Comprehensive Guide to Alleviating Swollen Ankles: Effective Treatments and Preventive Measures
Swollen ankles are a common issue caused by fluid buildup due to various factors like prolonged standing, injury, or medical conditions. This comprehensive guide explores effective treatment options including compression therapy, leg elevation, physical activity, and dietary adjustments. It emphasizes the importance of preventive measures, when to seek medical attention, and long-term management strategies to alleviate discomfort, promote circulation, and avoid recurrent swelling. Suitable for individuals experiencing persistent ankle edema, this article offers practical tips and professional advice to improve health and mobility.
Comprehensive Guide to Alleviating Swollen Ankles: Effective Treatments and Preventive Measures
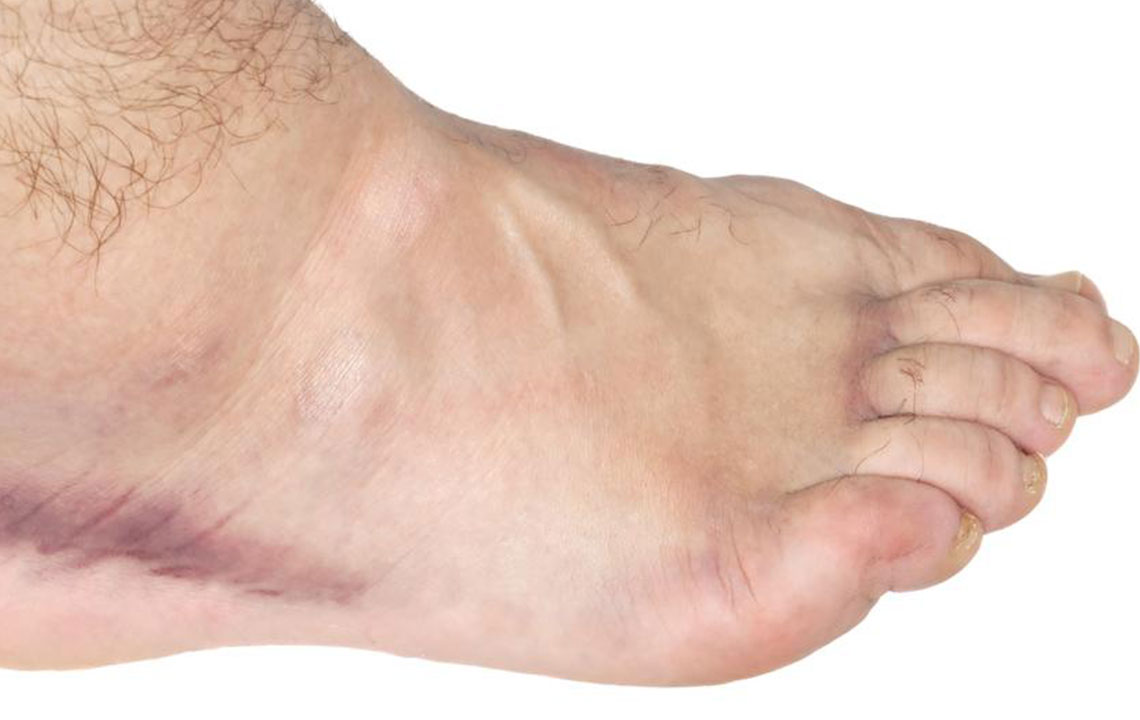
Swollen ankles are a common health concern experienced by many individuals across different age groups. This condition, often characterized by an abnormal buildup of fluid in the tissues of the ankles and lower legs, can result from various causes including prolonged standing, excessive walking, pregnancy, injury, or medical conditions such as heart or kidney problems. While minor swelling may resolve on its own, persistent or severe swelling warrants proper care and attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and most effective treatment options can help manage this discomfort and prevent recurrence.
The medical term for excess fluid accumulation in the body is edema, which frequently affects the lower extremities due to gravity and circulatory dynamics. Edema can be temporary or chronic, and its severity varies depending on underlying factors. When dealing with swollen ankles, adopting a combination of lifestyle modifications, home remedies, and medical interventions can significantly improve the quality of life.
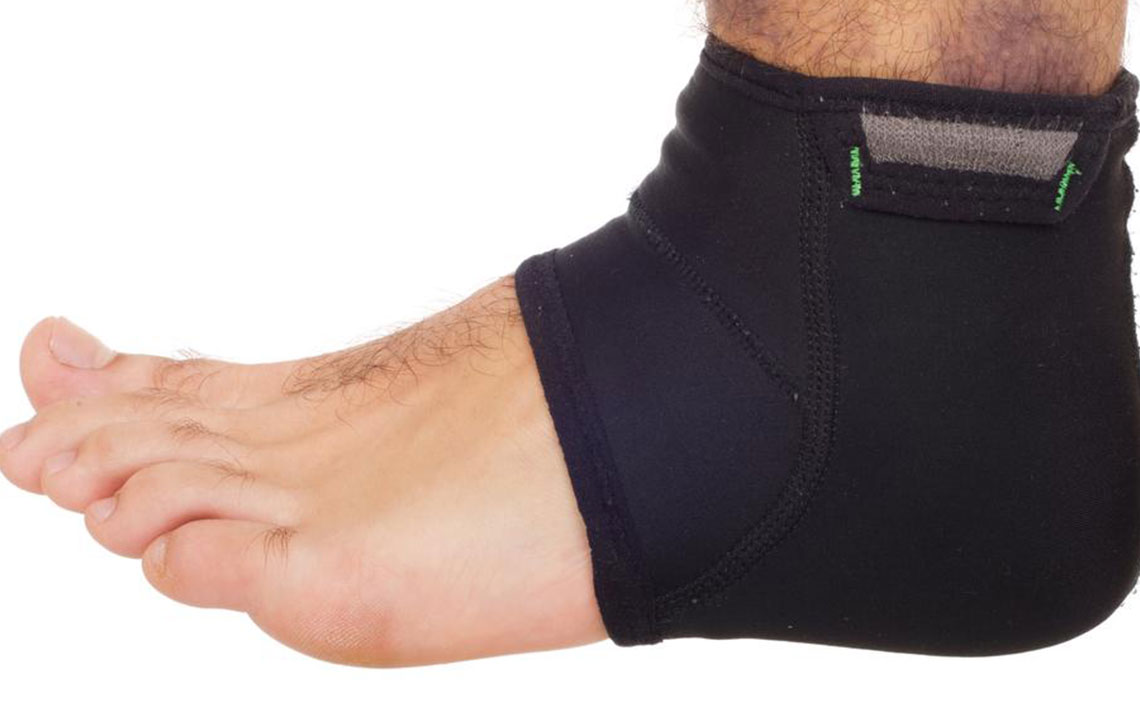
Utilize Compression Therapy
One of the most widely recommended strategies for reducing ankle swelling is wearing compression stockings or socks. These specially designed garments apply graduated pressure on the legs, promoting blood flow back toward the heart and preventing fluid buildup. Available in various compression levels—from mild (around 12-15 mm Hg) to higher pressures (20-30 mm Hg)—they should be chosen based on individual needs and proper fitting. Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures selecting the appropriate compression level and garment type to avoid circulation restriction or skin irritation.
Leg Elevation Techniques
Elevating the legs above heart level helps facilitate venous drainage and reduces edema. Using a footstool, pillows, or lying flat in bed with legs elevated can make a significant difference. Incorporating regular elevation into daily routines—such as during breaks at work or before bed—can effectively diminish swelling. Additionally, performing gentle yoga poses like legs-up-the-wall or Viparita Karani can enhance circulation and drainage.
Engage in Physical Activity
Staying active is essential for maintaining good circulation and preventing fluid retention. Gentle exercises such as ankle circles, calf raises, and stretching improve blood flow in the legs. Swimming is an excellent low-impact activity that minimizes joint stress while promoting movement and circulation. Avoid prolonged inactivity—sitting or standing in one position for extended periods—as it can exacerbate swelling.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight imposes additional pressure on the lower limbs and joints, contributing to swelling. A balanced diet combined with regular exercise can assist in weight management, alleviating stress on the ankles and improving overall vascular health. Long-term weight control is a vital component of preventing recurrent swelling and related complications.
Epsom Salt Baths
Soaking the affected ankles in a cool bath with Epsom salts (magnesium sulfate) for 15 to 20 minutes can provide soothing relief. The magnesium in Epsom salts helps relax muscles and reduce inflammation, thereby decreasing swelling. Diabetic individuals or those with sensitive skin should ensure water temperature is comfortable and not too hot to prevent burns or skin irritation.
Magnesium Supplementation
Magnesium plays a role in regulating fluid balance and muscle function. Incorporating 200–400 mg of magnesium daily through diet or supplements may aid in reducing water retention and alleviating associated discomfort. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advised before starting supplements, especially for individuals with heart, kidney, or other health conditions.
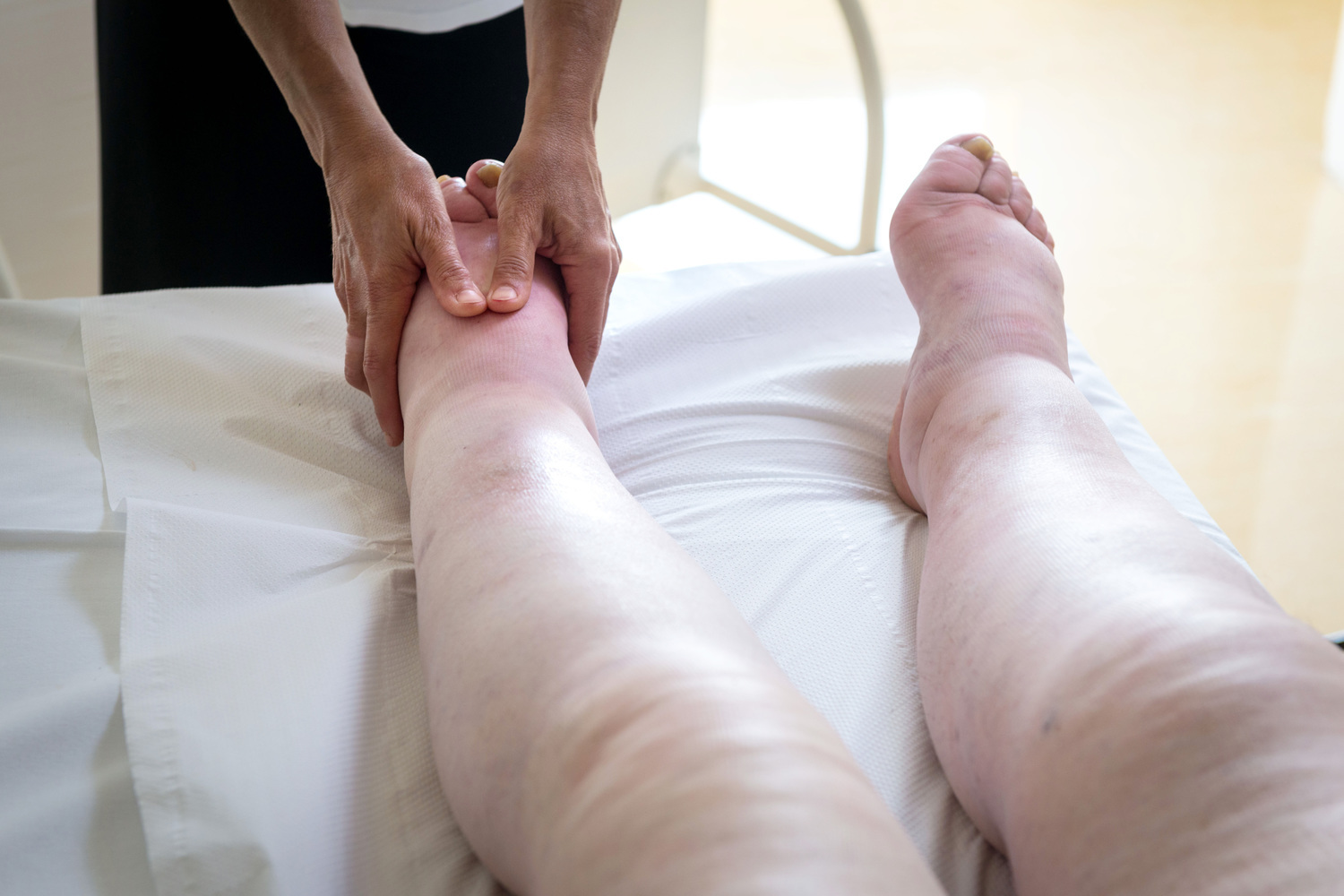
When to Seek Medical Care
Persistent swelling accompanied by skin ulcers, blisters, or sores requires prompt medical evaluation to prevent infection. Sudden or unilateral swelling could indicate more serious issues such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which demands immediate attention. Avoid tight footwear that constricts blood flow and worsens swelling or causes injury. Regular medical checkups can help identify underlying health issues contributing to edema and guide appropriate treatment.
Addressing swollen ankles involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, home remedies, and medical interventions when necessary. Recognizing early symptoms and adhering to recommended strategies can greatly relieve discomfort, enhance mobility, and prevent future episodes. If swelling persists despite self-care, consult a healthcare provider for personalized assessment and treatment options.