Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Effectively Managing Swollen Ankles
Swollen ankles are a common condition that can result from various causes including injury, fluid retention, pregnancy, or underlying health issues. This comprehensive guide explains how to identify, prevent, and treat ankle edema effectively, emphasizing the importance of medical evaluation for persistent swelling. Self-care methods such as rest, elevation, and compression are effective for minor cases, but severe cases require professional intervention. By understanding the causes and available treatments, individuals can better manage symptoms and prevent complications, ensuring healthier, pain-free ankles.

Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Effectively Managing Swollen Ankles
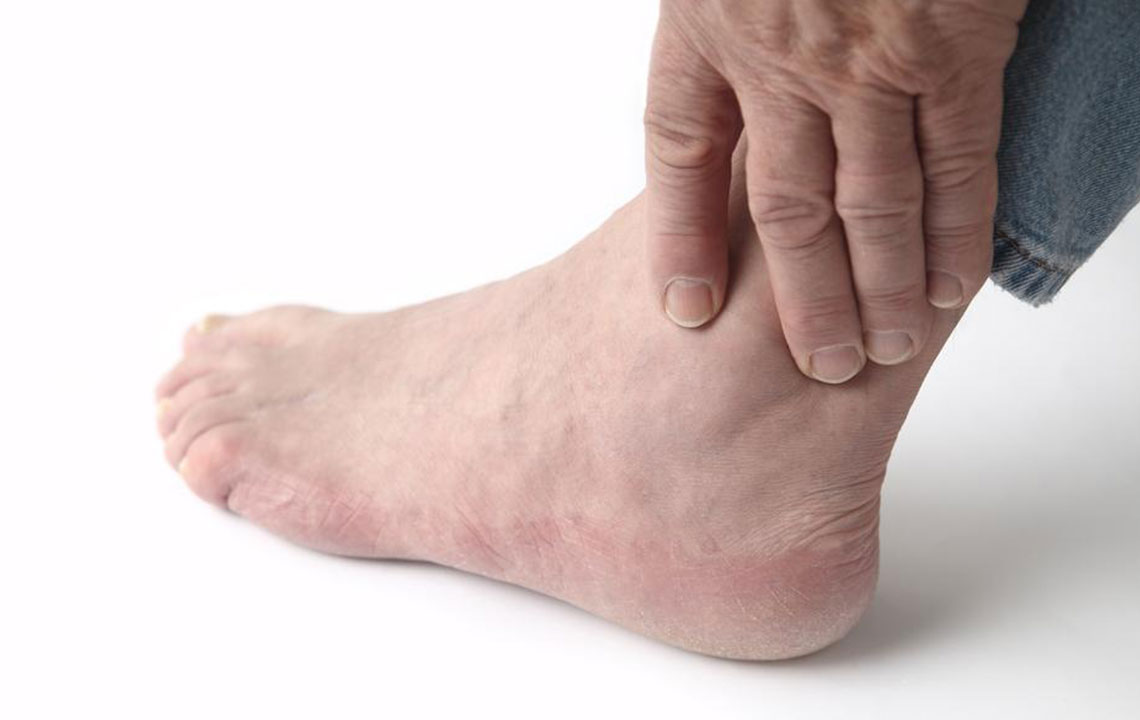
Swelling in the ankles, medically known as ankle edema, is among the most common discomforts experienced by individuals of all ages. Although often considered benign, persistent or severe swelling can sometimes point to underlying health issues that require prompt medical attention. Many people encounter swollen ankles after long periods of standing, walking, or exposure to hot weather, which can cause temporary fluid accumulation. However, understanding the root causes and knowing how to manage this condition is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing complications.
In this detailed guide, we explore the numerous causes behind swollen ankles, effective treatment options, preventive measures, and when it is necessary to seek professional medical care. Recognizing the underlying reasons behind ankle swelling is essential for choosing the correct treatment approach and ensuring optimal recovery.
Swollen ankles can be caused by various factors, including physiological changes during pregnancy, environmental conditions like high temperatures, injuries, fluid retention (edema), and lymphatic system issues such as lymphedema. During pregnancy, hormonal fluctuations and increased body weight can lead to edema, which is usually harmless but sometimes signals more serious conditions like preeclampsia. Hot weather causes blood vessels to dilate, affecting blood flow and leading to swelling. Injuries from sprains or fractures can induce inflammatory responses, resulting in swelling and discomfort. Edema, characterized by abnormal fluid buildup, often results from cardiovascular, kidney, or liver problems, while lymphedema stems from lymphatic fluid obstruction following surgeries or radiation therapy for cancer.
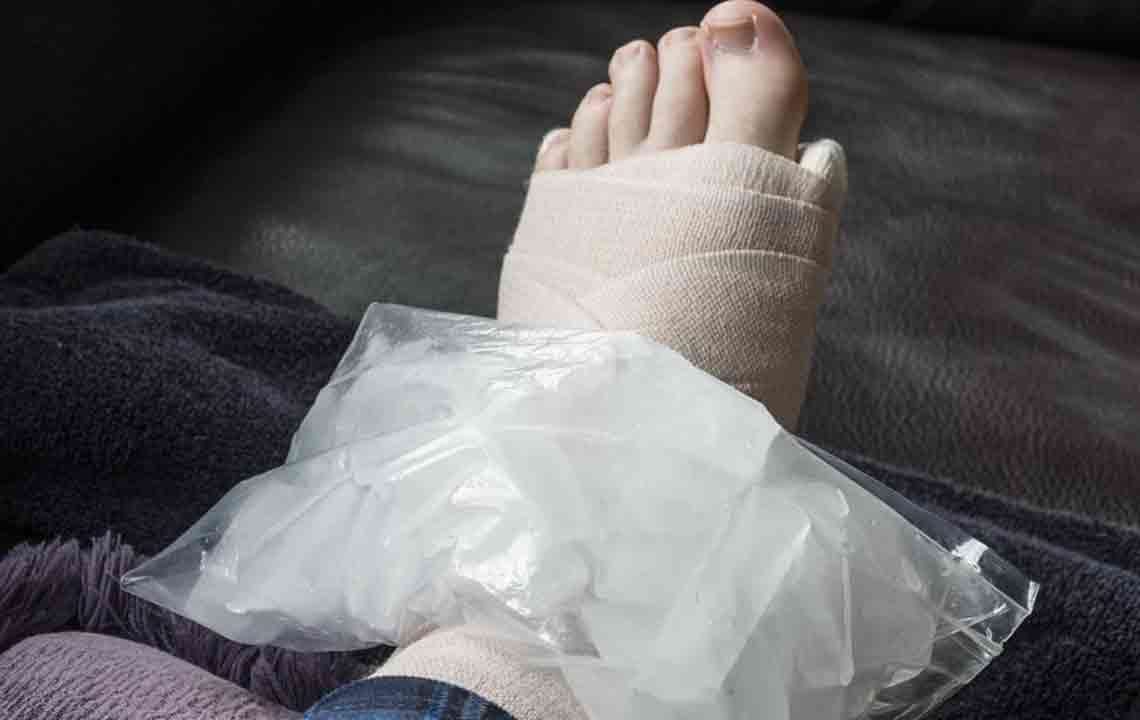
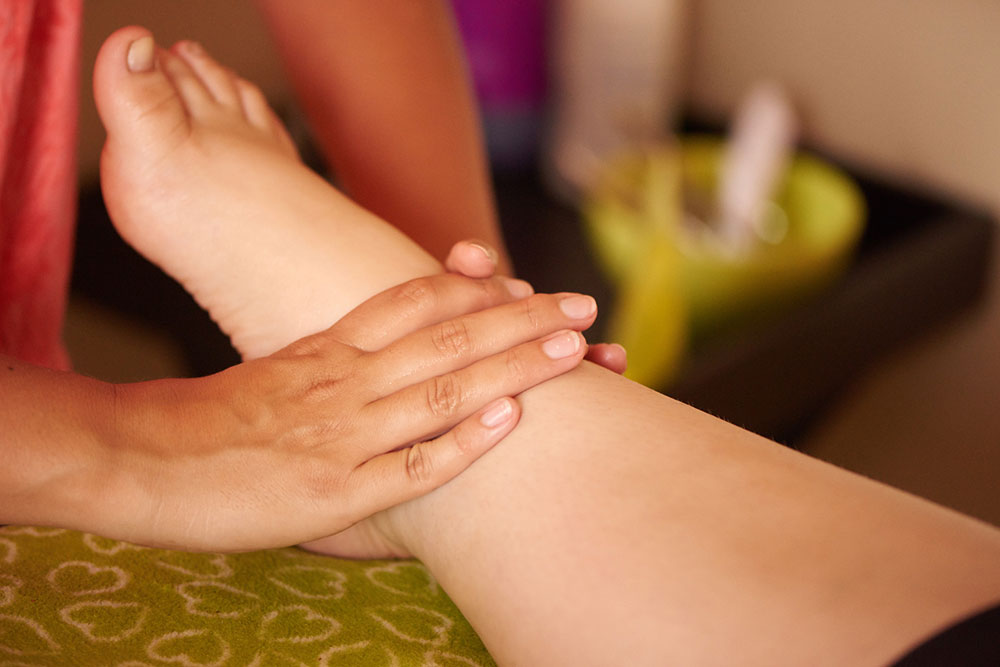
Usually, the swelling is temporary and can be relieved with simple self-care methods such as rest, elevating the legs, compression therapy, and cold packs. However, persistent swelling warrants diagnostic investigations like blood tests, urinalysis, ultrasound scans, and imaging studies to identify underlying issues. Treatment options vary depending on the causative condition: diuretics may be prescribed to manage fluid retention, compression garments for lymphedema, or specific medications for cardiovascular or renal issues. Severe or resistant cases might necessitate surgical procedures or specialized interventions to address the root problem effectively.
Implementing self-care techniques like the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is highly effective for mild edema. Resting the affected limbs, applying cold compresses, wearing compression stockings designed to improve circulation, and elevating the legs above the heart level can significantly reduce swelling and discomfort. It is important to monitor symptoms; if swelling persists beyond a few days, worsens, or is accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, or fever, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial to rule out serious conditions such as deep vein thrombosis, heart failure, or kidney disease.
In summary, while swollen ankles are often benign and resolve with basic self-care, persistent or severe cases require medical evaluation to identify and treat underlying health issues. Timely diagnosis and appropriate intervention help prevent complications and improve quality of life. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing contributing factors like obesity, and staying active are key measures to prevent recurrent ankle swelling and maintain overall vascular health.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and treatment options for swollen ankles empowers individuals to take proactive steps. Whether caused by trivial factors or underlying medical conditions, proper management and timely consultation with healthcare professionals ensure effective resolution and long-term health benefits.