Comprehensive Guide to the HbA1c Blood Test: Why It Matters for Your Health
Discover the critical role of the HbA1c blood test in diagnosing and managing diabetes. Learn how it reflects long-term blood sugar control, the importance of maintaining ideal levels, and effective strategies to optimize your health through regular monitoring and lifestyle changes. This comprehensive guide empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward better health by understanding their HbA1c results and preventing complications associated with poor glycemic control.
The HbA1c blood test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test, has become an essential tool in diagnosing and managing diabetes. This comprehensive screening provides an average measurement of blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, offering a more accurate reflection of long-term blood sugar control than daily blood glucose testing. Understanding the intricacies of this test can help individuals make informed health choices, effectively manage diabetes, and prevent potential complications associated with poor blood sugar regulation.
The key component in this test is hemoglobin, a vital protein found in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body. When blood sugar levels are elevated over sustained periods, glucose molecules tend to bind irreversibly to hemoglobin in a process called glycation. This process results in the formation of glycated hemoglobin, or HbA1c. The higher the blood glucose levels, the more hemoglobin becomes glycated, making HbA1c levels a reliable indicator of overall glycemic control.
The Significance of Monitoring HbA1c Levels
Regular monitoring of HbA1c levels is critical for individuals with diabetes, as it provides deep insights into the effectiveness of their treatment regimens and lifestyle modifications. An optimal HbA1c level is typically below 5%, which indicates good blood sugar management and minimal risk of developing diabetes-related complications. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest prediabetes, a warning sign indicating the need for lifestyle adjustments to prevent the onset of diabetes.
For those diagnosed with diabetes, maintaining an HbA1c level below 7% is generally recommended by healthcare providers to reduce the risk of complications such as neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular diseases. Striving for optimal HbA1c levels not only improves quality of life but also significantly decreases long-term health risks. It is equally vital for non-diabetics, especially those with risk factors like obesity, family history, or sedentary lifestyle, to undergo regular HbA1c testing to identify potential issues early and implement preventive measures.
How the Test is Conducted
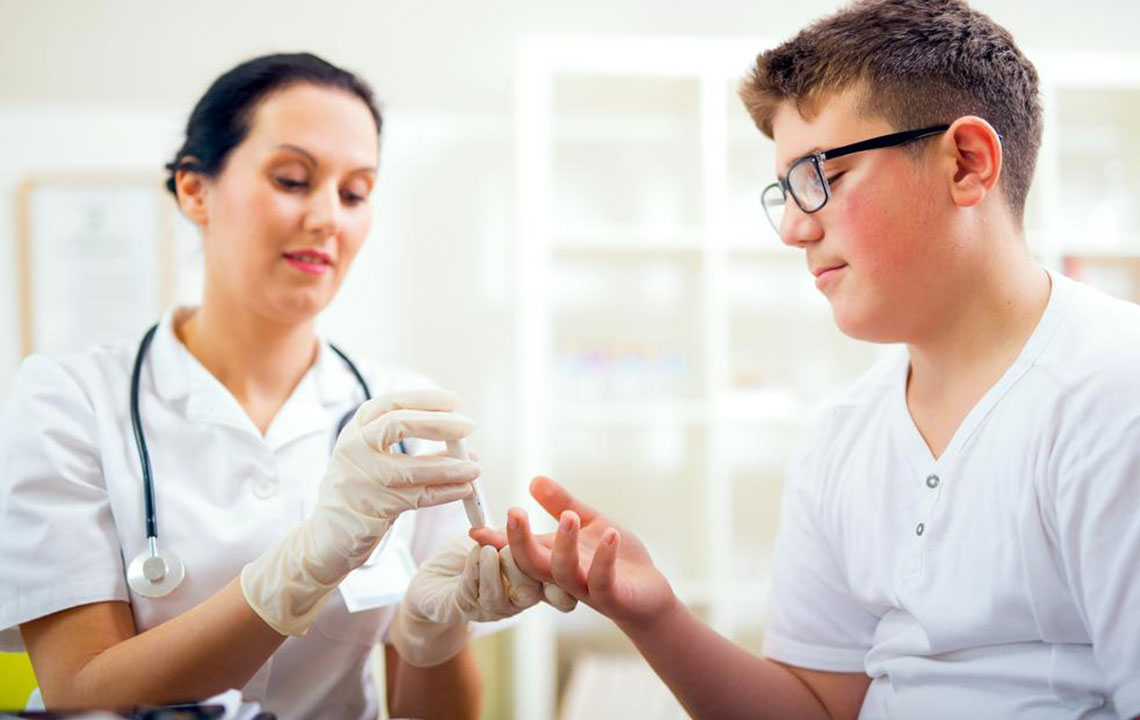
The procedure for an HbA1c test is straightforward and minimally invasive. A small sample of blood is usually drawn from a vein, similar to standard blood tests. The sample is then analyzed in a laboratory to determine the percentage of glycated hemoglobin present. These results are typically available within a few days and can be used by healthcare providers to assess overall blood sugar management.
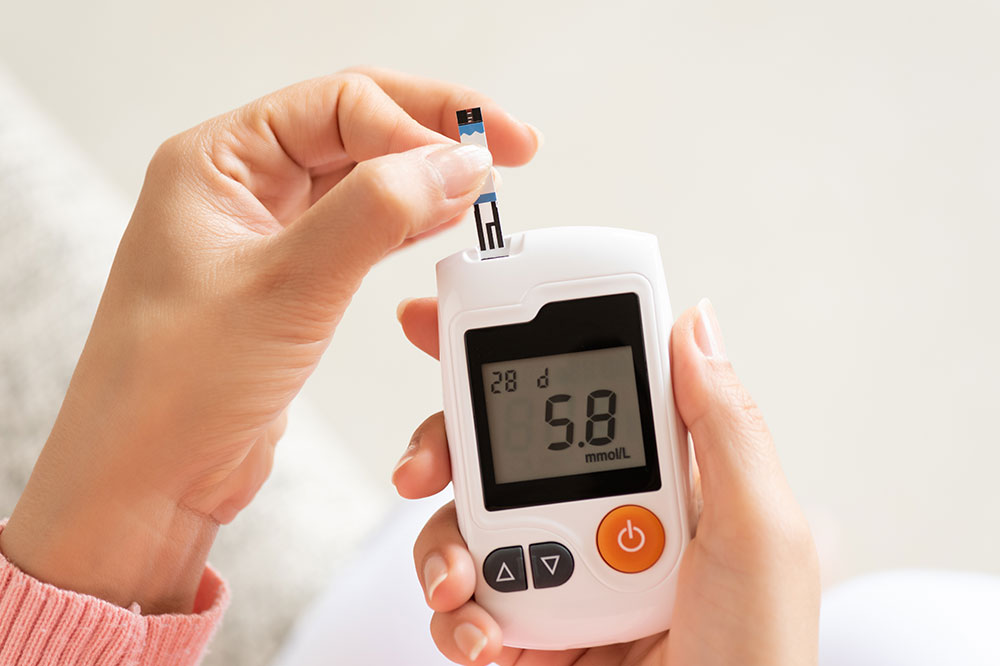
In some cases, especially in remote or resource-limited settings, there are point-of-care HbA1c testing devices that provide immediate results, allowing for quick assessment and timely intervention. It's advisable to follow your healthcare provider's recommendations regarding the frequency of testing, which might range from every three to six months depending on individual health status and treatment goals.
Factors Affecting HbA1c Accuracy
While HbA1c testing is a valuable tool, certain factors can influence its accuracy. Conditions such as anemia, hemoglobinopathies (like sickle cell disease), kidney disease, or recent blood transfusions can affect hemoglobin structure or lifespan, leading to skewed results. Additionally, race and ethnicity have been observed to influence normal HbA1c ranges, necessitating a contextual understanding of results.
Patients should inform their healthcare providers about any underlying health conditions or medications that might impact the test results. In some cases, alternative tests like fasting blood glucose or oral glucose tolerance tests may be employed alongside HbA1c to obtain a comprehensive view of glycemic control.
Strategies for Improving HbA1c Levels
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and regular monitoring. A balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and low in processed sugars and saturated fats plays a pivotal role. Incorporating regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, helps improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose levels.
Medications prescribed by healthcare providers, including insulin and oral hypoglycemics, must be taken as directed. Regular check-ups and blood testing help track progress and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Additionally, managing stress and ensuring sufficient sleep are integral components of effective blood sugar control.
Conclusion: Your Role in Managing Blood Sugar
The HbA1c blood test is more than a diagnostic tool; it's a vital component of ongoing health management for individuals at risk of or living with diabetes. It empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions that promote health and prevent complications. Early detection through regular testing can lead to timely interventions, ultimately improving health outcomes and quality of life.
Whether you have diabetes or are simply proactive about your health, understanding the significance of HbA1c testing can motivate you to adopt healthier habits and ensure your blood sugar remains within a safe range. Remember, consistent monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and medical guidance are key to maintaining optimal HbA1c levels and enjoying a healthier life.