Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Treatments for Swollen Ankles
Swollen ankles can result from injuries, systemic health issues, or circulation problems. This comprehensive guide explores common causes such as injuries, blood clots, pregnancy, infections, and chronic conditions. It also offers effective treatment strategies like physical activity, compression therapy, dietary adjustments, and medical interventions. By understanding these causes and remedies, you can better manage ankle swelling, reduce discomfort, and maintain healthy ankle function. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice, especially if swelling persists or worsens. Prioritize your ankle health today for improved mobility and comfort.

Understanding the Causes and Remedies for Swollen Ankles
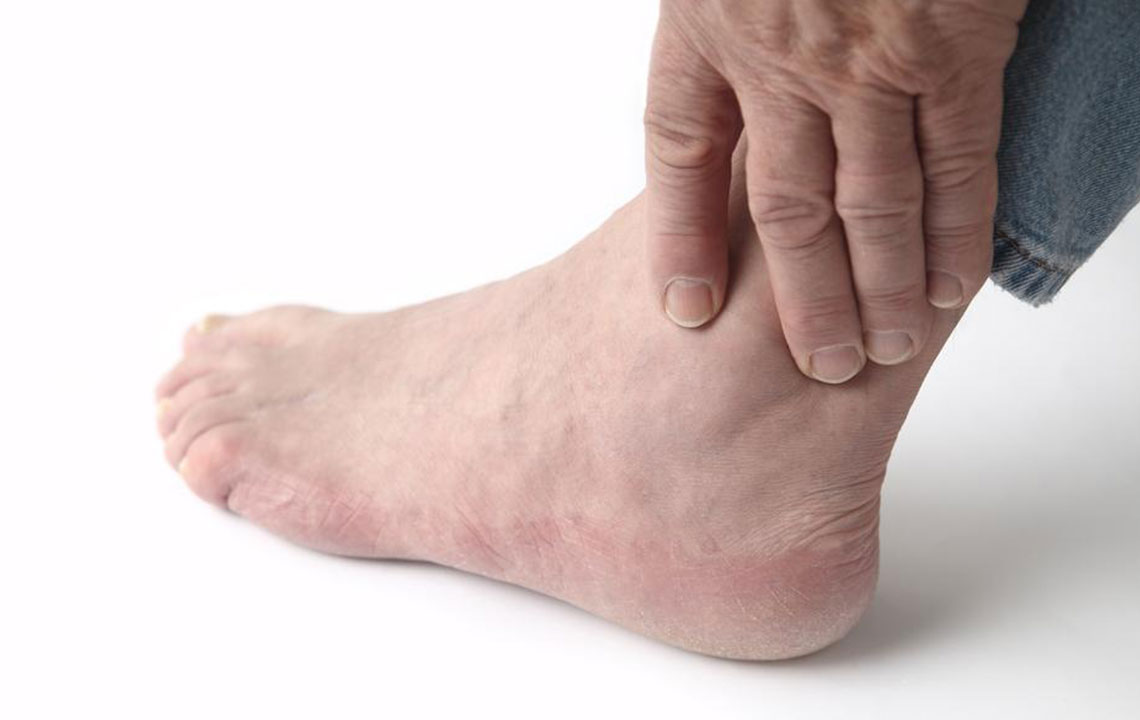
Swelling in the ankle region is a common concern that can stem from a variety of causes. Whether due to minor injuries or underlying health issues, swollen ankles can be uncomfortable and sometimes indicate more serious conditions. Recognizing the root causes and exploring effective treatment options are essential steps towards alleviating this condition and promoting better ankle health. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deeply into the common causes of ankle swelling, their symptoms, and detailed remedies to help you manage and prevent this issue effectively.
Primary Causes of Swollen Ankles
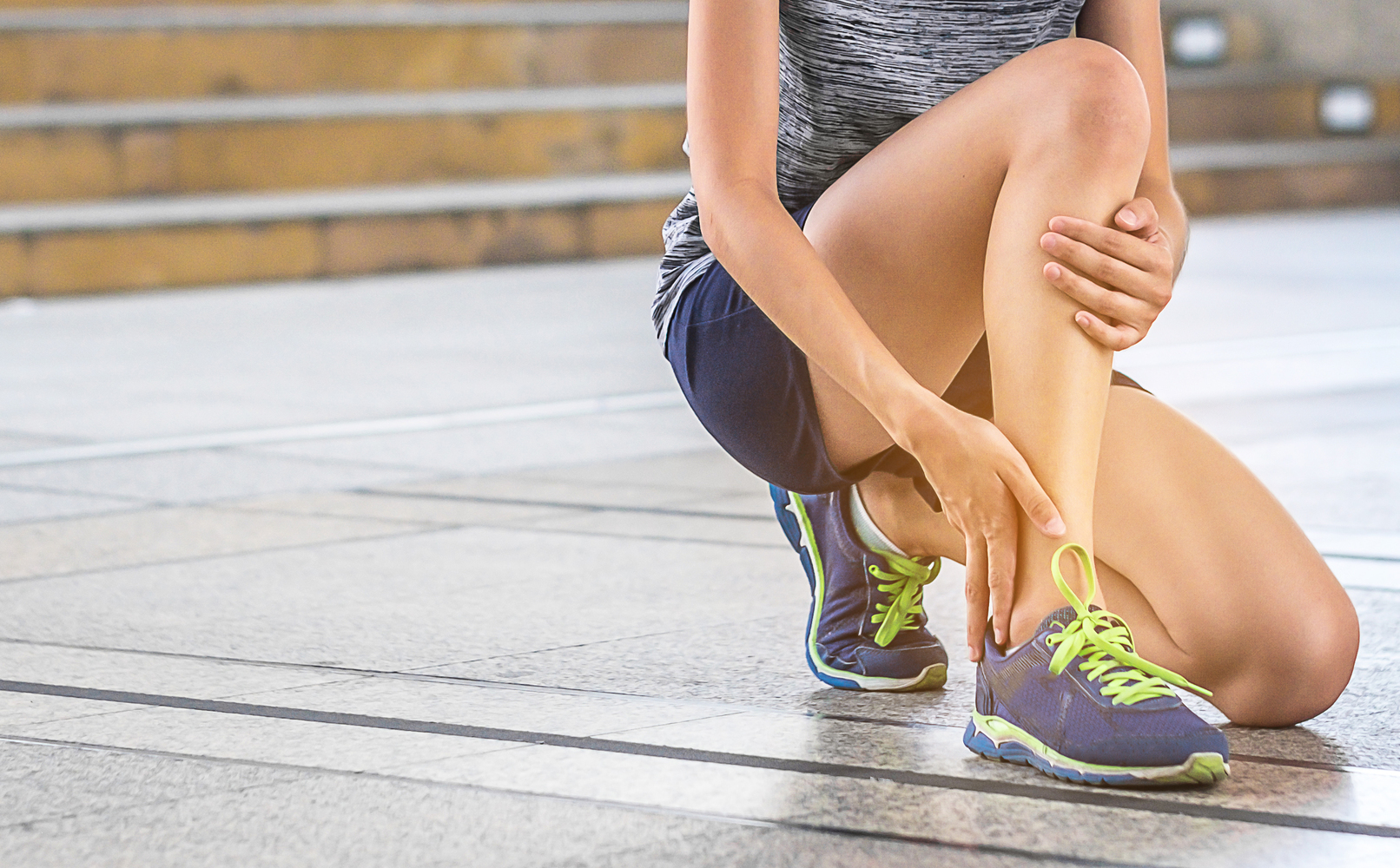
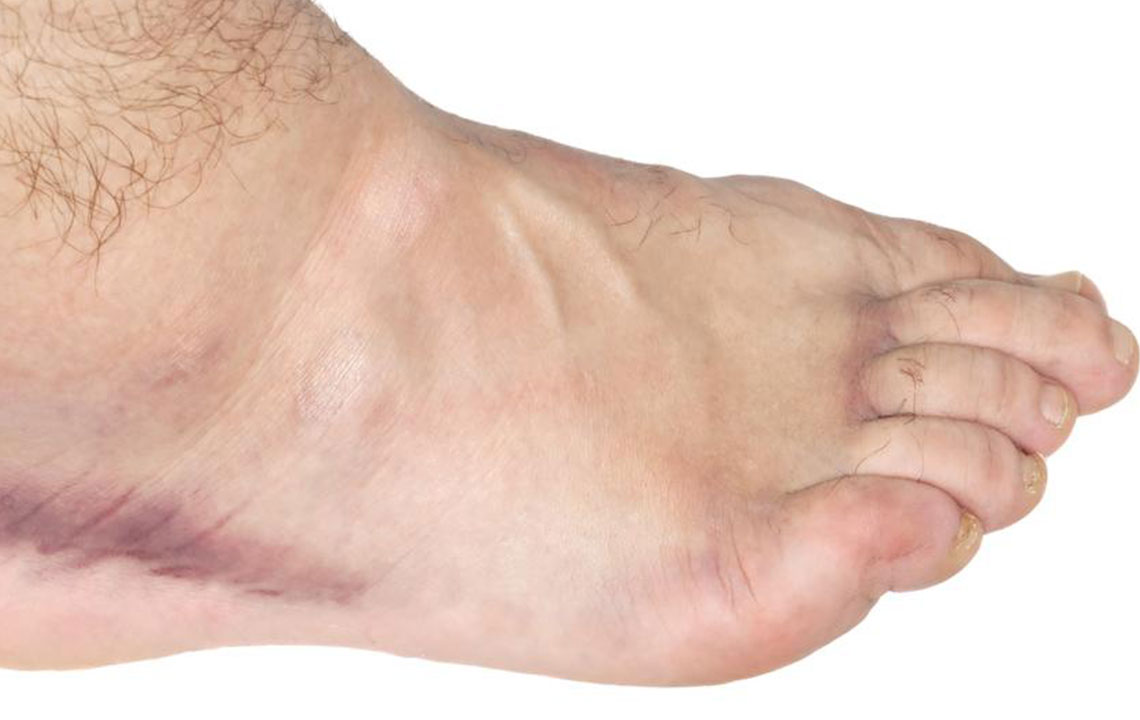
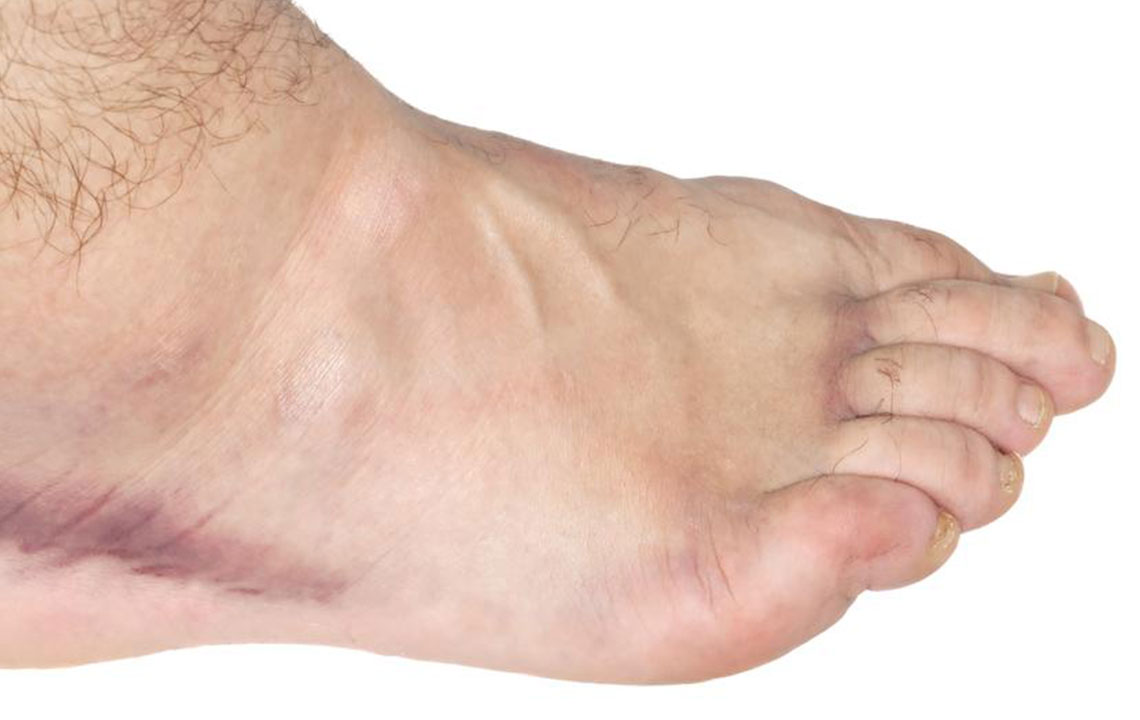
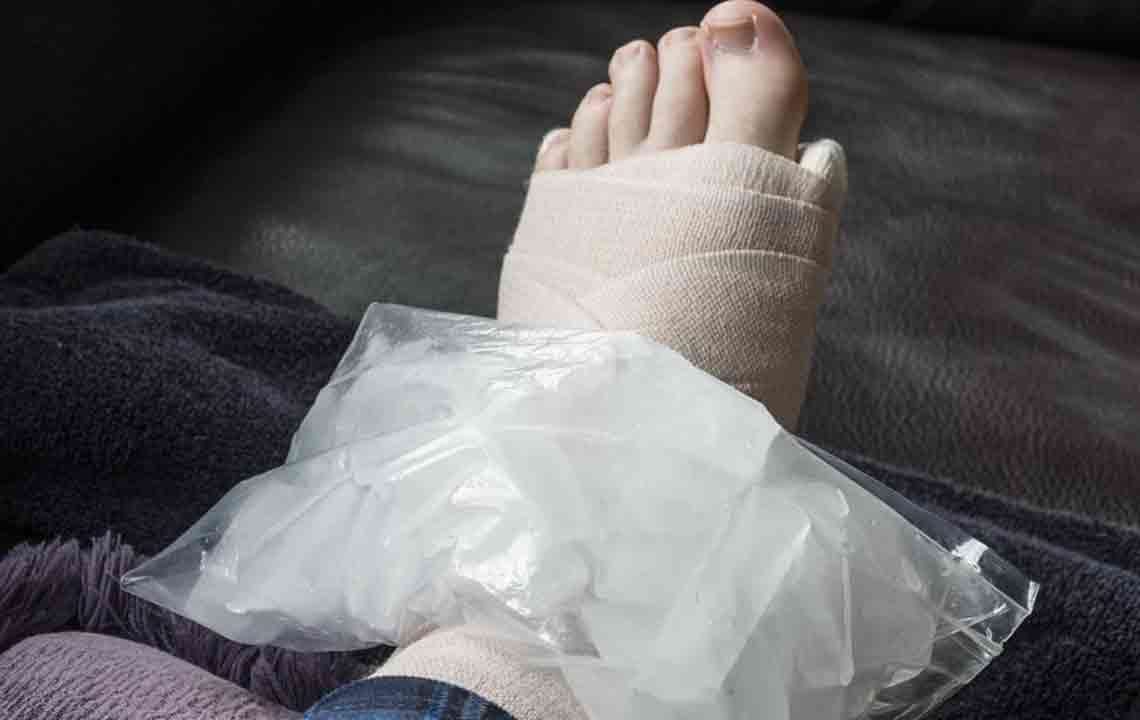
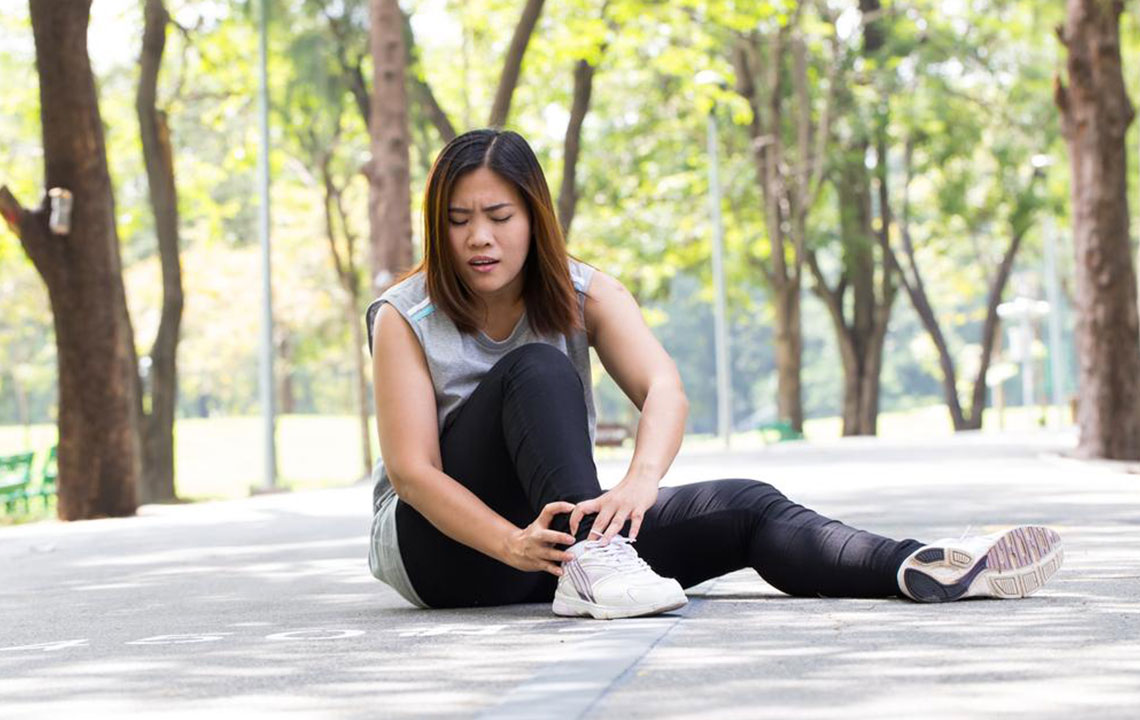
Injuries and Trauma – One of the most frequent reasons for ankle swelling is injury. Trauma such as sprains, strains, or fractures can cause inflammation and fluid accumulation. These injuries often present with additional symptoms such as pain, bruising, and limited mobility. Immediate management involves rest, applying ice, compressing the area, and elevating the foot, known as the R.I.C.E. method, which promotes healing and reduces swelling. Avoiding unnecessary movement during this period is crucial to prevent worsening of the injury.
Applying an ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the affected ankle for at least 30 minutes, elevating the foot on pillows or cushions, and using elastic compression bandages are proven methods to reduce swelling and manage pain. Proper rest during the initial phases is vital to prevent further injury and facilitate healing.
Blood Clots and DVT – Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and superficial blood clots in the leg veins can impede proper blood flow, resulting in swelling of the ankle and foot. While superficial clots are less dangerous, DVT can pose serious health risks, including pulmonary embolism. Warning signs such as sudden swelling, redness, warmth, pain, or fever require immediate medical evaluation. Diagnostic tests like Doppler ultrasound are necessary for confirmation, and treatment may involve blood thinners and lifestyle modifications.
Pregnancy-Related Edema – Mild swelling during pregnancy is common due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume. However, if swelling becomes severe or is accompanied by symptoms such as high blood pressure, headaches, visual disturbances, or nausea, it could indicate pre-eclampsia, a serious condition that demands urgent medical attention. Managing pregnancy-related swelling involves regular prenatal care, staying hydrated, avoiding standing for long periods, and wearing supportive compression stockings.
Lymphoedema – This condition involves persistent swelling caused by lymphatic system malfunctions, often following surgeries for cancer involving lymph node removal. Lymphoedema may cause swelling, hardness, and skin changes in the affected limb. Professional assessment and specialized therapies like manual lymph drainage and compression therapy are necessary for effective management and to prevent complications.
Infections – Skin infections, cellulitis, or abscesses can result in localized swelling around the ankle, especially if bacteria infiltrate through sores or cuts. For diabetics and individuals with peripheral nerve deficits, minor cuts might go unnoticed, leading to severe infections. Regular foot inspections, prompt treatment of any injuries, and maintaining good foot hygiene are essential preventive measures.
Venous Insufficiency and Valve Dysfunction – When the veins in the legs fail to effectively return blood to the heart due to damaged or weakened valves, fluid leaks into surrounding tissues, causing swelling and skin changes such as discoloration or ulcers. Chronic venous insufficiency often requires compression therapy, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes surgical intervention to improve circulation.
Underlying Systemic Conditions – Heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and liver problems can all cause fluid retention, leading to bilateral ankle swelling. Additional symptoms, such as fatigue, shortness of breath, weight gain, or abdominal swelling, should prompt a healthcare visit. Managing these systemic illnesses is crucial to controlling ankle edema.
Medication Side Effects – Several medications, including hormonal therapies, antihypertensives like calcium channel blockers, antidepressants, and corticosteroids, are known to cause fluid retention as a side effect. If you notice swelling after starting a new medication, consult your healthcare provider for alternatives or dosage adjustments.
Effective and Proven Remedies for Swollen Ankles
Managing swollen ankles effectively requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, self-care routines, and medical treatments where necessary. The following strategies can help reduce inflammation, alleviate discomfort, and prevent recurrent swelling:
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in gentle exercises like walking, ankle rotations, or swimming encourages circulation and prevents fluid buildup. Avoid prolonged sitting or standing, and take frequent breaks to elevate your legs whenever possible. Incorporating yoga or stretching routines can also promote venous return and tissue health. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on your lower limbs, further preventing swelling.
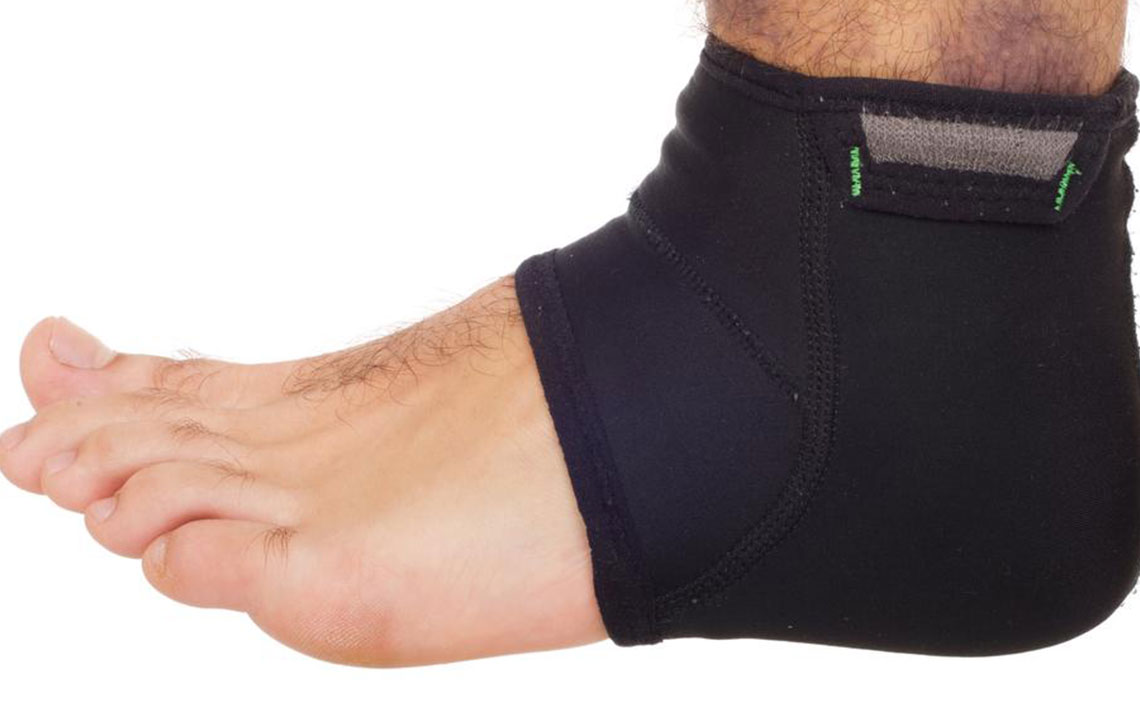
Leg Elevation and Compression: Elevating your legs above heart level several times a day helps promote venous drainage and reduces fluid retention. Wearing compression stockings or socks, especially during the day, supports blood flow and prevents the formation of edema. Choosing appropriately sized and graduated compression wear enhances efficacy and comfort.
Dietary and Supplementary Approaches: Reducing salt intake minimizes water retention. Consulting with a healthcare professional about taking magnesium supplements can help improve circulation and lessen swelling. Epsom salt baths, where the feet and ankles are soaked in warm water with Epsom salts for around 30 minutes, can provide relief by relaxing tissues and improving blood flow.
Stay Hydrated and Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Drinking sufficient water flushes out excess fluids and toxins, aiding in overall circulation. Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports tissue health and immune function. Smoking cessation and limiting alcohol intake further improve vascular health.
Medications and Medical Interventions: In some cases, diuretics or medications prescribed for underlying health issues may be necessary. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice before starting or adjusting any medication.
In conclusion, swollen ankles can stem from various causes—ranging from benign injuries to serious systemic health conditions. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and implementing effective remedies can significantly improve quality of life. Always seek professional medical advice for persistent or severe symptoms to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Taking proactive steps toward ankle health can prevent complications and promote swift recovery, helping you maintain optimal mobility and comfort.