Comprehensive Guide to Ringworm: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Prevention Methods
This comprehensive article explores ringworm, covering its causes, how it spreads, symptoms to watch for, diagnosis methods, and effective prevention tips. It emphasizes the importance of hygiene, early treatment, and veterinary care, offering practical advice for individuals of all ages. Understanding these key aspects helps reduce the risk of infection and curtail transmission, especially in communal settings or among pets. With proper hygiene and awareness, the spread of this common fungal infection can be effectively controlled, ensuring healthier skin for everyone.
Understanding Ringworm: Causes, Symptoms, Transmission, and Prevention Strategies
Ringworm is a ubiquitous fungal infection that affects millions worldwide, characterized by distinctive circular skin rashes. Despite its name, it has nothing to do with worms; rather, it is caused by dermatophyte fungi that thrive on keratin, the protein found in skin, hair, and nails. This infection is highly contagious and can spread rapidly through various modes of contact, making awareness and timely intervention essential. Fortunately, with proper hygiene practices and preventive measures, the risk of contracting or spreading ringworm can be significantly reduced.
What Is Ringworm?
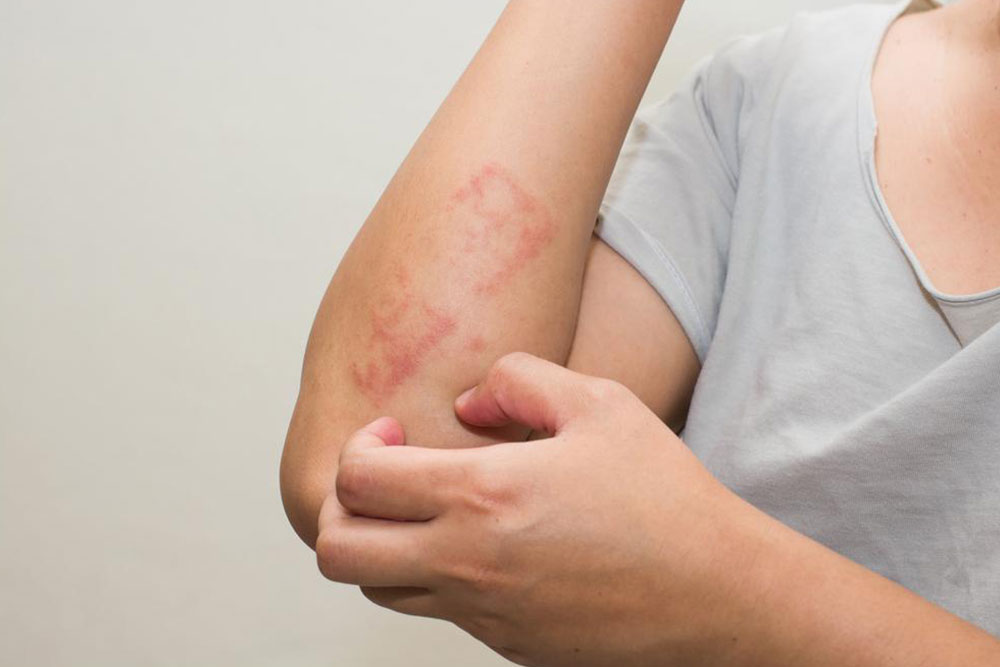
Ringworm, medically known as dermatophytosis, is a common superficial fungal infection affecting different parts of the body. The hallmark of this condition is a red, circular, sometimes scaly rash that often appears itchy and inflamed. Despite its name, there are no worms involved; instead, fungi called dermatophytes cause the infection. These fungi flourish on the outer layers of skin and can be transmitted between humans, animals, and contaminated surfaces. The infection is prevalent across all age groups but tends to be more common among children, athletes, and individuals with compromised immune systems.
How Does Ringworm Spread?
The transmission of ringworm occurs primarily through contact with infected individuals or animals, as well as contact with contaminated surfaces. The fungi responsible for ringworm can persist on objects for extended periods, posing a risk to others who come into contact with them. The main routes of transmission include:
Direct skin-to-skin contact with someone who is infected. This is particularly common among children and athletes engaged in contact sports.
Contact with contaminated clothing, towels, bedding, or clothing that harbor fungal spores.
Handling infected animals, especially cats, dogs, and livestock, which are common reservoirs for dermatophyte fungi.
Touching contaminated soil or playing in outdoor environments with fungal spores present.
Risk Factors Contributing to Ringworm Infection
While anyone can develop ringworm, certain factors increase susceptibility, including:
Wearing tight or restrictive clothing, which may trap moisture and promote fungal growth.
Having a weakened immune system due to illness, medication, or chronic conditions.
Living in warm, humid environments that facilitate fungal proliferation.
Participation in contact sports like wrestling, football, or martial arts without proper hygiene measures.
Sharing personal items such as towels, clothes, hats, or bedding with infected individuals or animals.
Understanding these factors can help individuals take proactive steps to minimize their risk of infection.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Ringworm
Early detection of ringworm is key to effective treatment and preventing spread. Common signs and symptoms include:
Itchy skin patches that may feel scaly or rough.
Ring-shaped or circular red areas with clear centers, giving the classic 'ring' appearance.
Raised, inflamed borders that may be slightly swollen or blistered.
Overlapping rings or multiple lesions that expand over time.
In cases involving the scalp or nails, hair loss or thickened, discolored nails may be observed.
Infected areas may sometimes crack, peel, or ooze if scratched excessively.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Ringworm
Accurate diagnosis is usually straightforward. Healthcare professionals typically examine the affected skin, noting characteristic changes. To confirm the diagnosis, they may perform:
Skin scrapings examined under a microscope to identify fungal elements.
Fungal cultures to determine the specific dermatophyte involved.
Wood's lamp examination to detect certain fungal strains that fluoresce under UV light.
Treatment depends on the affected area and severity:
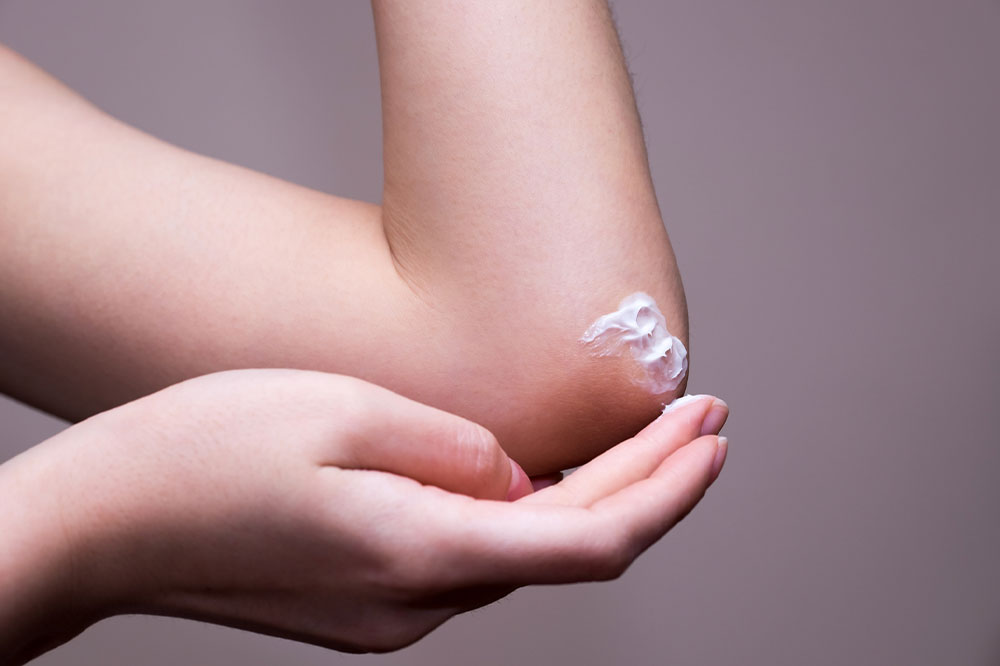
For mild skin infections, over-the-counter antifungal creams, lotions, or powders containing clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine are often sufficient. Applying them consistently and for the recommended duration is vital to prevent recurrence.
Persistent or extensive infections may require prescription oral antifungal medications, such as griseofulvin or terbinafine, especially for scalp or nail involvement. These medications have systemic effects and should be used under medical supervision.
In scalp infections, medicated shampoos containing ketoconazole or selenium sulfide might be prescribed to reduce fungal load and promote healing.
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers ensures proper management and protective measures to avoid reinfection.
Precautions Against Unwise Use of Steroid Creams
Applying steroid creams without medical guidance can temporarily reduce inflammation but may worsen fungal infections by suppressing immune responses and enabling fungi to penetrate deeper layers. Always consult a healthcare professional before using topical steroids on suspected ringworm lesions.
Effective Prevention Strategies to Avoid Ringworm
Preventing ringworm requires a combination of good hygiene practices and behavioral measures:
Maintain daily personal hygiene, including regular handwashing with soap and water.
Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, combs, hats, or clothing.
Keep bedding, clothing, and towels clean and thoroughly dry before reuse.
Change socks and underwear daily to prevent moisture buildup.
Wear protective footwear, particularly in public showers, swimming pools, and locker rooms where fungi may be present.
Pet owners should regularly check their animals for signs of infection and seek veterinary care when necessary.
Educate children and family members about the importance of hygiene and early detection of skin changes.
Implementing these preventive measures can significantly lower the likelihood of developing or spreading ringworm, protecting both individual and community health.