Comprehensive Guide to Swollen Neck Lymph Nodes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Swollen neck lymph nodes are often a sign of infection or illness, but can sometimes indicate more serious health issues like cancer. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for lymphadenopathy in detail, helping readers understand when to seek medical attention and how to manage this condition effectively. Recognizing the signs early and consulting healthcare providers can lead to quicker diagnosis and better health outcomes.
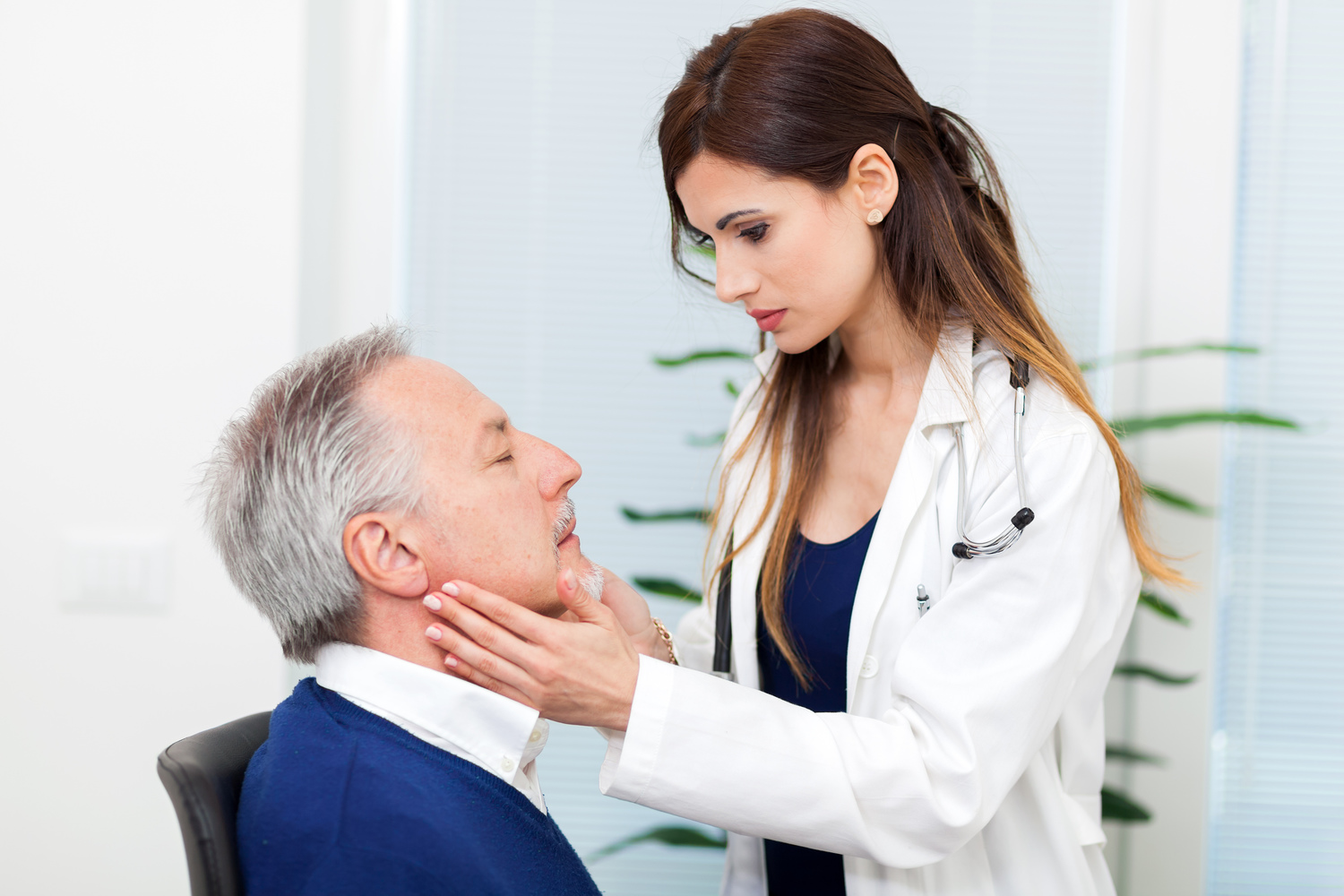

Comprehensive Guide to Swollen Neck Lymph Nodes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
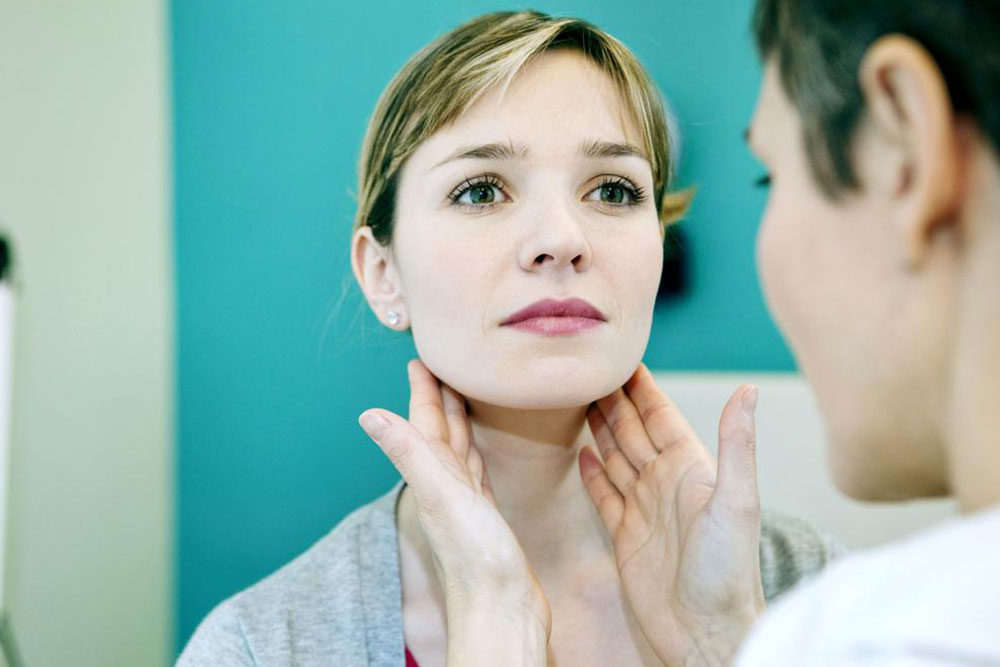
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck are a common concern that often indicates your body's natural response to various infections or underlying health issues. These enlarged glands, known medically as lymphadenopathy, are part of the lymphatic system—a vital component of immune defense. While most cases of swollen neck lymph nodes resolve on their own once the infection or cause subsides, understanding the underlying factors, symptoms, and appropriate responses is essential for maintaining health and seeking timely medical intervention.
Understanding the Physiology of Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small, round, or bean-shaped structures that are distributed throughout the body, with a concentration in the neck, armpits, groin, and abdomen. These nodes act as filters for harmful substances and are packed with lymphocytes—white blood cells that identify and fight infections. When your body detects bacteria, viruses, or other foreign substances, these lymphocytes become active, causing the lymph nodes to swell as they work to eliminate the threat.
Why Do Lymph Nodes Swell? Causes and Triggers
Swelling of lymph nodes generally occurs due to immune response activation. The typical causes include:
Infections: Common infections like the common cold, influenza, ear infections, and throat infections are among the most frequent reasons for swollen neck lymph nodes. As the immune system responds to these pathogens, the lymph nodes in the vicinity enlarge to produce more lymphocytes.
Localized infections: Dental abscesses, skin infections, or tonsillitis can also cause swelling in the nearby lymph nodes.
Chronic infections: Conditions such as tuberculosis or mononucleosis can result in persistent lymphadenopathy.
Rare but Significant Causes of Swollen Lymph Nodes
While infections are the most common triggers, some underlying health issues are less frequent but require prompt attention:
Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (lupus) or rheumatoid arthritis can cause the immune system to attack tissues, leading to swollen lymph nodes.
Malignancies: Cancers such as lymphoma, leukemia, or metastasis from other primary tumors can be the root cause of persistent or enlarging lymph nodes. These are often accompanied by other signs like unexplained weight loss, night sweats, or fatigue.
Other rare causes: Certain medications or granulomatous diseases can also contribute to lymphadenopathy.
When To Seek Medical Attention
Most swollen lymph nodes are harmless and resolve without specific treatment. However, it is crucial to recognize warning signs that indicate a need for professional medical evaluation:
The swelling appears suddenly and enlarges rapidly.
The nodes are hard, immovable, or feel matted together.
The swelling persists beyond two weeks in adults or more than five days in children.
The area around the lymph nodes becomes red, warm, or tender.
You experience systemic symptoms such as fever, unexplained weight loss, night sweats, fatigue, or persistent malaise.
You notice additional swelling or symptoms in other parts of your body.
Diagnosis Methods for Swollen Lymph Nodes
If your lymph nodes remain swollen or if you notice concerning symptoms, healthcare providers will perform thorough evaluations to determine the cause. These may include:
PET scan: This imaging technique detects metabolic activity within tissues, helping identify areas of infection, inflammation, or malignancy.
CT scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of your neck and chest, revealing the size, shape, location, and characteristics of the swollen glands.
Biopsy: In cases where malignancy is suspected, a small tissue sample from the lymph node is extracted and examined under a microscope to identify cancerous cells or other abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Swollen Neck Lymph Nodes
The management of swollen lymph nodes depends on the diagnosis:
Infections: Bacterial infections are typically treated with antibiotics, while viral infections may resolve on their own or require supportive care such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications for symptom relief.
Autoimmune conditions: Immunosuppressive drugs or corticosteroids may be prescribed to control the immune response.
Cancer: Treatment can involve chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or surgical removal of affected lymph nodes, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing symptoms early, and consulting healthcare professionals promptly can significantly affect outcomes. Regular checkups and awareness of your body's signals can help maintain overall immune health and address serious conditions before they progress.