Understanding Causes of Swollen Ankles and Effective Treatment Strategies
Swollen ankles can stem from injuries, heart or kidney issues, obesity, or medication side effects. Recognizing the cause is vital for effective treatment. This comprehensive guide explains common reasons behind ankle swelling and offers practical solutions to manage and prevent discomfort, enhancing mobility and overall health.
Understanding Causes of Swollen Ankles and Effective Treatment Strategies
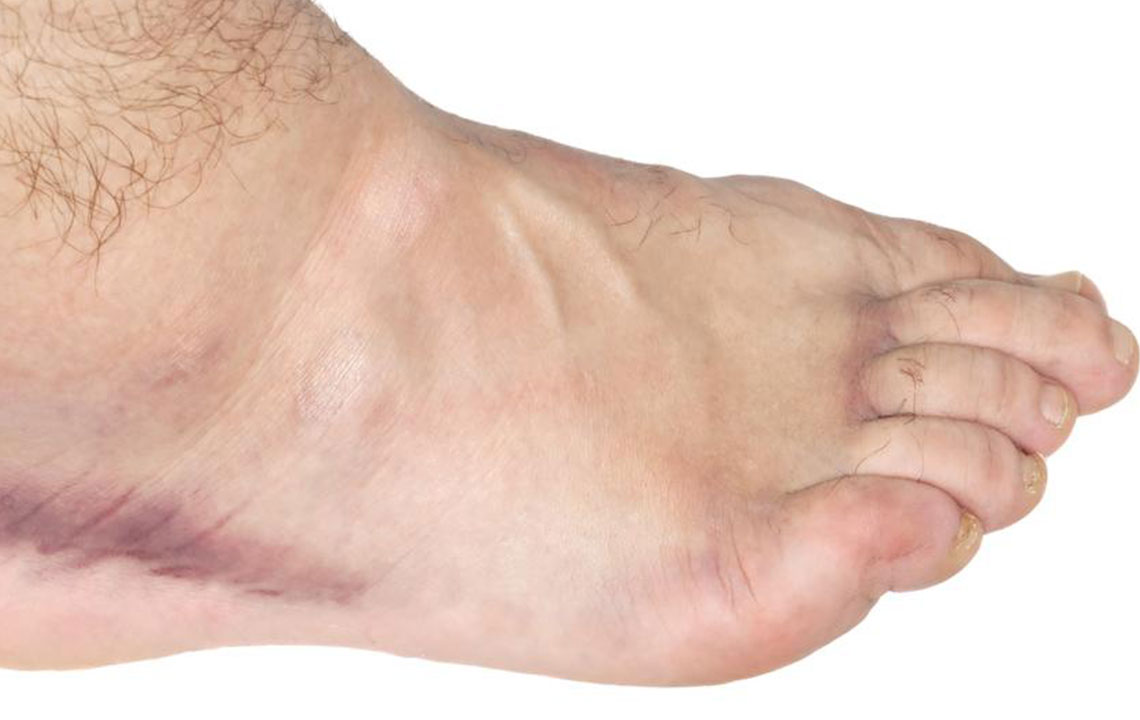
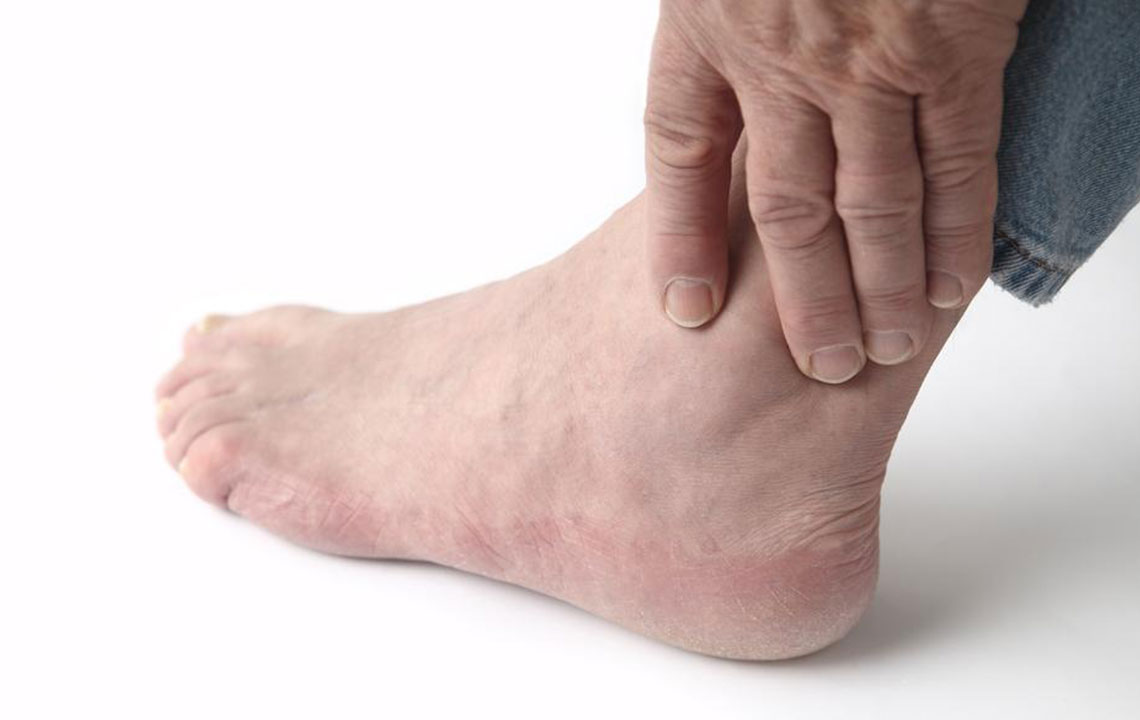
The health and functionality of our lower limbs, particularly the legs and ankles, are vital for maintaining mobility, independence, and overall well-being. These areas are constantly engaged in daily activities such as walking, standing, and running, which unfortunately makes them susceptible to various injuries and medical conditions resulting in swelling or edema. Swelling in the ankles can significantly impact quality of life, causing discomfort and limited movement. Recognizing the underlying causes of ankle swelling is essential for developing appropriate treatment plans and preventing complications.
Inflammation and swelling of the ankles can arise from a wide range of reasons, spanning from injuries to chronic health issues. While some causes are temporary and resolve quickly, others require long-term management and medical intervention. Here, we delve into the most common reasons behind swollen ankles, providing insight into how each condition manifests and the best ways to address them.
Common Causes of Swollen Ankles
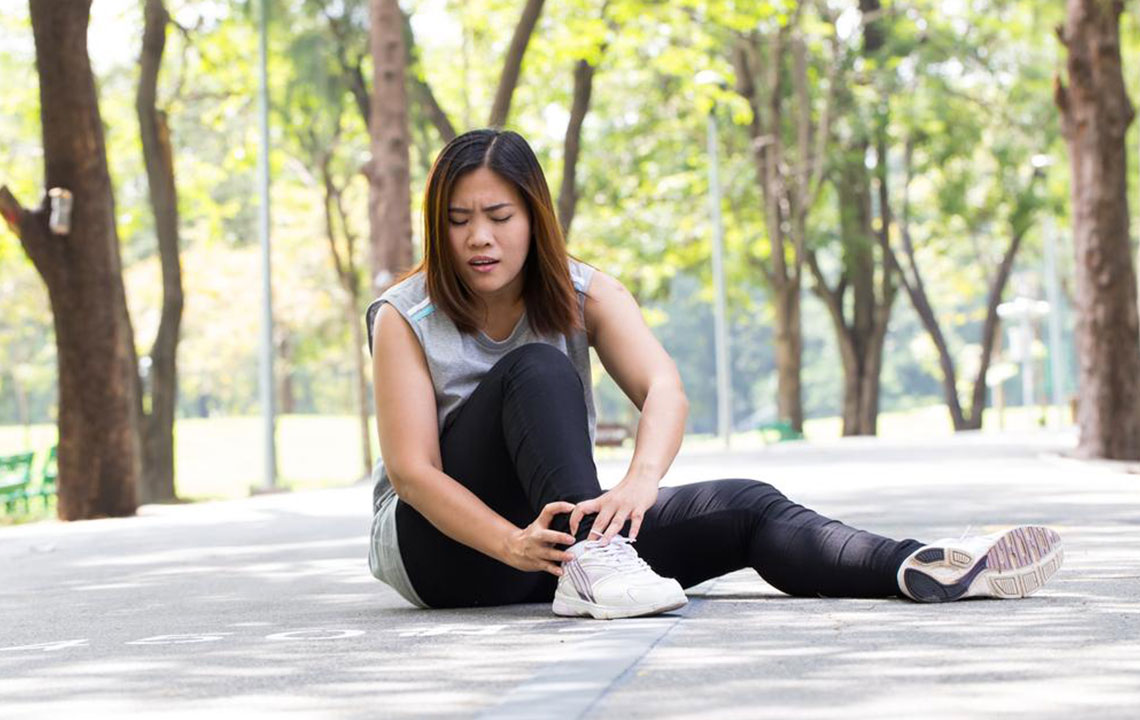
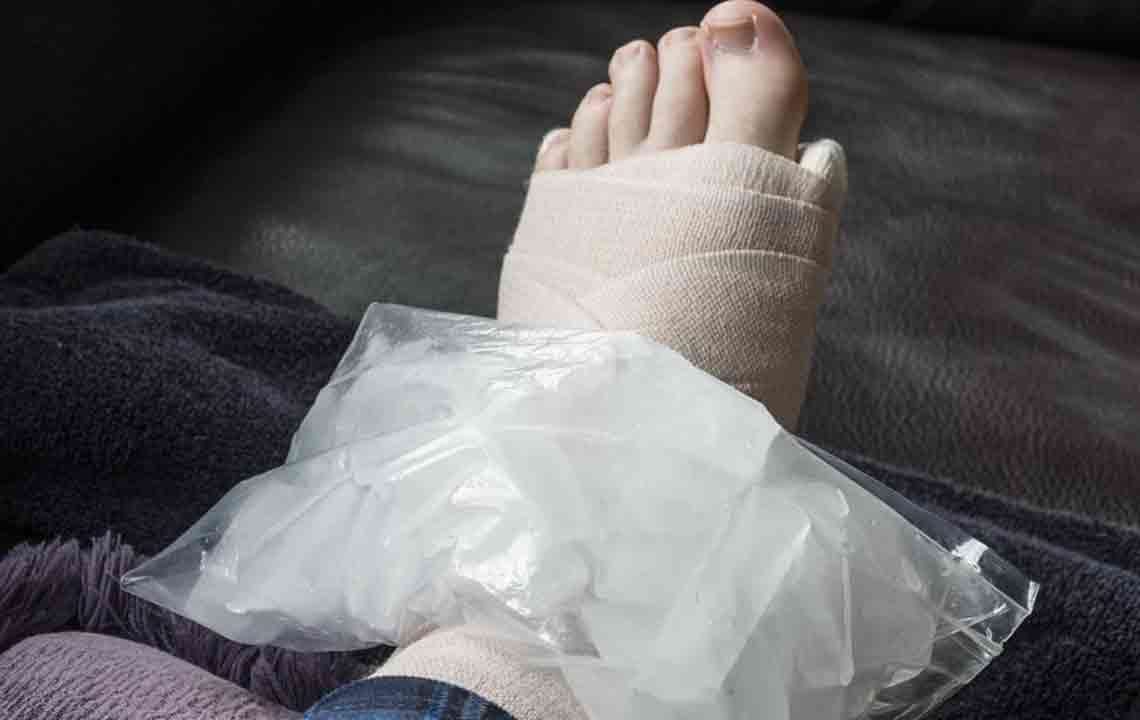
Ankle Sprains: Ankle sprains are among the most frequent injuries leading to swelling, often resulting from sudden twists, falls, or missteps. This injury occurs when the ligaments supporting the ankle are stretched or torn, leading to pain, inflammation, and visible swelling. Athletes involved in sports like basketball, football, or running are particularly prone to such injuries. Prompt treatment, including rest, ice application, compression, and elevation (the R.I.C.E. method), is crucial. Severe sprains may require medical evaluation and physical therapy for full recovery.
Heart-Related Conditions: Conditions such as congestive heart failure (CHF) can cause fluid retention in lower extremities. When the heart's chambers are weakened or inefficient, blood circulation diminishes, leading to fluid buildup in legs and ankles. This type of swelling often occurs symmetrically and worsens throughout the day. Managing heart-related swelling involves medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes physiotherapy that minimizes stress on the heart to improve circulation.
Excess Body Weight and Obesity: Carrying extra weight puts increased pressure on the lower limbs, especially the feet and ankles. This added load can impair lymphatic and venous return, leading to chronic swelling or edema. Losing weight through a balanced diet and engaging in regular, controlled physical activity significantly reduces swelling and improves overall vascular health.
Kidney Dysfunction: Impaired kidney function reduces the body's ability to filter waste and excess fluid from the blood. This can lead to systemic edema, prominently affecting the ankles and lower legs. Symptoms may include swelling, fatigue, and changes in urine output. Managing kidney-related swelling necessitates medical intervention, including medications, dietary adjustments, and sometimes dialysis, depending on the severity of kidney disease.
Liver Diseases and Cirrhosis: Liver conditions can alter blood flow and protein levels in the blood, leading to fluid leakage into surrounding tissues. Edema resulting from liver issues often presents as swelling in the ankles, along with abdominal distention and jaundice. Proper diagnosis and treatment of liver ailments are essential for alleviating swelling and addressing the root cause.
Medications and Side Effects: Certain medications, including antihypertensives, steroids, and NSAIDs, may cause fluid retention as a side effect. If swelling develops after starting a new medication, consultation with a healthcare provider is vital to adjust dosage or consider alternative therapies.
Other Causes: Conditions such as lymphatic obstruction, pregnancy-related edema, infections, and physical inactivity can also contribute to ankle swelling. Each scenario requires tailored management strategies to reduce swelling and prevent further health complications.
Effective Strategies to Address Swollen Ankles
Treatment approaches depend heavily on diagnosing the underlying cause. Nevertheless, certain general measures can help reduce ankle swelling, alleviate discomfort, and restore mobility:
Rest and Elevation: Keeping the affected ankle elevated above heart level helps facilitate fluid drainage and reduces swelling. Resting minimizes further injury or aggravation of swelling.
Applying Ice: Cold therapy constricts blood vessels, reducing inflammation and pain. Ice packs should be applied for 15-20 minutes every few hours during the initial phase of injury or flare-up.
Compression: Using compression stockings or bandages can support the ankle, prevent fluid accumulation, and improve circulation.
Physical Therapy and Exercise: Guided exercises improve muscle tone, enhance blood flow, and promote lymphatic drainage. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in recovery from sprains and chronic conditions.
Medication and Medical Treatment: In cases of systemic issues like heart or kidney disease, medications aimed at managing the primary condition are essential. Diuretics may be prescribed to help eliminate excess fluid, but only under medical supervision.
Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, reducing salt intake, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption are vital for controlling swelling related to chronic health issues.
Monitoring and Regular Check-ups: Regular health assessments enable early detection and management of underlying conditions, preventing severe edema or complications.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Persistent or severe swelling should never be ignored. If ankle swelling lasts more than a few days despite home remedies, or if it is accompanied by symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, fever, or significant discomfort, immediate medical attention is necessary. These signs may indicate serious health issues requiring urgent intervention. A healthcare professional can perform diagnostic tests, including ultrasound, blood work, or imaging, to determine the precise cause and formulate an effective treatment plan.
In summary, swollen ankles are common but often manageable with timely diagnosis and appropriate care. Understanding the various causes helps in implementing effective preventive and treatment strategies, ensuring better mobility, comfort, and overall health.