management of Enlarged Lymph Nodes in the Neck
Experiencing a noticeable lump in your neck can be a source of significant concern and anxiety. These enlarged lymph nodes, commonly referred to as swollen glands, are crucial components of your immune system. They are small, bean-shaped structures that are distributed throughout your body, especially concentrated in areas such as the neck, underarms, and groin. Their primary function is to filter lymph fluid and harbor immune cells that play a vital role in defending the body against infections and diseases.
When your body detects an infection or inflammation, lymph nodes respond by swelling as they ramp up white blood cell production to combat the threat. This process often results in a lump or swelling in the affected area. Typically, these swollen lymph nodes may be tender and painful, especially during vigorous activities or when touched. However, in some cases, they can be painless, which may require closer medical assessment. Recognizing the underlying causes and symptoms that indicate a need for medical intervention is essential for proper diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
The presence of swelling in the neck can vary from a minor temporary phenomenon to a sign of a more serious health issue. The swelling manifests as a visible mass under the skin, which may be tender or painful upon touch. Some individuals may experience discomfort during simple activities such as turning the head, walking, or bending neck. To better understand this condition, it is important to explore the various underlying causes, observe associated symptoms, and identify when medical evaluation is critical.
What Are the Common Causes of Swollen Neck Lymph Nodes?
Infections such as ear infections, sore throat, sinusitis, tonsillitis, mouth sores, and dental abscesses are frequent triggers. These infections lead to immune activation, causing lymph node swelling as they work to fight bacterial or viral invasion.
Autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, can cause diffuse lymphadenopathy due to abnormal immune responses attacking the body's tissues.
Thyroid gland disorders such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or goiter may present with neck swelling, sometimes mistaken for lymph node enlargement.
Cancers affecting the lymphatic system, notably lymphoma and leukemia, often manifest as persistent, hard, and sometimes painless lumps in the neck area. These require prompt medical attention for diagnosis and treatment.
Severe infections including HIV/AIDS can cause generalized lymphadenopathy, sometimes accompanied by systemic symptoms.
Sexually transmitted infections like syphilis and gonorrhea may also involve lymph node swelling, typically near the groin but sometimes affecting neck regions as well.
Other illnesses such as measles, toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis, gingivitis, and cat scratch disease are among less common but significant causes of lymph node enlargement.
Additional Symptoms Indicating the Need for Medical Review
Cough, nasal congestion, or phlegm production that suggests respiratory infections.
Fever, chills, and muscle aches indicating systemic infection.
Persistent fatigue, unexplained night sweats, or weight loss signaling more serious underlying conditions.
Triggers for Urgent Medical Consultation
The formation of a lump lasting longer than two weeks without signs of shrinking.
Hard, immovable, or fixed lumps that do not fluctuate with neck movement.
Swelling that appears in multiple regions such as armpits or groin in conjunction with neck lumps.
Associated symptoms like persistent fever, coughing, or night sweats which do not improve with time.
Unexplained weight loss, skin changes in the area of swelling, or pain and tenderness in lymph nodes warrant immediate attention.
Diagnostic Procedures for Swollen Neck Lymph Nodes
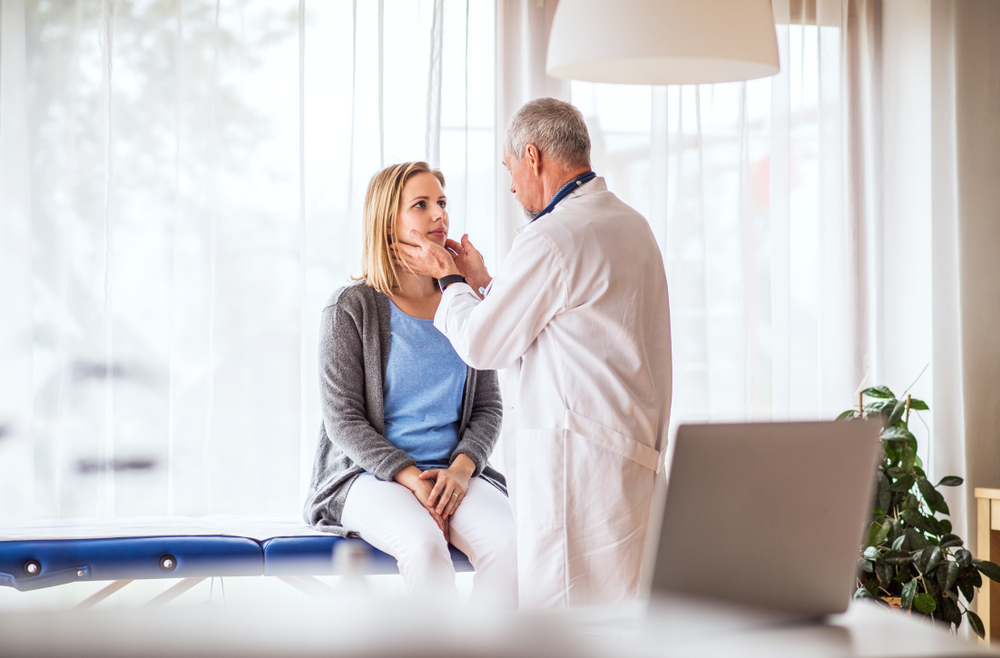
Comprehensive physical examination by a healthcare professional to assess characteristics like size, consistency, mobility, and tenderness of the lump.
Detailed medical history focusing on recent infections, systemic symptoms, and exposure risks.
Laboratory tests including blood work, biopsies, and imaging studies such as ultrasounds, PET scans, or CT scans to identify the underlying cause and evaluate the extent of the condition.
Effective Treatment Strategies
Bacterial infections are primarily treated with appropriate antibiotics along with supportive care like rest and hydration.
Cancerous lymph nodes often require comprehensive treatment plans, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgical removal depending on the diagnosis.
Autoimmune conditions are managed with anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants to control immune response and reduce lymph node swelling.
Addressing the root cause is crucial for effective management and long-term health outcomes. Regular follow-up and monitoring are essential to evaluate treatment response and adjust strategies as needed.