Comprehensive Guide to Managing Eczema: Effective Treatments and Home Remedies
This comprehensive guide explores effective eczema treatments, including medications, therapies, and natural home remedies. It offers practical tips on preventing flare-ups and managing symptoms through lifestyle adjustments. Readers will learn about various medical interventions, natural soothing techniques, and preventative strategies to improve skin health and reduce eczema severity. Perfect for those seeking a detailed, reliable resource on managing chronic eczema, this article emphasizes a holistic approach to skin care and symptom relief, enhancing quality of life for sufferers.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Eczema: Effective Treatments and Home Remedies
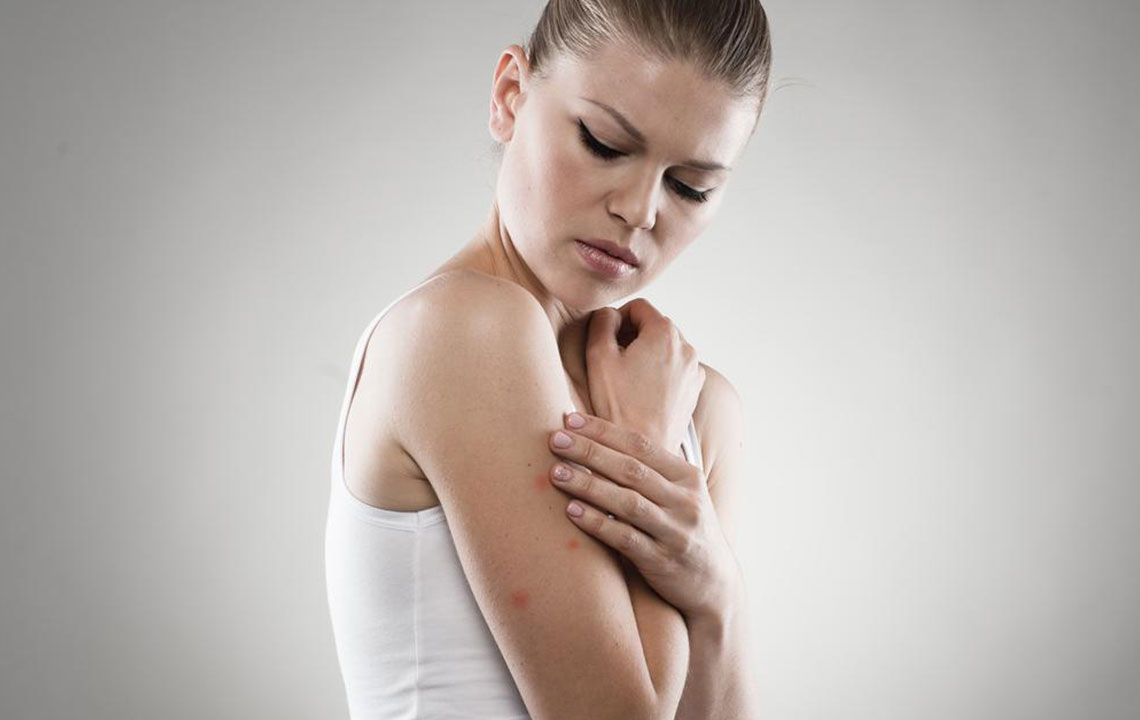
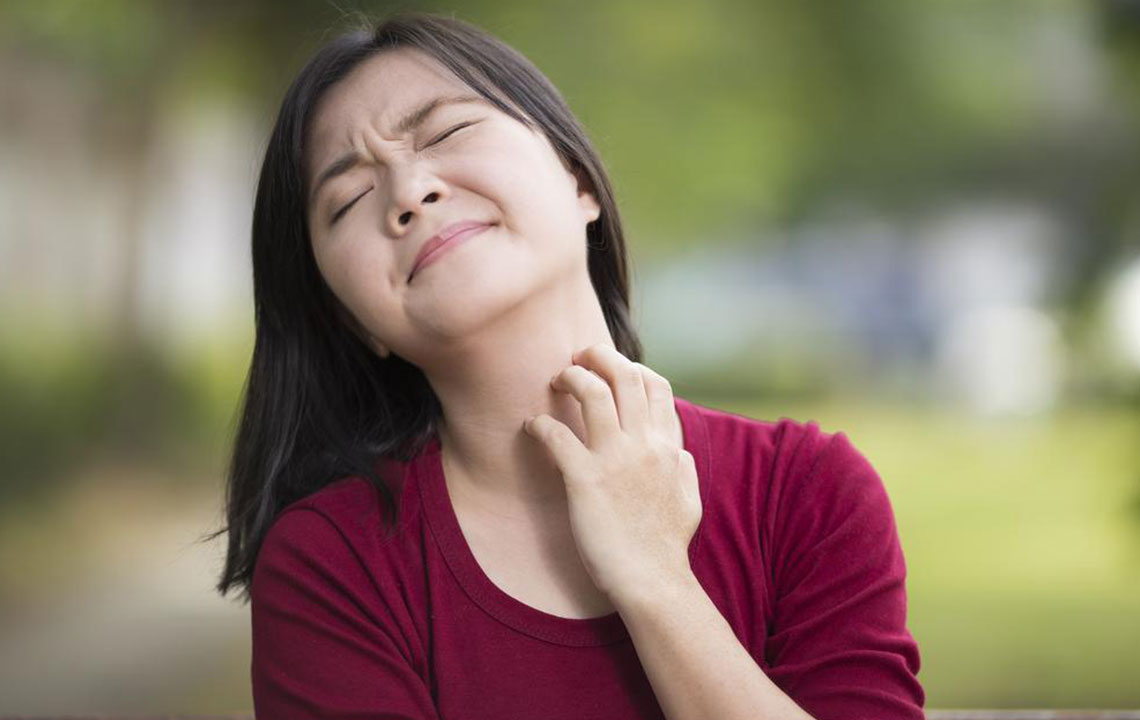
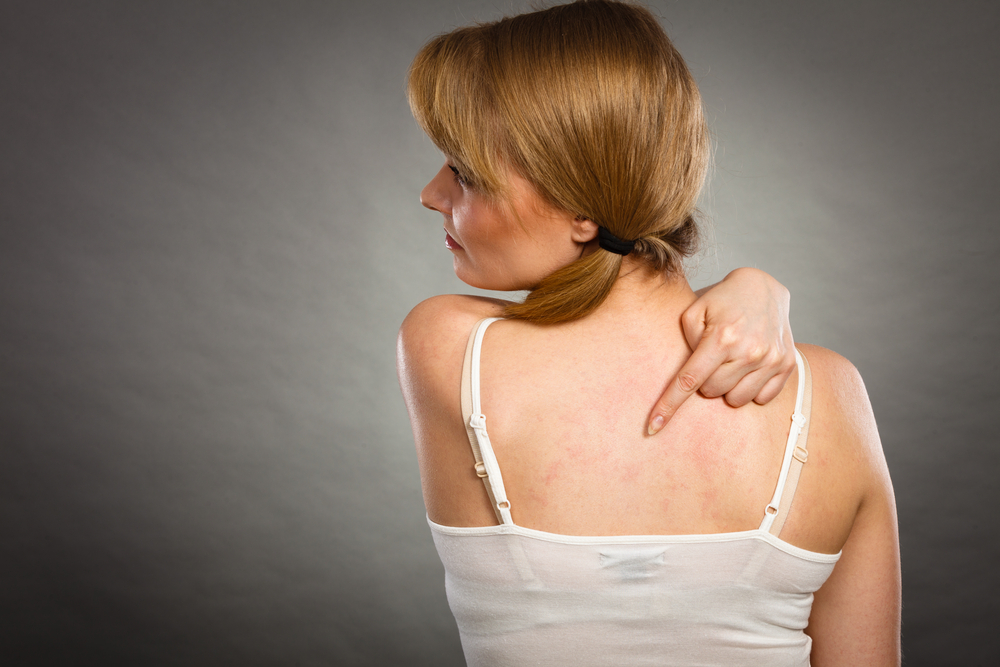
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Living with eczema requires patience and a strategic approach to manage symptoms effectively and prevent flare-ups. While the condition can be persistent, understanding available treatments and home care strategies can significantly improve quality of life. This comprehensive guide covers various treatment options, including medications, specialized therapies, and natural remedies, along with practical tips for preventing eczema episodes and managing symptoms at home.
Effective eczema management often involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments. Regularly monitoring skin condition, comparing it to eczema reference images, helps healthcare providers track progress and tailor treatments. The primary goal is to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, prevent infections, and restore skin barrier strength. Whether you're dealing with mild or severe eczema, understanding your options will empower you to make informed decisions and adopt effective routines for healthier skin.
Leading Medical Treatments for Eczema
Managing eczema often begins with the right medications, prescribed by healthcare professionals after careful assessment of your skin's condition. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation, control itching, and prevent infections or complications. Understanding the different options can help patients collaborate effectively with their healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans.
Medications Frequently Used for Eczema Relief
Topical Corticosteroids: These are the most common medications used to combat inflammation directly on the skin. Available in various strengths, corticosteroid creams and ointments are effective for mild to moderate eczema. However, overuse or prolonged use can cause side effects such as skin thinning or stretch marks. Therefore, it's essential to follow your doctor's instructions carefully and avoid excessive application.
Calcineurin Inhibitors: These are non-steroidal topical medications like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, which help modulate immune responses in the skin. They are especially useful for sensitive areas such as the face or around the eyes, where corticosteroids might cause adverse effects.
Antibiotics: Eczema can sometimes be complicated by bacterial infections, especially Staphylococcus aureus. When this occurs, antibiotics or antibiotic ointments may be prescribed to eliminate bacterial colonization and prevent further skin deterioration.
Antihistamines: To control severe itching and allergic reactions, oral antihistamines can be beneficial, especially during flare-ups or when associated with allergies.
Advanced Therapies for Severe Eczema Cases
For more persistent or extensive eczema, healthcare providers may recommend specialized therapeutic interventions designed to target stubborn symptoms and promote skin healing.
Wet Dressings: This technique involves applying corticosteroids or emollients under damp dressings, which can help soothe inflamed skin and accelerate healing. Typically performed in clinical settings, wet dressings are highly effective for severe or widespread eczema.
Phototherapy: Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light, particularly narrowband UVB or UVA light. This method helps suppress immune responses contributing to eczema inflammation and is suitable for cases resistant to topical treatments.
Systemic Medications: In very severe cases, doctors might prescribe systemic medications like immunosuppressants or biologics. These drugs modulate the immune system more broadly to control extensive or refractory eczema but require careful supervision due to potential side effects.
Natural and Home Remedies for Eczema Relief
In addition to medical treatments, many individuals find relief through natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments. Proper skin care routines and home-based interventions can support overall skin health and reduce eczema flare-ups.
Vegetable Shortening and Barrier Repair: Applying a thick layer of kitchen-grade vegetable shortening or similar emollients on affected areas can help lock in moisture and protect irritated skin. Covering the area with plastic wrap after application may enhance absorption. This simple home remedy can soothe dry, inflamed patches temporarily.
Aloe Vera Gel: Known for its healing and anti-inflammatory properties, fresh aloe vera gel directly from a plant leaf can be applied to calm itching and reduce redness. Regular use can support skin hydration and accelerate healing processes.
Coconut Oil: Virgin coconut oil is another natural moisturizer with antimicrobial properties. Regular application can restore the skin barrier and prevent bacterial colonization.
Oatmeal Baths: Colloidal oatmeal baths are a popular home remedy to soothe itchy, inflamed skin. Adding finely ground oats to warm bathwater can provide relief and moisturization.
Preventative Measures and Skin Care Tips
Prevention is a crucial aspect of managing eczema effectively. Implementing good skin care practices and avoiding known triggers can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
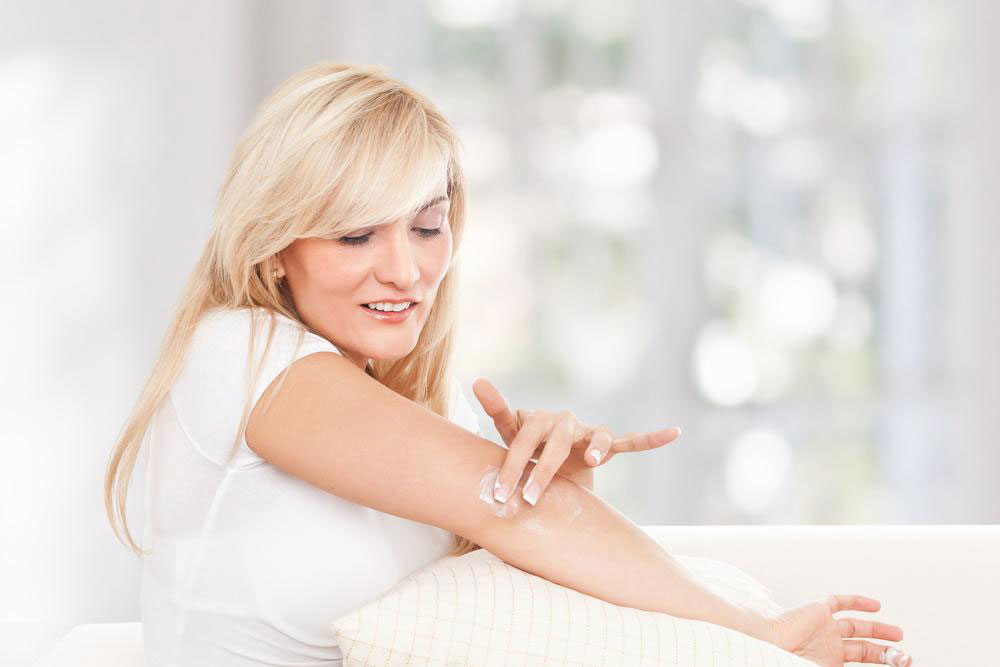
Consistent Skin Moisturization: Regularly applying emollients, creams, or ointments, particularly after bathing, forms a protective barrier on the skin. For infants or sensitive skin, petroleum jelly or mineral oil can be highly effective and safe options.
Trigger Avoidance: Identifying and steering clear of common eczema triggers is vital. These include allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods (eggs, dairy, soy, wheat), as well as irritants such as soaps, fragrances, and harsh detergents. Managing stress and avoiding excessive sweating can also help prevent flare-ups.
Bathing Practices: Taking lukewarm baths rather than hot water avoids stripping natural oils. Using gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and patting dry instead of rubbing helps maintain skin integrity.
Bleach or Bacterial Control Baths: Diluted bleach baths, recommended by dermatologists, can reduce bacterial colonization, helping to prevent infections and prolong remission periods.
Eczema management is most effective when combining appropriate medical treatment with proactive skincare and lifestyle choices. Staying informed about your condition, working closely with healthcare professionals, and adopting healthy habits can lead to significant improvements in skin health and overall comfort.