Comprehensive Guide to Effective Management of Scabies Skin Rash
This comprehensive guide explains effective strategies for managing scabies, including recognizing symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods. It emphasizes the importance of prompt, correct treatment and environmental decontamination to prevent transmission, ensuring quick recovery and minimizing complications from this highly contagious skin condition.
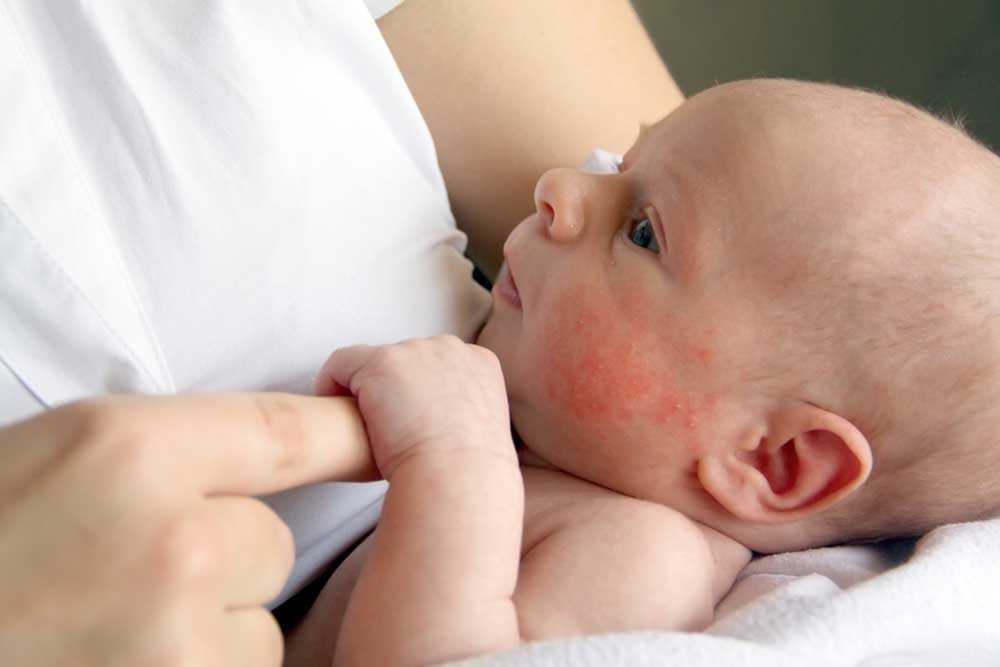
Effective Strategies for Managing Scabies Skin Rash
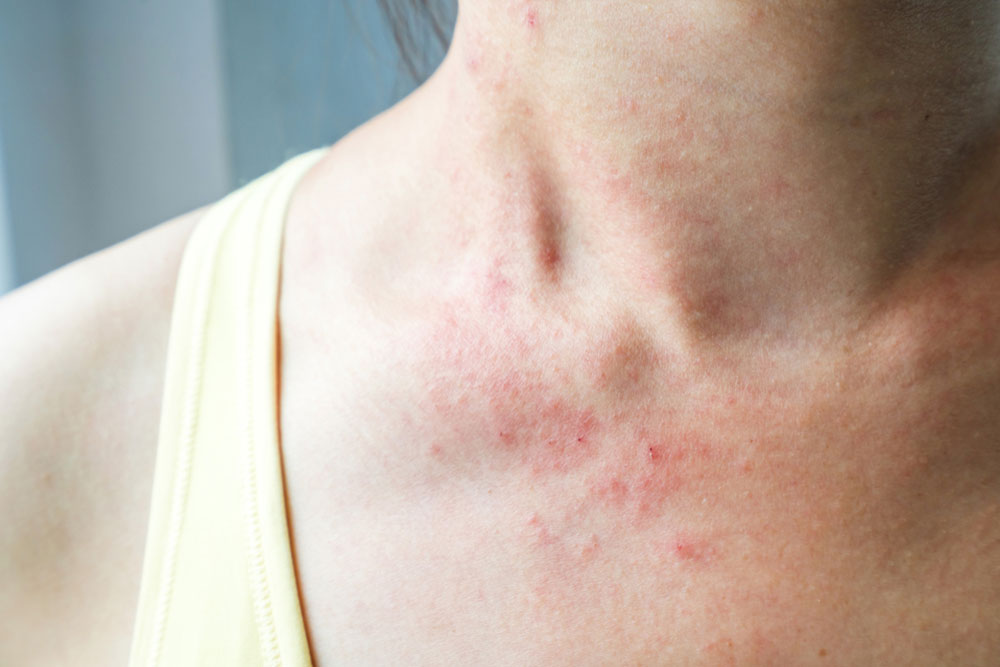
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei. It manifests primarily through intense itching, redness, and rash, often leading to significant discomfort and sometimes secondary infections. Understanding the nature of scabies, its symptoms, and the best treatment approaches is crucial to managing this condition effectively. This detailed guide explores the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for scabies, helping patients and healthcare providers alike to combat this common yet often misunderstood skin disorder.
Scabies occurs when the Sarcoptes scabiei mite burrows into the skin to lay its eggs, leading to a persistent rash and relentless itching. Because the mites can survive on or inside the human skin for months if untreated, scabies becomes highly contagious, spreading rapidly among close contacts and in crowded environments. Prompt recognition and comprehensive treatment are essential to prevent reinfection and control outbreaks.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Scabies
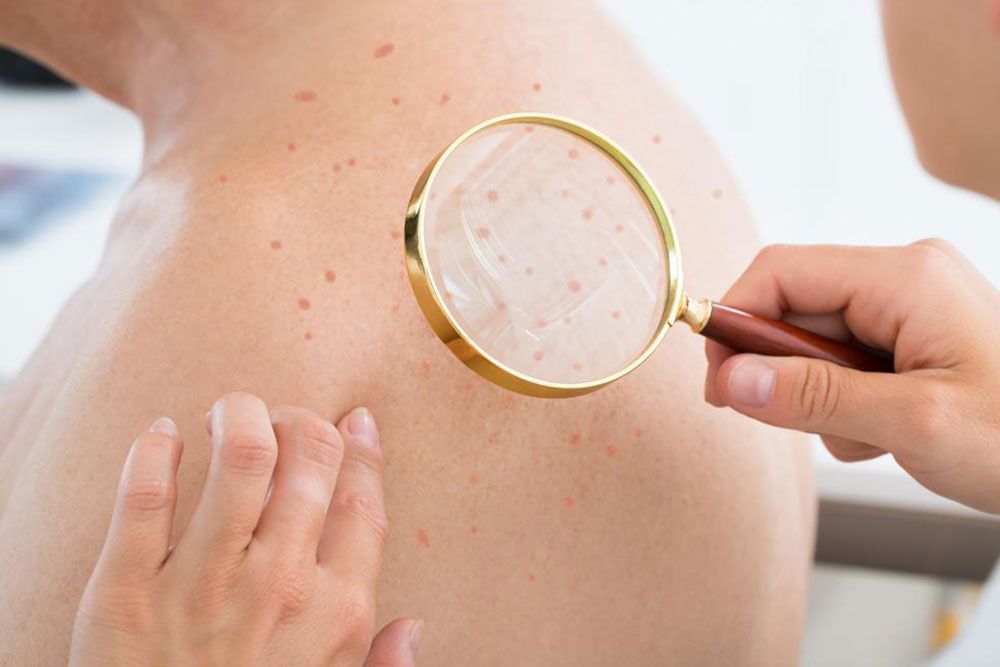
Detecting scabies early can significantly aid in effective management. The most common symptoms include:
Intense, persistent itching that worsens at night
The appearance of small blisters, pimple-like bumps, or scales
Rash that resembles pimples or insect bites
Sores or crusted lesions resulting from excessive scratching
In the initial stages, scabies can mimic other skin conditions like insect bites, eczema, or acne. Due to the subtlety of early symptoms, it’s advisable to photograph the rash and consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis before initiating treatment.
Effective Treatment Options for Scabies
Managing scabies involves eradicating the mites and their eggs using prescribed medications. Topical treatments remain the mainstay of therapy and are most effective when applied correctly and consistently. Here are the key approaches:
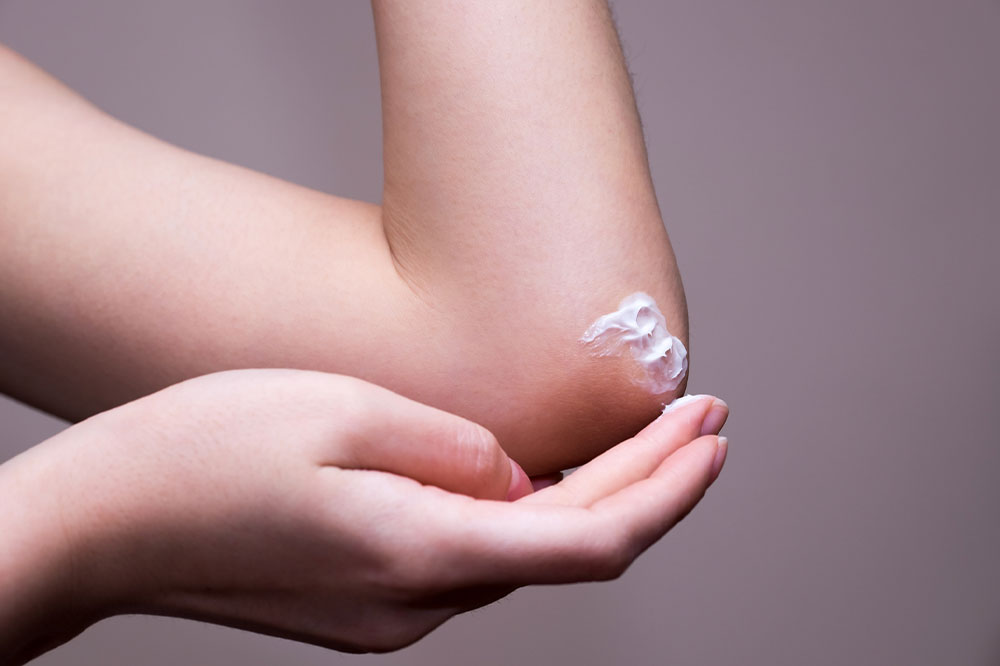
Topical Medications: These include ointments, lotions, and creams directly applied to affected areas. The most common agents include permethrin cream, crotamiton, lindane lotion, sulfur ointment, and benzoate lotions. To maximize effectiveness, topical treatments should be applied at night when mites are most active, usually covering the entire body, excluding the face unless otherwise directed. The treatment is typically left on for 8-14 hours and washed off in the morning. In many cases, a repeat application is recommended after one week to eliminate any remaining mites and eggs.
Oral Medications: When topical treatments fail, or in severe cases such as crusted or Norwegian scabies, systemic therapy may be necessary. Common oral options include ivermectin, which is administered in doses dictated by the patient’s weight and severity of infestation. Oral treatments are often used in conjunction with topical therapy to ensure complete eradication of mites.
During treatment, it's critical to follow healthcare provider instructions precisely. This includes proper application techniques and adherence to prescribed schedules to prevent re-infestation.
Managing Symptoms and Preventing Spread
Alongside anti-mite medications, managing symptoms and preventing reinfection require additional measures:
Secondary Infection Control: Scratching can cause open sores, which may become infected with bacteria. Antibiotics—either topical or oral—are prescribed if signs of bacterial infection such as pus or increased pain appear.
Reducing Inflammation and Discomfort: Steroid creams can help reduce inflammation and swelling caused by the immune response. Antihistamines or soothing lotions like pramoxine may also be recommended to control itching.
Hygienic Measures and Decontamination: Washing bedding, clothing, and towels in hot water and sealing non-washable items in plastic bags can minimize the risk of re-infestation. Vacuuming furniture and carpets adds a further layer of control.
It's essential to treat all close contacts simultaneously, even if asymptomatic, to prevent re-infection and halt the spread within households, schools, or care facilities.
Understanding the Timeline and Follow-Up
Most patients start to notice an improvement within the first week of proper treatment, with itching gradually decreasing. Significant relief is often observed within two weeks. Complete resolution of symptoms and skin healing generally takes about four weeks. However, if symptoms persist beyond this period or worsen, additional consultation with a healthcare provider is necessary. They might need to reassess the diagnosis or suggest alternative treatments. Documenting progress through photographs and maintaining a symptom diary can be helpful during follow-up appointments.
In summary, managing scabies requires a comprehensive approach involving accurate diagnosis, effective medication application, symptom management, environmental decontamination, and caregiver education. With prompt and correct treatment, the prognosis for scabies is excellent, minimizing discomfort and preventing further transmission.